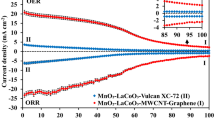
Abstract
Rational design and tailoring of the structural features of Co—N—C catalysts are urgently required to construct highly efficient bifunctional non-noble metal electrocatalysts for both oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Herein, we report a series of carbon-based catalysts with varied structural features, specifically the graphitic degree of carbon, porosity, and the configuration of active sites, and their effects on bifunctional oxygen electrocatalytic reactions. Through the synergistic tuning of these structural factors, the well-tailored Co—N—C catalyst exhibits a high bifunctional electrocatalytic activity, as revealed by a half-wave potential of 0.84 V for ORR and a low overpotential of 420 mV at 10 mA·cm−2 for OER. More impressively, the Zn-air battery using the optimum catalyst delivers excellent performance including a peak power density of 125.2 mW·cm−2 and a specific capacity of 790.8 mAh·gZn−1, as well as stable cycling durability, outperforming the noble metals-based catalysts. The first-principles calculations reveal that the interlayer interaction between the pyridinic N-doped graphene and the confined Co nanoparticles increases the electronic states of the active C atoms near the Fermi level, thus enhancing the adsorption of the HOO* intermediate and generating superior catalytic activity for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. By comprehensively studying the structural factors of catalysts, the bifunctional catalytic behaviors, the use in a practical Zn-air device, and theoretical simulations, this work may also give inspirations to the design, use, and understanding of other kinds of catalysts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gewirth, A. A.; Varnell, J. A.; DiAscro, A. M. Nonprecious metal catalysts for oxygen reduction in heterogeneous aqueous systems. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 2313–2339.
Seh, Z. W.; Kibsgaard, J.; Dickens, C. F.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J. K.; Jaramillo, T. F. Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: Insights into materials design. Science 2017, 355, eaad4998.
Wang, B.; Cui, X. Y.; Huang, J. Q.; Cao, R.; Zhang, Q. Recent advances in energy chemistry of precious-metal-free catalysts for oxygen electrocatalysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1757–1767.
Ren, S. S.; Duan, X. D.; Liang, S.; Zhang, M. D.; Zheng, H. G. Bifunctional electrocatalysts for Zn-air batteries: Recent developments and future perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 6144–6182.
Wang, Y. J.; Fang, B. Z.; Wang, X. M.; Ignaszak, A.; Liu, Y. Y.; Li, A. J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. J. Recent advancements in the development of bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen electrodes in unitized regenerative fuel cells (URFCs). Prog. Mater Sci. 2018, 98, 108–167.
Liu, J. Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, H. J.; Du, X. W.; Zhang, B.; Hong, Z. L.; Sun, S. S.; Wang, W. C. Progress and challenges toward the rational design of oxygen electrocatalysts based on a descriptor approach. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1901614.
Wu, G.; More, K. L.; Johnston, C. M.; Zelenay, P. High-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction derived from polyaniline, iron, and cobalt. Science 2011, 332, 443–447.
Chung, H. T.; Cullen, D. A.; Higgins, D.; Sneed, B. T.; Holby, E. F.; More, K. L.; Zelenay, P. Direct atomic-level insight into the active sites of a high-performance PGM-free ORR catalyst. Science 2017, 357, 479–484.
Xia, B. Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, H. B.; Lou, X. W.; Wang, X. A metal—organic framework-derived bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 15006.
Zhang, M. D.; Dai, Q. B.; Zheng, H. G.; Chen, M. D.; Dai, L. M. Novel MOF-derived Co@N—C bifunctional catalysts for highly efficient Zn-air batteries and water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705431.
Yan, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M. Y.; Hao, S. M.; Cui, X.; Li, Z. W.; Lin, Z. Q. Robust wrinkled MoS2/N—C bifunctional electrocatalysts interfaced with single Fe atoms for wearable zinc-air batteries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2110036118.
Huang, X. X.; Zhang, Y. L.; Shen, H. M.; Li, W.; Shen, T.; Ali, Z.; Tang, T. Y.; Guo, S. J.; Sun, Q.; Hou, Y. L. N-doped carbon nanosheet networks with favorable active sites triggered by metal nanoparticles as bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2914–2920.
Martinaiou, I.; Monteverde Videla, A. H. A.; Weidler, N.; Kübler, M.; Wallace, W. D. Z.; Paul, S.; Wagner, S.; Shahraei, A.; Stark, R. W.; Specchia, S. et al. Activity and degradation study of an Fe—N—C catalyst for ORR in direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC). Appl. Catal. B 2020, 262, 118217.
