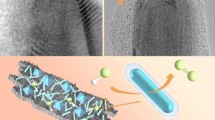
Abstract
The sluggish charge transfer and poor intrinsic activity are the bottlenecks that hamper the further development of electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. A novel core-shell heterostructure of Cu3P@Ni is fabricated, which is composed of Cu3P nanorods covered by metallic Ni. The as-prepared Cu3P@Ni exhibits a durable and superior activity toward hydrogen evolution, with an overpotential of 42 mV to deliver 10 mA·cm−2 and a Tafel slope of 41 mV·dec−1. Charge redistribution is observed after successfully constructing the core-shell heterostructure, leading to the altered electronic structure. The theoretical calculations have manifested that Cu3P@Ni exhibits a zero bandgap and optimized adsorption strength of intermediates, which could give rise to the accelerated charge transfer as well as increased intrinsic activity. This work could shed light on the development of novel electrocatalysts with modulated electronic structure for highly efficient hydrogen evolution.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Züttel, A.; Remhof, A.; Borgschulte, A.; Friedrichs, O. Hydrogen: The future energy carrier. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. A:Math., Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 3329–3342.
Ali, A.; Shen, P. K. Nonprecious metal’s graphene-supported electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction: Fundamentals to applications. Carbon Energy 2020, 2, 99–121.
Wang, H. X.; Cui, Y. Nanodiamonds for energy. Carbon Energy 2019, 1, 13–18.
Yuan, Y. F.; Lu, J. Demanding energy from carbon. Carbon Energy 2019, 1, 8–12.
Zhao, H.; Zhang, H. Z.; Cui, G. W.; Dong, Y. M.; Wang, G. L.; Jiang, P. P.; Wu, X. M.; Zhao, N. A photochemical synthesis route to typical transition metal sulfides as highly efficient cocatalyst for hydrogen evolution: From the case of NiS/g-C3N4. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2018, 225, 284–290.
Sun, Y. G.; Alimohammadi, F.; Zhang, D. T.; Guo, G. S. Enabling colloidal synthesis of edge-oriented MoS2 with expanded interlayer spacing for enhanced HER catalysis. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1963–1969.
Li, Y. G.; Wang, H. L.; Xie, L. M.; Liang, Y. Y.; Hong, G. S.; Dai, H. J. MoS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: An advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7296–7299.
Chen, Y. T.; Ren, R.; Wen, Z. H.; Ci, S. Q.; Chang, J. B.; Mao, S.; Chen, J. H. Superior electrocatalysis for hydrogen evolution with crumpled graphene/tungsten disulfide/tungsten trioxide ternary nanohybrids. Nano Energy 2018, 47, 66–73.
Ma, B.; Yang, Z. C.; Yuan, Z. H.; Chen, Y. T. Effective surface roughening of three-dimensional copper foam via sulfurization treatment as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 1620–1626.
Wang, H. T.; Kong, D. S.; Johanes, P.; Cha, J. J.; Zheng, G. Y.; Yan, K.; Liu, N.; Cui, Y. MoSe2 and WSe2 nanofilms with vertically aligned molecular layers on curved and rough surfaces. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3426–3433.
Zhou, X. L.; Liu, Y.; Ju, H. X.; Pan, B. C.; Zhu, J. F.; Ding, T.; Wang, C. D.; Yang, Q. Design and epitaxial growth of MoSe2-NiSe vertical heteronanostructures with electronic modulation for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1838–1846.
Mao, S.; Wen, Z. H.; Ci, S. Q.; Guo, X. R.; Ostrikov, K.; Chen, J. H. Perpendicularly oriented MoSe2/graphene nanosheets as advanced electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Small 2015, 11, 414–419.
Shen, S. J.; Lin, Z. P.; Song, K.; Wang, Z. P.; Huang, L. G.; Yan, L. H.; Meng, F. Q.; Zhang, Q. H.; Gu, L.; Zhong, W. W. Reversed active sites boost the intrinsic activity of graphene-like cobalt selenide for hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 12360–12365.
Conley, H. J.; Wang, B.; Ziegler, J. I.; Haglund, R. F. Jr.; Pantelides, S. T.; Bolotin, K. I. Bandgap engineering of strained monolayer and bilayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3626–3630.
Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, J.; Jia, Y. A.; Chen, C. M.; Komarneni, S.; Yang, D. J.; Yao, X. D. Electronic structure tuning in Ni3FeN/r-GO aerogel toward bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 245–253.
Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. T.; Ren, H.; Pan, Y.; Yan, Y. G.; Sun, F. C.; Wang, X. Y.; Wang, S. T.; Zhang, J. Mo doping induced metallic CoSe for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2020, 268, 118467.
Chen, X. H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L. L.; Shen, L.; Fu, H. C.; Luo, J.; Li, X. L.; Lei, J. L.; Luo, H. Q.; Li, N. B. Regulation of the electronic structure of Co4N with novel Nb to form hierarchical porous nanosheets for electrocatalytic overall water splitting. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 15, 100268.
Xu, K.; Sun, Y. Q.; Sun, Y. M.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Jia, G. C.; Zhang, Q. H.; Gu, L.; Li, S. Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, H. J. Yin-Yang harmony: Metal and nonmetal dual-doping boosts electrocatalytic activity for alkaline hydrogen evolution. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 2750–2756.
Hinnemann, B.; Moses, P. G.; Bonde, J.; Jørgensen, K. P.; Nielsen, J. H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J. K. Biomimetic hydrogen evolution: MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5308–5309.
Jaramillo, T. F.; Jørgensen, K. P.; Bonde, J.; Nielsen, J. H.; Horch, S.; Chorkendorff, I. Identification of active edge sites for electrochemical H2 evolution from MoS2 nanocatalysts. Science 2007, 317, 100–102.
