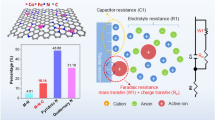
Abstract
Electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) paves a new way to cost-efficient production of ammonia, but is still challenging in the sluggish kinetics caused by hydrogen evolution reaction competition and chemical inertness of N≡N bond. Herein, we report a “dual-site” strategy for boosting NRR performance. A high-performance catalyst is successfully constructed by anchoring isolated Fe and Mo atoms on hierarchical N doped carbon nanotubes through a facile self-sacrificing template route, which exhibits a remarkably improved NH3 yield rate of 26.8 \(\mu {\rm{g}} \cdot {{\rm{h}}^{ - 1}} \cdot {\rm{mg}}_{{\rm{cat}}}^{ - 1}\) with 11.8% Faradaic efficiency, which is 2.5 and 1.6 times larger than those of Fe/NC and Mo/NC. The enhancement can be attributed to the unique hierarchical structure that profits from the contact of electrode and electrolyte, thus improving the mass and electron transport. More importantly, the in situ Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (in situ FTIR) result firmly demonstrates the crucial role of the coupling of Fe and Mo atoms, which can efficiently boost the generation and transmission of *N2Hy intermediates, leading to an accelerated reaction rate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rafiqul, I.; Weber, C.; Lehmann, B.; Voss, A. Energy efficiency improvements in ammonia production—Perspectives and uncertainties. Energy 2005, 30, 2487–2504.
Li, Y. X.; Liu, Y. X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. L.; Cheng, Y. Y.; Zhang, P.; Deng, P. J.; Deng, J. J.; Kang, Z. H.; Li, H. T. Fe-doped SnO2 nanosheet for ambient electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6026–6035.
Guo, W. H.; Zhang, K. X.; Liang, Z. B.; Zou, R. Q.; Xu, Q. Electrochemical nitrogen fixation and utilization: Theories, advanced catalyst materials and system design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5658–5716.
Schlögl, R. Catalytic synthesis of ammonia—A “never-ending story”? Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2004–2008.
Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y. X.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Zhang, T. R. Photocatalytic ammonia synthesis: Recent progress and future. EnergyChem 2019, 1, 100013.
Cui, X. Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Q. A review of electrocatalytic reduction of dinitrogen to ammonia under ambient conditions. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800369.
Kandemir, T.; Schuster, M. E.; Senyshyn, A.; Behrens, M.; Schlögl, R. The Haber—Bosch process revisited: On the real structure and stability of “ammonia iron” under working conditions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12723–12726.
Hao, Y. C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L. W.; Shu, M.; Wang, X. Y.; Bu, T. A.; Gao, W. Y.; Zhang, N.; Su, X.; Feng, X. et al. Promoting nitrogen electroreduction to ammonia with bismuth nanocrystals and potassium cations in water. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 448–456.
Shi, L.; Yin, Y.; Wang, S. J.; Xu, X. Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J. Q.; Wang, S. B.; Sun, H. Q. Rigorous and reliable operations for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2020, 278, 119325.
Chen, S. M.; Perathoner, S.; Ampelli, C.; Mebrahtu, C.; Su, D. S.; Centi, G. Electrocatalytic synthesis of ammonia at room temperature and atmospheric pressure from water and nitrogen on a carbon-nanotube-based electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2699–2703.
Liu, G. H.; Niu, L. J.; Ma, Z. X.; An, L.; Qu, D.; Wang, D. D.; Wang, X. Y.; Sun, Z. C. Fe2Mo3O8/XC-72 electrocatalyst for enhanced electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction under ambient conditions. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5940–5945.
Zhao, X.; Hu, G. Z.; Chen, G. F.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhang, S. S.; Wang, H. H. Comprehensive understanding of the thriving ambient electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007650.
Jiang, J.; Zhao, K.; Xiao, X. Y.; Zhang, L. Z. Synthesis and facet-dependent photoreactivity of BiOCl single-crystalline nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4473–4476.