Peng, H. L.; Liu, F. F.; Liu, X. J.; Liao, S. J.; You, C. H.; Tian, X. L.; Nan, H. X.; Luo, F.; Song, H. Y.; Fu, Z. Y. et al. Effect of transition metals on the structure and performance of the doped carbon catalysts derived from polyaniline and melamine for ORR application. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3797–3805.
Wang, X. X.; Cullen, D. A.; Pan, Y. T.; Hwang, S.; Wang, M. Y.; Feng, Z. X.; Wang, J. Y.; Engelhard, M. H.; Zhang, H. G.; He, Y. H. et al. Nitrogen-coordinated single cobalt atom catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706758.
Gadipelli, S.; Zhao, T. T.; Shevlin, S. A.; Guo, Z. X. Switching effective oxygen reduction and evolution performance by controlled graphitization of a cobalt—nitrogen—carbon framework system. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1661–1667.
Li, S.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, X. J.; Schmidt, J.; Thomas, A. Active salt/silica-templated 2D mesoporous FeCo—Nx-carbon as bifunctional oxygen electrodes for zinc-air batteries. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1856–1862.
Li, M. T.; Zhang, L. P.; Xu, Q.; Niu, J. B.; Xia, Z. H. N-doped graphene as catalysts for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions: Theoretical considerations. J. Catal 2014, 314, 66–72.
Kim, H. W.; Bukas, V. J.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Diederichsen, K. M.; Lim, J.; Cho, Y. H.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Han, T. H. et al. Mechanisms of two-electron and four-electron electrochemical oxygen reduction reactions at nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 852–863.
Chen, Y. Z.; Wang, C. M.; Wu, Z. Y.; Xiong, Y. J.; Xu, Q.; Yu, S. H.; Jiang, H. L. From bimetallic metal—organic framework to porous carbon: High surface area and multicomponent active dopants for excellent electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 5010–5016.
Qiao, M. F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, G. Z.; Mamat, X.; Zhang, S. S.; Wang, S. Y. Hierarchically ordered porous carbon with atomically dispersed FeN4 for ultraefficient oxygen reduction reaction in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2688–2694.
Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, W. T.; Wang, Q.; Cuello, N. C.; Nafady, A.; Al-Enizi, A. M.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Goenaga, G. A.; Zawodzinski, T. A. et al. Tunable synthesis of hollow metal—nitrogen—carbon capsules for efficient oxygen reduction catalysis in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8087–8098.
Aijaz, A.; Masa, J.; Rösler, C.; Xia, W.; Weide, P.; Botz, A. J. R.; Fischer, R. A.; Schuhmann, W.; Muhler, M. Co@Co3O4 encapsulated in carbon nanotube-grafted nitrogen-doped carbon polyhedra as an advanced bifunctional oxygen electrode. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4087–4091.
Hou, C. C.; Zou, L. L.; Xu, Q. A hydrangea-like superstructure of open carbon cages with hierarchical porosity and highly active metal sites. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904689.
Liu, H. M.; Liu, Q. L.; Wang, Y. R.; Wang, Y. F.; Chou, S. L.; Hu, Z. Z.; Zhang, Z. Q. Bifunctional carbon-based cathode catalysts for zinc-air battery: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 683–692.
Duan, X. D.; Ren, S. S.; Pan, N.; Zhang, M. D.; Zheng, H. G. MOF-derived Fe,Co@N—C bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for Zn-air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9355–9363.
Duan, X. D.; Pan, N.; Sun, C.; Zhang, K. X.; Zhu, X. K.; Zhang, M. D.; Song, L.; Zheng, H. G. MOF-derived Co-MOF,O-doped carbon as trifunctional electrocatalysts to enable highly efficient Zn-air batteries and water-splitting. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 56, 290–298.
Duan, X. D.; Ren, S. S.; Ge, F. Y.; Zhu, X. K.; Zhang, M. D.; Zheng, H. G. MOF-derived CoNi,CoO,NiO@N—C bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for liquid and all-solid-state Zn-air batteries. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17655–17662.
Wu, G.; Mack, N. H.; Gao, W.; Ma, S. G.; Zhong, R. Q.; Han, J. T.; Baldwin, J. K.; Zelenay, P. Nitrogen-doped graphene-rich catalysts derived from heteroatom polymers for oxygen reduction in nonaqueous lithium-O2 battery cathodes. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9764–9776.
Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: Spectral analysis and structural information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742.
Zhang, H. B.; Zhou, W.; Chen, T.; Guan, B. Y.; Li, Z.; Lou, X. W. A modular strategy for decorating isolated cobalt atoms into multichannel carbon matrix for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1980–1984.
Yamaguchi, T.; Bandow, S.; Iijima, S. Synthesis of carbon nanohorn particles by simple pulsed arc discharge ignited between pre-heated carbon rods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 389, 181–185.
