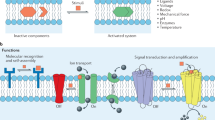
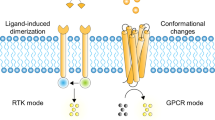
Abstract
Signal transduction across lipid bilayers is of profound importance in biological processes. In biological systems, natural enzymes mediate biochemical effects by binding to substrates and facilitating the conversion of external signals into physiological responses. Sequential transmission of biological signals from one enzyme to the next promotes signal transduction with feedforward and feedback mechanisms. Reconstructing these processes in an artificial system provides potential applications and offers a new way to understand fundamental biological processes in depth. However, the design of artificial signal transduction systems regulated by artificial enzyme receptors in a predictable and intelligent manner remains a challenge. Herein, benefiting from the polarity-regulated characteristics of Se-containing compounds with artificial glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity, we constructed an artificial transmembrane signaling receptor with a Se-containing GPx-like recognition head group, a membrane-anchoring group, and a pre-enzyme end group. The artificial supramolecular signal transduction system containing such signal transduction receptors extends the range of signaling systems based on enzyme regulation, which provides a new way to study natural signal processes in cells and artificially regulated biological processes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singer, S. J. Intercellular communication and cell-cell adhesion. Science 1992, 255, 1671–1677.
Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D. M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293.
Kofuji, P.; Araque, A. G-protein-coupled receptors in astrocyteneuron communication. Neuroscience 2021, 456, 71–84.
Natarajan, K.; McShan, A. C.; Jiang, J. S.; Kumirov, V. K.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H. Y.; Schuck, P.; Tilahun, M. E.; Boyd, L. F.; Ying, J. F. et al. An allosteric site in the T-cell receptor Cβ domain plays a critical signalling role. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15260.
Li, X.; Shen, B.; Yao, X. Q.; Yang, D. Synthetic chloride channel regulates cell membrane potentials and voltage-gated calcium channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13676–13680.
Shetty, S. C.; Yandrapalli, N.; Pinkwart, K.; Krafft, D.; Vidakovic-Koch, T.; Ivanov, I.; Robinson, T. Directed signaling cascades in monodisperse artificial eukaryotic cells. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15656–15666.
Hindley, J. W.; Elani, Y.; McGilvery, C. M.; Ali, S.; Bevan, C. L.; Law, R. V.; Ces, O. Light-triggered enzymatic reactions in nested vesicle reactors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1093.
Hindley, J. W.; Zheleva, D. G.; Elani, Y.; Charalambous, K.; Barter, L. M. C.; Booth, P. J.; Bevan, C. L.; Law, R. V.; Ces, O. Building a synthetic mechanosensitive signaling pathway in compartmentalized artificial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16711–16716.
Li, P.; Xie, G. H.; Liu, P.; Kong, X. Y.; Song, Y. L.; Wen, L. P.; Jiang, L. Light-driven ATP transmembrane transport controlled by DNA nanomachines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16048–16052.
Tao, Y.; Chan, H. F.; Shi, B. Y.; Li, M. Q.; Leong, K. W. Light: A magical tool for controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005029.
Bickerton, L. E.; Johnson, T. G.; Kerckhoffs, A.; Langton, M. J. Supramolecular chemistry in lipid bilayer membranes. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 11252–11274.
Langton, M. J. Engineering of stimuli-responsive lipid-bilayer membranes using supramolecular systems. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 46–61.
Cockroft, S. L. Membrane messengers. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 406–407.
De Poli, M.; Zawodny, W.; Quinonero, O.; Lorch, M.; Webb, S. J.; Clayden, J. Conformational photoswitching of a synthetic peptide foldamer bound within a phospholipid bilayer. Science 2016, 352, 575–580.
Lister, F. G. A.; Le Bailly, B. A. F.; Webb, S. J.; Clayden, J. Ligand-modulated conformational switching in a fully synthetic membrane-bound receptor. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 420–425.
Langton, M. J.; Williams, N. H.; Hunter, C. A. Recognition-controlled membrane translocation for signal transduction across lipid bilayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6461–6466.
Langton, M. J.; Scriven, L. M.; Williams, N. H.; Hunter, C. A. Triggered release from lipid bilayer vesicles by an artificial transmembrane signal transduction system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15768–15773.
Langton, M. J.; Keymeulen, F.; Ciaccia, M.; Williams, N. H.; Hunter, C. A. Controlled membrane translocation provides a mechanism for signal transduction and amplification. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 426–430.
Ding, Y. D.; Williams, N. H.; Hunter, C. A. A synthetic vesicle-to-vesicle communication system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17847–17853.
Bravin, C.; Duindam, N.; Hunter, C. A. Artificial transmembrane signal transduction mediated by dynamic covalent chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 14059–14064.
Trevisan, L.; Kocsis, I.; Hunter, C. A. Redox switching of an artificial transmembrane signal transduction system. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2196–2198.
Lingrel, J. B. The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na, K-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 395–412.
Li, Z. C.; Xie, Z. J. The Na/K-ATPase/Src complex and cardiotonic steroid-activated protein kinase cascades. Pflugers Arc. 2009, 457, 635–644.