Bao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, F. L.; Zhong, H. X.; Shi, M. M.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J. M.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. B. Electrochemical reduction of N2 under ambient conditions for artificial N2 fixation and renewable energy storage using N2/NH3 cycle. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604799.
Li, S. X.; Wang, Y. Y.; Liang, J.; Xu, T.; Ma, D. W.; Liu, Q.; Li, T. S.; Xu, S. R.; Chen, G.; Asiri, A. M. et al. TiB2 thin film enabled efficient NH3 electrosynthesis at ambient conditions. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 18, 100396.
Wang, T.; Liu, Q.; Li, T. S.; Lu, S. Y.; Chen, G.; Shi, X. F.; Asiri, A. M.; Luo, Y. L.; Ma, D. W.; Sun, X. P. A magnetron sputtered Mo3Si thin film: An efficient electrocatalyst for N2 reduction under ambient conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 884–888.
Xiao, L.; Zhu, S. L.; Liang, Y. Q.; Li, Z. Y.; Wu, S. L.; Luo, S. Y.; Chang, C. T.; Cui, Z. D. Nanoporous nickel-molybdenum oxide with an oxygen vacancy for electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation under ambient conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 30722–30730.
Chu, K.; Liu, Y. P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. NiO nanodots on graphene for efficient electrochemical N2 reduction to NH3. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 2288–2295.
Xue, Z. H.; Zhang, S. N.; Lin, Y. X.; Su, H.; Zhai, G. Y.; Han, J. T.; Yu, Q. Y.; Li, X. H.; Antonietti, M.; Chen, J. S. Electrochemical reduction of N2 into NH3 by donor—acceptor couples of Ni and Au nanoparticles with a 67.8% Faradaic efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14976–14980.
Tao, H. C.; Choi, C.; Ding, L. X.; Jiang, Z.; Han, Z. S.; Jia, M. W.; Fan, Q.; Gao, Y. N.; Wang, H. H.; Robertson, A. W. et al. Nitrogen fixation by Ru single-atom electrocatalytic reduction. Chem 2019, 5, 204–214.
Zhuang, Z. C.; Li, Y. H.; Yu, R. H.; Xia, L. X.; Yang, J. R.; Lang, Z. Q.; Zhu, J. X.; Huang, J. Z.; Wang, J. O.; Wang, Y. et al. Reversely trapping atoms from a perovskite surface for high-performance and durable fuel cell cathodes. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 300–310.
Wang, A. Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, T. Heterogeneous single-atom catalysis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 65–81.
Li, R. Z.; Wang, D. S. Understanding the structure—performance relationship of active sites at atomic scale. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6888–6923.
Zhang, L. L.; Ren, Y. J.; Liu, W. G.; Wang, A. Q.; Zhang, T. Single-atom catalyst: A rising star for green synthesis of fine chemicals. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 653–672.
Zhang, L. L.; Zhou, M. X.; Wang, A. Q.; Zhang, T. Selective hydrogenation over supported metal catalysts: From nanoparticles to single atoms. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 683–733.
Zhao, D.; Zhuang, Z. W.; Cao, X.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Q.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. D. Atomic site electrocatalysts for water splitting, oxygen reduction and selective oxidation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2215–2264.
Wen, J. F.; Chen, Y. J.; Ji, S. F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Metal-organic frameworks-derived nitrogen-doped carbon supported nanostructured PtNi catalyst for enhanced hydrosilylation of 1-octene. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2584–2588.
Deng, D. H.; Chen, X. Q.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, Q. F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H. X.; Tian, H. F.; Hu, Y. F.; Du, P. P. et al. A single iron site confined in a graphene matrix for the catalytic oxidation of benzene at room temperature. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500462.
Zhuang, Z. C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. H.; Huang, J. Z.; Wei, B.; Sun, R.; Ren, Y. J.; Ding, J.; Zhu, J. X.; Lang, Z. Q. et al. Atomically dispersed nonmagnetic electron traps improve oxygen reduction activity of perovskite oxides. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 1016–1028.