Chen, Y. J.; Gao, R.; Ji, S. F.; Li, H. J.; Tang, K.; Jiang, P.; Hu, H. B.; Zhang, Z. D.; Hao, H. G.; Qu, Q. Y. et al. Atomic-level modulation of electronic density at cobalt single-atom sites derived from metal—organic frameworks: Enhanced oxygen reduction performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3212–3221.
Meng, Y. Y.; Voiry, D.; Goswami, A.; Zou, X. X.; Huang, X. X.; Chhowalla, M.; Liu, Z. W.; Asefa, T. N-, O-, and S-tridoped nanoporous carbons as selective catalysts for oxygen reduction and alcohol oxidation reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13554–13557.
Wang, T. T.; Kou, Z. K.; Mu, S. C.; Liu, J. P.; He, D. P.; Amiinu, I. S.; Meng, W.; Zhou, K.; Luo, Z. X.; Chaemchuen, S. et al. 2D dual-metal zeolitic-imidazolate-framework-(ZIF)-derived bifunctional air electrodes with ultrahigh electrochemical properties for rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705048.
Ji, D. X.; Fan, L.; Li, L. L.; Peng, S. J.; Yu, D. S.; Song, J. N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Guo, S. J. Atomically transition metals on self-supported porous carbon flake arrays as binder-free air cathode for wearable zinc-air batteries. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808267.
Yang, L. P.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L. X.; Hou, J. H.; Zhou, Z.; Lv, R. T. Atomic Fe—N4/C in flexible carbon fiber membrane as binder-free air cathode for Zn-air batteries with stable cycling over 1,000 h. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105410.
Singh, H.; Zhuang, S. Q.; Ingis, B.; Nunna, B. B.; Lee, E. S. Carbon-based catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction: A review on degradation mechanisms. Carbon 2019, 151, 160–174.
Zhang, J. T.; Zhao, Z. H.; Xia, Z. H.; Dai, L. M. A metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 444–452.
Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. B.; Dai, L. M.; Yao, J. N. Scalable fabrication of nanoporous carbon fiber films as bifunctional catalytic electrodes for flexible Zn-air batteries. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3000–3006.
Tang, C.; Wang, H. F.; Chen, X.; Li, B. Q.; Hou, T. Z.; Zhang, B. S.; Zhang, Q.; Titirici, M. M.; Wei, F. Topological defects in metal-free nanocarbon for oxygen electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6845–6851.
Wang, J.; Wu, H. H.; Gao, D. F.; Miao, S.; Wang, G. X.; Bao, X. H. High-density iron nanoparticles encapsulated within nitrogen-doped carbon nanoshell as efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for zinc-air battery. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 387–396.
Liu, S. H.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zhou, S.; Yu, F. J.; Yu, M. Z.; Chiang, C. Y.; Zhou, W. Z.; Zhao, J. J.; Qiu, J. S. Metal—organic-framework-derived hybrid carbon nanocages as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700874.
Yu, P.; Wang, L.; Sun, F. F.; Xie, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, J. Y.; Wang, X. W.; Tian, C. G.; Li, J. H.; Fu, H. G. Co nanoislands rooted on Co—N—C nanosheets as efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for Zn-air batteries. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901666.
Qu, K. G.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, S.; Qiao, S. Z. Graphene oxide-polydopamine derived N,S-codoped carbon nanosheets as superior bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution. Nano Energy 2016, 19, 373–381.
Fei, H. L.; Dong, J. C.; Arellano-Jimenez, M. J.; Ye, G. L.; Dong Kim, N.; Samuel, E. L. G.; Peng, Z. W.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, F.; Bao, J. M. et al. Atomic cobalt on nitrogen-doped graphene for hydrogen generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8668.
Swart, J. C. W.; van Steen, E.; Ciobícă, I. M.; van Santen, R. A. Interaction of graphene with FCC-Co(111). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 803–807.
Chorkendorff, I.; Niemantsverdriet, J. W. Concepts of Modern Catalysis and Kinetics; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2007.
Nørskov, J. K.; Rossmeisl, J.; Logadottir, A.; Lindqvist, L.; Kitchin, J. R.; Bligaard, T.; Jónsson, H. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886–17892.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51425302, 51702062, and U20A20131), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFA1202802), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (No. 2021M690801), the CAS Pioneer Hundred Talents Program, and the China University of Petroleum (East China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2022_4497_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Synergistically tuning the graphitic degree, porosity, and the configuration of active sites for highly active bifunctional catalysts and Zn-air batteries
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Kong, D., Cao, F. et al. Synergistically tuning the graphitic degree, porosity, and the configuration of active sites for highly active bifunctional catalysts and Zn-air batteries. Nano Res. 15, 7959–7967 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4497-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4497-x