Tian, J.; Li, X.; Liang, M.; Liu, L. J.; Xie, J. X.; Ye, Q. Q.; Kometiani, P.; Tillekeratne, M.; Jin, R. M.; Xie, Z. J. Changes in sodium pump expression dictate the effects of ouabain on cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14921–14929.
Kometiani, P.; Liu, L. J.; Askari, A. Digitalis-induced signaling by Na+/K+-ATPase in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 929–936.
Makihira, S.; Nikawa, H.; Kajiya, M.; Kawai, T.; Mine, Y.; Kosaka, E.; Silva, M. J. B.; Tobiume, K.; Terada, Y. Blocking of sodium and potassium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase-α1 with ouabain and vanadate suppresses cell-cell fusion during RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 409–418.
Evgenov, O. V.; Pacher, P.; Schmidt, P. M.; Haskó, G.; Schmidt, H. H. H. W.; Stasch, J. P. NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase: Discovery and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 755–768.
Derbyshire, E. R.; Marletta, M. A. Structure and regulation of soluble guanylate cyclase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 533–559.
Murad, F. Nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in cell signaling and drug development. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2003–2011.
Lubos, E.; Handy, D. E.; Loscalzo, J. Role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in atherothrombosis. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5323–5344.
Liu, Y.; Pan, T. Z.; Fang, Y.; Ma, N. N.; Qiao, S. P.; Zhao, L. L.; Wang, R. D.; Wang, T. T.; Li, X. M.; Jiang, X. J. et al. Construction of smart glutathione S-transferase via remote optically controlled supramolecular switches. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6979–6983.
Yin, Y. Z.; Jiao, S. F.; Lang, C.; Liu, J. Q. A supramolecular microgel glutathione peroxidase mimic with temperature responsive activity. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3374–3385.
Yin, Y. Z.; Jiao, S. F.; Lang, C.; Liu, J. Q. A smart artificial glutathione peroxidase with temperature responsive activity constructed by host-guest interaction and self-assembly. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25040–25050.
Bhabak, K. P.; Mugesh, G. Amide-based glutathione peroxidase mimics: Effect of secondary and tertiary amide substituents on antioxidant activity. Chem.—Asian J. 2009, 4, 974–983.
Zou, H. X.; Sun, H. C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L. L.; Li, J. X.; Dong, Z. Y.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J. Y.; Liu, J. Q. Construction of a smart temperature-responsive GPx mimic based on the self-assembly of supraamphiphiles. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1192–1199.
Huang, Y. Y.; Su, E. Z.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. The recent biological applications of selenium-based nanomaterials. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101205.
Huang, Y. Y.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Nanozymes: Classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357–4412.
Huang, Z. P.; Luo, Q.; Guan, S. W.; Gao, J. X.; Wang, Y. G.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. Y.; Dong, Z. Y.; Liu, J. Q. Redox control of GPx catalytic activity through mediating self-assembly of Fmocphenylalanine selenide into switchable supramolecular architectures. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9695–9701.
Ren, H. F.; Wu, Y. T.; Ma, N.; Xu, H. P.; Zhang, X. Side-chain selenium-containing amphiphilic block copolymers: Redox-controlled self-assembly and disassembly. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1460–1466.
Wu, Z. P.; Hilvert, D. Selenosubtilisin as a glutathione peroxidase mimic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 5647–5648.
Dong, Z. Y.; Liu, J. Q.; Mao, S. Z.; Huang, X.; Yang, B.; Ren, X. J.; Luo, G. M.; Shen, J. C. Aryl thiol substrate 3-carboxy-4-nitrobenzenethiol strongly stimulating thiol peroxidase activity of glutathione peroxidase mimic 2, 2′-ditellurobis(2-deoxy-β-cyclodextrin). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 16395–16404.
Sun, H. C.; Miao, L.; Li, J. X.; Fu, S.; An, G.; Si, C. Y.; Dong, Z. Y.; Luo, Q.; Yu, S. J.; Xu, J. Y. et al. Self-assembly of cricoid proteins induced by “soft nanoparticles”: An approach to design multienzymecooperative antioxidative systems. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5461–5469.
Hou, J. X.; Jiang, X. J.; Yang, F. H.; Wang, L.; Yan, T. F.; Liu, S. D.; Xu, J. Y.; Hou, C. X.; Luo, Q.; Liu, J. Q. Supramolecularly regulated artificial transmembrane signal transduction for “ON/OFF”-switchable enzyme catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 5725–5728.
Hayes, J. D.; McLellan, L. I. Glutathione and glutathione-dependent enzymes represent a co-ordinately regulated defence against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 273–300.
Hayes, J. D.; Flanagan, J. U.; Jowsey, I. R. Glutathione transferases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 51–88.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2020YFA0908500 and 2018YFA0901600), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22161142015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4814_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Regulation of artificial supramolecular transmembrane signal transduction by selenium-containing artificial enzyme receptors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Xing, Y., Yan, T. et al. Regulation of artificial supramolecular transmembrane signal transduction by selenium-containing artificial enzyme receptors. Nano Res. 16, 964–969 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4814-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4814-4