Abstract
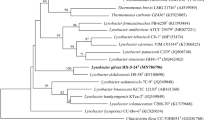
A Gram-negative, aerobic, rod shaped, non-spore-forming bacterial strain, designated Dae08T, was isolated from sediment of the stream near Daechung dam in South Korea, and was characterized in order to determine its taxonomic position, using a polyphasic approach. Comparative 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strain Dae08T belongs to the family Xanthomonadaceae of the Gammaproteobacteria, and is related to Lysobacter brunescens ATCC 29482T (97.3%). The phylogenetic distances from any other species with validly published names within the genus Lysobacter were greater than 3.7%. The G+C contents of the genomic DNA of strain Dae08T was 69.3 mol%. The detection of a quinone system with Q-8 as the predominant compound and a fatty acid profile with iso-C15:0, iso-C17:1, ω9c, iso-C17:0, iso-C16:0, and iso-C11:0 3-OH as the major acids supported the affiliation of strain Dae08T to the genus Lysobacter. DNA-DNA relatedness between strain Dae08T and its phylogenetically closest neighbour was 28%. On the basis of its phenotypic properties and phylogenetic distinctiveness, strain Dae08T (= KCTC 12600T) should be classified in the genus Lysobacter as the novel species, for which the name Lysobacter daecheongensis sp. nov. is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas, R.M. 1993. Handbook of Microbiological Media. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Bae, H.S., W.T. Im, and S.T. Lee. 2005. Lysobacter concretionis sp. nov., isolated from anaerobic granules in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 55, 1155–1161.
Buck, J.D. 1982. Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of Gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 44, 992–993.
Cappuccino, J.G. and N. Sherman. 2002. Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 6th ed. Pearson Education, Inc., California, USA.
Christensen, P. and F.D. Cook. 1978. Lysobacter, a new genus of nonfruiting, gliding bacteria with a high base ratio. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 28, 367–393.
Ezaki, T., Y. Hashimoto, and E. Yabuuchi. 1989. Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 224–229.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39, 783–791.
Fitch, W.M. 1971. Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool. 20, 406–416.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41, 95–98.
Hiraishi, A., Y. Ueda, J. Ishihara, and T. Mori. 1996. Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 42, 457–469.
Kim, M.K., W.T. Im, H. Ohta, M. Lee, and S.T. Lee. 2005. Sphingopyxis granuli sp. nov., a β-glucosidase producing bacterium in the family Sphingomonadaceae in α-4 subclass of the Proteobacteria. J. Microbiol. 43, 152–157.
Kimura, M. 1983. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, N.Y., USA.
Kouker, G. and K.E. Jaeger. 1987. Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 211–213.
Kumar, S., K. Tamura, and M. Nei. 2004. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 5, 150–163.
Lee, J.W., W.T. Im, M.K. Kim, and D.C. Yang. 2006. Lysobacter koreensis sp. nov., isolated from a ginseng field. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 231–235.
Mesbah, M., U. Premachandran, and W. Whitman. 1989. Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 39, 159–167.
Minnikin, D.E., A.G. O’Donnell, M. Goodfellow, G. Alderson, M. Athalye, K. Schaal, and J.H. Parlett. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2, 233–241.
Moore, D.D and D. Dowhan. 1995. Preparation and analysis of DNA, p. 2–11. In F.W. Ausubel, R. Brent, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.A. Smith, and K. Struhl (eds.), Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York, N.Y., USA.
Park, J.H., R. Kim, Z. Aslam, C.O. Jeon, and Y.R. Chung. 2008. Lysobacter capsici sp. nov., with antimicrobial activity, isolated from the rhizosphere of pepper and emended description of the genus Lysobacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 387–392.
Romanenko, L.A., M. Uchino, N. Tanaka, G.M. Frolova, and V.V. Mikhailov. 2007. Lysobacter spongiicola sp. nov., isolated from a deep-sea sponge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 58, 370–374.
Saitou, N. and M. Nei. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Sasser, M. 1990. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. DE: MIDI Inc., Newark, USA.
Stackebrandt, E. and B.M. Goebel. 1994. Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44, 846–849.
Ten, L.N., W.T. Im, M.K. Kim, M.S. Kang, and S.T. Lee. 2004. Development of a plate technique for screening of polysaccharide-degrading microorganisms by using a mixture of insoluble chromogenic substrates. J. Microbiol. Methods 56, 375–382.
Ten, L.N., Q.M. Liu, W.T. Im, M. Lee, D.C. Yang, and S.T. Lee. 2006. Pedobacter ginsengisoli sp. nov., a DNase producing bacterium isolated from soil of a ginseng field in South Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 2565–2570.
Thompson, J.D., T.J. Gibson, F. Plewniak, F. Jeanmougin, and D.G. Higgins. 1997. The Clustal_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4876–4882.
Wayne, L.G., D.J. Brenner, R.R. Colwell, P.A.D. Grimont, O. Kandler, M.I. Krichevsky, L.H. Moore, W.E.C. Moore, R.G.E. Murray, E. Stackebrandt, M.P. Starr, and H.G. Truper. 1987. International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37, 463–464.
Weon, H.Y., B.Y. Kim, Y.K. Baek, S.H. Yoo, S.W. Kwon, E. Stackebrandt, and S.J. Go. 2006. Two novel species, Lysobacter daejeonensis sp. nov. and Lysobacter yangpyeongensis sp. nov., isolated from Korean greenhouse soils. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 947–951.
Weon, H.Y., B.Y. Kim, M.K. Kim, S.H. Yoo, S.W. Kwon, S.J. Go, and E. Stackebrandt. 2007. Lysobacter niabensis sp. nov. and Lysobacter niastensis sp. nov., isolated from greenhouse soils in Korea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 548–551.
Yassin, A.F., W.M. Chen, H. Hupfer, C. Siering, R.M. Kroppenstedt, A.B. Arun, W.A. Lai, F.T. Shen, P.D. Rekha, and C.C. Young. 2007. Lysobacter defluvii sp. nov., isolated from municipal solid waste. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1131–1136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ten, L.N., Jung, HM., Im, WT. et al. Lysobacter daecheongensis sp. nov., isolated from sediment of stream near the Daechung dam in South Korea. J Microbiol. 46, 519–524 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0047-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-008-0047-9