Abstract
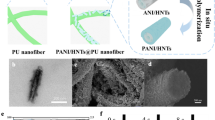
Janus electrospinning nanofiber membranes have attracted extensive attention in the fields such as solar-driven interfacial desalination, liquid filtration, and waterproof and breathable fabrics. However, the Janus structures suffer from weak interfacial bonding and vulnerability to damage, making the durability and sustainability are highly sought after in real-word applications. Herein, we fabricate the simply reconfigurable and entirely self-healing Janus evaporator by electrospinning polypropylene glycol based polyurethane (PPG@PU) and polydimethylsiloxane based polyurethane-CNTs (PDMS@PU-CNTs) with different wettability, which are both designed based on dynamic Diels—Alder (DA) bond. The interface of the Janus membrane is stitched by the covalent bonds to directly improve the interface adhesion to 22 N·m−1, constructing an integrated evaporator, and thereby achieving a stable desalination rate of 1.34 kg·m−2·h−1 under one sun. Reversible dissociation of DA networks allows the evaporators for self-healing and reconfiguration abilities, after which the photothermal performance is maintained. This is the first work for the crosslinked self-healing polymer to be directly electrospun, achieving the improved interfacial bond and reconfiguration of entire evaporators, which presented promising new design principles and materials for interfacial solar seawater desalination.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou, L.; Tan, Y. L.; Ji, D. X.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J.; Gan, Q. Q.; Yu, Z. F.; Zhu, J. Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501227.
Ghasemi, H.; Ni, G.; Marconnet, A. M.; Loomis, J.; Yerci, S.; Miljkovic, N.; Chen, G. Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4449.
Li, R. Y.; Zhang, L. B.; Shi, L.; Wang, P. MXene Ti3C2: An effective 2D light-to-heat conversion material. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3752–3759.
Kashyap, V.; Al-Bayati, A.; Sajadi, S. M.; Irajizad, P.; Wang, S. H.; Ghasemi, H. A flexible anti-clogging graphite film for scalable solar desalination by heat localization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15227–15234.
Qi, Q. B.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D. Robust light-driven interfacial water evaporator by electrospinning SiO2/MWCNTs-COOH/PAN photothermal fiber membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116595.
Huang, Q. L.; Gao, S. P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M. Y.; Xiao, C. F. Study on photothermal PVDF/ATO nanofiber membrane and its membrane distillation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 203–210.
Zha, X. J.; Zhao, X.; Pu, J. P.; Tang, L. S.; Ke, K.; Bao, R. Y.; Bai, L.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, M. B.; Yang, W. Flexible anti-biofouling MXene/cellulose fibrous membrane for sustainable solar-driven water purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 36589–36597.
Shi, S.; Si, Y. F.; Han, Y. T.; Wu, T.; Iqbal, M. I.; Fei, B.; Li, R. K. Y.; Hu, J. L.; Qu, J. P. Recent progress in protective membranes fabricated via electrospinning: Advanced materials, biomimetic structures, and functional applications. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107938.
Gao, S. W.; Dong, X. L.; Huang, J. Y.; Dong, J. N.; di Maggio, F.; Wang, H. C.; Guo, F.; Zhu, T. X.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. K. Bioinspired soot-deposited Janus fabrics for sustainable solar steam generation with salt-rejection. Glob. Chall. 2019, 3, 1800117.
Yang, Y. W.; Zhao, H. Y.; Yin, Z. Y.; Zhao, J. Q.; Yin, X. T.; Li, N.; Yin, D. D.; Li, Y. N.; Lei, B.; Du, Y. P. et al. A general salt-resistant hydrophilic/hydrophobic nanoporous double layer design for efficient and stable solar water evaporation distillation. Mater. Horiz. 2018, 5, 1143–1150.
Ma, X.; Fang, W. Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z. Y.; Chen, D. K.; Ying, W.; Xu, Z.; Gao, C.; Peng, X. S. Hierarchical porous SWCNT stringed carbon polyhedrons and PSS threaded MOF bilayer membrane for efficient solar vapor generation. Small 2019, 15, 1900354.
Hu, R.; Zhang, J. Q.; Kuang, Y. B.; Wang, K. B.; Cai, X. Y.; Fang, Z. Q.; Huang, W. Q.; Chen, G.; Wang Z. X. A Janus evaporator with low tortuosity for long-term solar desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 15333–15340.
Qin, D. D.; Zhu, Y. J.; Yang, R. L.; Xiong, Z. C. A salt-resistant Janus evaporator assembled from ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and nickel oxide for efficient and recyclable solar desalination. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6717–6728.
Zhang, Q.; Yi, G.; Fu, Z.; Yu, H. T.; Chen, S.; Quan, X. Vertically aligned Janus MXene-based aerogels for solar desalination with high efficiency and salt resistance. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13196–13207.