Ji, S. F.; Chen, Y. J.; Wang, X. L.; Zhang, Z. D.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Chemical synthesis of single atomic site catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11900–11955.
Li, Z.; Ji, S. F.; Liu, Y. W.; Cao, X.; Tian, S. B.; Chen, Y. J.; Niu, Z. Q.; Li, Y. D. Well-defined materials for heterogeneous catalysis: From nanoparticles to isolated single-atom sites. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 623–682.
Zhang, J.; Huang, Q. A.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. J.; Zhao, Y. F. Supported dual-atom catalysts: Preparation, characterization, and potential applications. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 783–798.
Zhang, W. Y.; Chao, Y. G.; Zhang, W. S.; Zhou, J. H.; Lv, F.; Wang, K.; Lin, F. X.; Luo, H.; Li, J.; Tong, M. P. et al. Emerging dual-atomic-site catalysts for efficient energy catalysis. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102576.
Liu, M. M.; Li, H. X.; Liu, S. J.; Wang, L. L.; Xie, L. B.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, M.; Sun, S. J. et al. Tailoring activation sites of metastable distorted 1T’-phase MoS2 by Ni doping for enhanced hydrogen evolution. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5946–5952.
Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. D. Structural regulation with atomic-level precision: From single-atomic site to diatomic and atomic interface catalysis. Matter 2020, 2, 78–110.
Rong, H. P.; Ji, S. F.; Zhang, J. T.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Synthetic strategies of supported atomic clusters for heterogeneous catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5884.
Chen, J. Y.; Li, H.; Fan, C.; Meng, Q. W.; Tang, Y. W.; Qiu, X. Y.; Fu, G. T.; Ma, T. Y. Dual single-atomic Ni-N4 and Fe-N4 sites constructing Janus hollow graphene for selective oxygen electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003134.
Lin, L.; Li, H. B.; Yan, C. C.; Li, H. F.; Si, R.; Li, M. R.; Xiao, J. P.; Wang, G. X.; Bao, X. H. Synergistic catalysis over iron-nitrogen sites anchored with cobalt phthalocyanine for efficient CO2 electroreduction. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1903470.
Zhou, Y.; Song, E. H.; Chen, W.; Segre, C. U.; Zhou, J. D.; Lin, Y. C.; Zhu, C.; Ma, R. G.; Liu, P.; Chu, S. F. et al. Dual-metal interbonding as the chemical facilitator for single-atom dispersions. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003484.
Li, H. L.; Wang, L. B.; Dai, Y. Z.; Pu, Z. T.; Lao, Z. H.; Chen, Y. W.; Wang, M. L.; Zheng, X. S.; Zhu, J. F.; Zhang, W. H. et al. Synergetic interaction between neighbouring platinum monomers in CO2 hydrogenation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 411–417.
Yang, Y.; Qian, Y. M.; Li, H. J.; Zhang, Z. H.; Mu, Y. W.; Do, D.; Zhou, B.; Dong, J.; Yan, W. J.; Qin, Y. et al. O-coordinated W-Mo dual-atom catalyst for pH-universal electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba6586.
Liu, Z. H.; Du, Y.; Zhang, P. F.; Zhuang, Z. C.; Wang, D. S. Bringing catalytic order out of chaos with nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous carbon. Matter 2021, 4, 3161–3194.
Zhang, L.; Fan, G. L.; Xu, W. C.; Yu, M.; Wang, L.; Yan, Z. H.; Cheng, F. Y. Isolated diatomic Zn-Fe in N-doped carbon for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction to ammonia. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 11957–11960.
Han, L. L.; Ren, Z. H.; Ou, P. F.; Cheng, H.; Rui, N.; Lin, L. L.; Liu, X. J.; Zhuo, L. C.; Song, J.; Sun, J. Q. et al. Modulating single-atom palladium sites with copper for enhanced ambient ammonia electrosynthesis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 345–350.
Lü, F.; Zhao, S. Z.; Guo, R. J.; He, J.; Peng, X. Y.; Bao, H. H.; Fu, J. T.; Han, L. L.; Qi, G. C.; Luo, J. et al. Nitrogen-coordinated single Fe sites for efficient electrocatalytic N2 fixation in neutral media. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 420–427.
Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449.
Zhang, M. L.; Wang, Y. G.; Chen, W. X.; Dong, J. C.; Zheng, L. R.; Luo, J.; Wan, J. W.; Tian, S. B.; Cheong, W. C.; Wang D. S. et al. Metal (hydr)oxides@polymer core—shell strategy to metal single-atom materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10976–10979.
Jiang, R.; Li, L.; Sheng, T.; Hu, G. F.; Chen, Y. G.; Wang, L. Y. Edge-site engineering of atomically dispersed Fe-N4 by selective C—N bond cleavage for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction activities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11594–11598.
Li, Q. H.; Chen, W. X.; Xiao, H.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Zheng, L. R.; Zheng, X. S.; Yan, W. S.; Cheong, W. C.; Shen, R. A. et al. Fe isolated single atoms on S, N codoped carbon by copolymer pyrolysis strategy for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800588.
Li, J. S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C. H.; Li, S. L.; Wang, Y. G.; Dong, L. Z.; Dai, Z. H.; Li, Y. F.; Lan, Y. Q. Coupled molybdenum carbide and reduced graphene oxide electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11204.
Han, L. L.; Liu, X. J.; Chen, J. P.; Lin, R. Q.; Liu, H. X.; Lü, F.; Bak, S.; Liang, Z. X.; Zhao, S. Z.; Stavitski, E. et al. Atomically dispersed molybdenum catalysts for efficient ambient nitrogen fixation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2321–2325.
Zhu, D.; Zhang, L. H.; Ruther, R. E.; Hamers, R. J. Photo-illuminated diamond as a solid-state source of solvated electrons in water for nitrogen reduction. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 836–841.
Watt, G. W.; Chrisp, J. D. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of hydrazine. Anal. Chem. 1952, 24, 2006–2008.
Guo, W. H.; Liang, Z. B.; Zhao, J. L.; Zhu, B. J.; Cai, K. T.; Zou, R. Q.; Xu, Q. Hierarchical cobalt phosphide hollow nanocages toward electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis under ambient pressure and room temperature. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800204.
Wu, T. W.; Kong, W. H.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, J. X.; Wang, T.; Shi, X. F.; Luo, Y. L.; Sun, X. P. Greatly enhanced electrocatalytic N2 reduction on TiO2 via V doping. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900356.
Song, P. F.; Kang, L.; Wang, H.; Guo, R.; Wang, R. M. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P)-codoped porous carbon as a metal-free electrocatalyst for N2 reduction under ambient conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12408–12414.
Song, P. F.; Wang, H.; Kang, L.; Ran, B. C.; Song, H. H.; Wang, R. M. Electrochemical nitrogen reduction to ammonia at ambient conditions on nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 687–690.
Yao, Y.; Zhu, S. Q.; Wang, H. J.; Li, H.; Shao, M. H. A spectroscopic study on the nitrogen electrochemical reduction reaction on gold and platinum surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1496–1501.
Li, M. Q.; Huang, H.; Low, J.; Gao, C.; Long, R.; Xiong, Y. J. Recent progress on electrocatalyst and photocatalyst design for nitrogen reduction. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800388.
Hirakawa, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Hirai, T. Photocatalytic conversion of nitrogen to ammonia with water on surface oxygen vacancies of titanium dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10929–10936.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the financial aid from National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2021YFB3500700), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22020102003, 22025506, and 22271274), Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. ZDRW-CN-2021-3-3), K. C. Wong Education Foundation (No. GJTD-2018-09), and Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Jilin Province (No. E2390202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_5246_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Coupling Fe and Mo single atoms on hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes enhances electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction performance
12274_2022_5246_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Coupling Fe and Mo single atoms on hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes enhances electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction performance
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, W., Geng, B., Chu, X. et al. Coupling Fe and Mo single atoms on hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes enhances electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction performance. Nano Res. 16, 5743–5749 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5246-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5246-x