Popczun, E. J.; McKone, J. R.; Read, C. G.; Biacchi, A. J.; Wiltrout, A. M.; Lewis, N. S.; Schaak, R. E. Nanostructured nickel phosphide as an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9267–9270.
Zhang, R.; Wang, X. X.; Yu, S. J.; Wen, T.; Zhu, X. W.; Yang, F. X.; Sun, X. N.; Wang, X. K.; Hu, W. P. Ternary NiCo2Px nanowires as pH-universal electrocatalysts for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 2011, 29, 1605502.
Ma, B.; Yang, Z. C.; Chen, Y. T.; Yuan, Z. H. Nickel cobalt phosphide with three-dimensional nanostructure as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in both acidic and alkaline electrolytes. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 375–380.
Wang, Y. P.; Ma, B.; Chen, Y. T. Iron phosphides supported on three-dimensional iron foam as an efficient electrocatalyst for water splitting reactions. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 14872–14883.
Xiao, P.; Sk, M. A.; Thia, L.; Ge, X. M.; Lim, R. J.; Wang, J. Y.; Lim, K. H.; Wang, X. Molybdenum phosphide as an efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 1, 2624–2629.
Zhao, J. P.; Fu, B.; Li, X.; Ge, Z. H.; Ma, B.; Chen, Y. T. Construction of the Ni2P/MoP heterostructure as a high-performance cocatalyst for visible-light-driven hydrogen production. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 10910–10919.
Ma, B.; Zhao, J. P.; Ge, Z. H.; Chen, Y. T.; Yuan, Z. H. 5 nm NiCoP nanoparticles coupled with g-C3N4 as high-performance photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 63, 258–266.
Callejas, J. F.; McEnaney, J. M.; Read, C. G.; Crompton, J. C.; Biacchi, A. J.; Popczun, E. J.; Gordon, T. R.; Lewis, N. S.; Schaak, R. E. Electrocatalytic and photocatalytic hydrogen production from acidic and neutral-pH aqueous solutions using iron phosphide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11101–11107.
Xie, J. Q.; Ji, Y. Q.; Kang, J. H.; Sheng, J. L.; Mao, D. S.; Fu, X. Z.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. P. In situ growth of Cu(OH)2@FeOOH nanotube arrays on catalytically deposited Cu current collector patterns for high-performance flexible in-plane micro-sized energy storage devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 194–205.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, N. Y.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Self-supported Cu3P nanowire arrays as an integrated high-performance three-dimensional cathode for generating hydrogen from water. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9577–9581.
Li, X.; Liu, P. F.; Zhang, L.; Zu, M. Y.; Yang, Y. X.; Yang, H. G. Enhancing alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction activity through NiMn3O4 nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10566–10569.
Wang, R.; Dong, X. Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, J. Y.; Zang, S. Q. MOF-derived bifunctional Cu3P nanoparticles coated by a N, P-codoped carbon shell for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703711.
Li, G. X.; Wang, J. G.; Yu, J. Y.; Liu, H.; Cao, Q.; Du, J. L.; Zhao, L. L.; Jia, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W. J. Ni-Ni3P nanoparticles embedded into N, P-doped carbon on 3D graphene frameworks via in situ phosphatization of saccharomycetes with multifunctional electrodes for electrocatalytic hydrogen production and anodic degradation. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2020, 261, 118147.
Hou, C. C.; Chen, Q. Q.; Wang, C. J.; Liang, F.; Lin, Z. S.; Fu, W. F.; Chen, Y. Self-supported cedarlike semimetallic Cu3P nanoarrays as a 3D high-performance janus electrode for both oxygen and hydrogen evolution under basic conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23037–23048.
Shang, L. M.; Lv, X. M.; Shen, H.; Shao, Z. Z.; Zheng, G. F. Selective carbon dioxide electroreduction to ethylene and ethanol by core-shell copper/cuprous oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 426–431.
Song, S.; Yao, S. K.; Cao, J. H.; Di, L.; Wu, G. J.; Guan, N. J.; Li, L. D. Heterostructured Ni/NiO composite as a robust catalyst for the hydrogenation of levulinic acid to β-valerolactone. Appl. Catal. B:Environ. 2011, 217, 115–124.
Jiang, X. C.; Li, H. M.; Li, S. L.; Huang, S. W.; Zhu, C. L.; Hou, L. X. Metal-organic framework-derived Ni-Co alloy@carbon microspheres as high-performance counter electrode catalysts for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 419–431.
Zhou, W. J.; Wu, X. J.; Cao, X. H.; Huang, X.; Tan, C. L.; Tian, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Y.; Zhang, H. Ni3S2 nanorods/Ni foam composite electrode with low overpotential for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2921–2924.
Shen, R. C.; Xie, J.; Ding, Y. N.; Liu, S. Y.; Adamski, A.; Chen, X. B.; Li, X. Carbon nanotube-supported Cu3P as high-efficiency and low-cost cocatalysts for exceptional semiconductor-free photocatalytic H2 evolution. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3243–3250.
Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M. R.; Wang, S. Y.; Li, X. M.; Zhu, H. W. Cobalt and nickel selenide nanowalls anchored on graphene as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14789–14795.
Li, F.; Han, G. F.; Noh, H. J.; Jeon, J. P.; Ahmad, I.; Chen, S. S.; Yang, C.; Bu, Y. F.; Fu, Z. P.; Lu, Y. L. et al. Balancing hydrogen adsorption/desorption by orbital modulation for efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4060.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51702234) and the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City (No. 18JCQNJC78800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Li, X., Ma, B. et al. Cu3P@Ni core-shell heterostructure with modulated electronic structure for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. Nano Res. 15, 2935–2942 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3915-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3915-9