Zhao, J. Q.; Yang, Y. W.; Yang, C. H.; Tian, Y. P.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Yin, X. T.; Que, W. X. A hydrophobic surface enabled salt-blocking 2D Ti3C2 MXene membrane for efficient and stable solar desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16196–16204.
Xu, N.; Li, J. L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, C.; Li, X. Q.; Wang, Y. X.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, S. N. et al. A water lily-inspired hierarchical design for stable and efficient solar evaporation of high-salinity brine. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw7013.
Saleque, A. M.; Ma, S. N.; Ahmed, S.; Hossain, M. I.; Qarony, W.; Tsang, Y. H. Solar driven interfacial steam generation derived from biodegradable luffa sponge. Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2021, 5, 2000291.
Hu, N.; Xu, Y. J.; Liu, Z. T.; Liu, M.; Shao, X. Y.; Wang, J. Double-layer cellulose hydrogel solar steam generation for high-efficiency desalination. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 243, 116480.
Yang, L.; Chen, G. L.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y. X.; Xu, X. F. Sustainable biochar-based solar absorbers for high-performance solar-driven steam generation and water purification. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19311–19320.
Xu, Y. F.; Zhang, J. L.; Wu, S. Y.; Di, Y. S.; Liu, C. H.; Dong, L. F.; Yu, L. Y.; Gan, Z. X. Solar-driven airflow-enhanced all-daytime solar steam generation based on inverse-bowl-shaped graphene aerogels. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2100757.
Zou, Z. A.; Zhu, C. P.; Li, Y.; Lei, X. F.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, J. L. Rehealable, fully recyclable, and malleable electronic skin enabled by dynamic covalent thermoset nanocomposite. Sci. Adv. 2018, 3, eaaq0508.
Yu, S.; Zhang, R. C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, T. H.; Sun, P. C. Bio-inspired high-performance and recyclable cross-linked polymers. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4912–4917.
Zechel, S.; Geitner, R.; Abend, M.; Siegmann, M.; Enke, M.; Kuhl, N.; Klein, M.; Vitz, J.; Gräfe, S.; Dietzek, B. et al. Intrinsic self-healing polymers with a high E-modulus based on dynamic reversible urea bonds. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e420.
Ji, S. B.; Cao, W.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H. P. Dynamic diselenide bonds: Exchange reaction induced by visible light without catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6781–6785.
Zheng, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. Dynamic covalent polymer networks: A molecular platform for designing functions beyond chemical recycling and self-healing. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1716–1745.
Zou, W. K.; Jin, B. J.; Wu, Y.; Song, H. J.; Luo, Y. W.; Huang, F. H.; Qian, J.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. Light-triggered topological programmability in a dynamic covalent polymer network. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz2362.
Miao, W. S.; Zou, W. K.; Jin, B. J.; Ni, C. J.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, T. On demand shape memory polymer via light regulated topological defects in a dynamic covalent network. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4257.
Zhang, Z. M.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. Y.; Liu, Y. H.; Bai, R. X.; Pan, H.; Yu, W.; Yan, X. Z. Muscle-mimetic synergistic covalent and supramolecular polymers: Phototriggered formation leads to mechanical performance boost. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 902–911.
Zhang, Q.; Shi, C. Y.; Qu, D. H.; Long, Y. T.; Feringa, B. L.; Tian, H. Exploring a naturally tailored small molecule for stretchable, self-healing, and adhesive supramolecular polymers. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat8192.
Xia, Q. Q.; Chen, C. J.; Yao, Y. G.; Li, J. G.; He, S. M.; Zhou, Y. B.; Li, T.; Pan, X. J.; Yao, Y.; Hu, L. B. A strong, biodegradable and recyclable lignocellulosic bioplastic. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 627–635.
Guo, Y. F.; Chen, S.; Sun, L. J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Z.; Lou, J. M.; You, Z. W. Degradable and fully recyclable dynamic thermoset elastomer for 3D-printed wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009799.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the grants (Nos. 51973027 and 52003044) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2232020A-08), International Cooperation Fund of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 21130750100), and Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Projects of Shandong Province (No. 2021CXGC011004). This work has also been supported by the Chang Jiang Scholars Program and the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 2019-01-07-00-03-E00023) to Prof. X. H. Q., Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST, State Key Laboratory for Modification of Chemical Fibers and Polymer Materials (KF2216) and DHU Distinguished Young Professor Program to Prof. L. M. W.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Gu, J., Liu, Y. et al. Reconfiguration and self-healing integrated Janus electrospinning nanofiber membranes for durable seawater desalination. Nano Res. 16, 489–495 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4733-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4733-4