Abstract
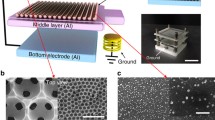
Miniaturized mobile electronic devices have aroused great attention due to their convenience to daily life. However, they still face a problem that power supply from the conventional cell needs to be regularly charged or replaced. Portable electricity supply collecting energy from environment is highly desired. Herein, a highly flexible and stretchable Miura folding based triboelectric nanogenerator (MF-TENG) is prepared by using flexible polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as a folding substrate with a double working side design, specifically one side as the main TENG (M-TENG) and other side as the excitation TENG (E-TENG). The E-TENG supplements charge to M-TENG by a half-wave rectifier circuit. This design increases the TENG working area and reduces its volume. The output performance of the TENG based on Miura folding with charge excitation called MF-CE-TENG is greatly boosted. The optimal output charge and maximum peak power of MF-CE-TENG achieves 1.54 µC and 5.17 mW at 1 Hz, respectively, which is 4.61 and 10.55 times as much as that of MF-TENG without charge excitation. To demonstrate its applications, the MF-CE-TENG is used to light up 456 LEDs brightly and charge a 100 µF capacitor to 6.07 V in 5 min. A calculator and a temperature-humidity sensor work normally powered by MF-CE-TENG with an energy management module. This work provides a new strategy to enhance the output energy of Miura folding TENG by applying a charge excitation mode for the first time, which might be an effective approach to be used in other TENGs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel, M.; Wang, J. F. Applications, challenges, and prospective in emerging body area networking technologies. IEEE Wirel. Commun.2010, 17, 80–88.
Mojarradi, M.; Binkley, D.; Blalock, B.; Andersen, R.; Ulshoefer, N.; Johnson, T.; Del Castillo, L. A miniaturized neuroprosthesis suitable for implantation into the brain. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng.2003, 11, 38–42.
Chen, G. R.; Li, Y. Z.; Bick, M.; Chen, J. Smart textiles for electricity generation. Chem. Rev.2020, 120, 3668–3720.
Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N. N.; Zou, H. Y.; Liu, R. Y.; Tao, C. Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z. L. Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nat. Energy2016, 1, 16138.
Zhang, N. N.; Huang, F.; Zhao, S. L.; Lv, X. H.; Zhou, Y. H.; Xiang, S. W.; Xu, S. M.; Li, Y. Z.; Chen, G. R.; Tao, C. Y. et al. Photo-rechargeable fabrics as sustainable and robust power sources for wearable bioelectronics. Matter2020, 2, 1260–1269.
Zou, Y. J.; Raveendran, V.; Chen, J. Wearable triboelectric nanogenerators for biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy2020, 77, 105303.
Wang, P. H.; Pan, L.; Wang, J. Y.; Xu, M. Y.; Dai, G. Z.; Zou, H. Y.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z. L. An ultra-low-friction triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator for rotation energy harvesting and self-powered wind speed sensor. ACS Nano2018, 12, 9433–9440.
Li, Y. J.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J. N. A miniaturized electromagnetic energy harvester with volt-level output based on stacked flexible coils. Smart. Mater. Struct.2018, 27, 115040.
Tan, Y. S.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X. H. Review of MEMS electromagnetic vibration energy harvester. J. Microelectromech. Syst.2017, 26, 1–16.
Wang, S. W.; Bi, M. Z.; Cao, Z. Y.; Ye, X. Y. Linear freestanding electret generator for harvesting swinging motion energy: Optimization and experiment. Nano Energy2019, 65, 104013.
Zhang, Y. L.; Wang, T. Y.; Luo, A. X.; Hu, Y. S.; Li, X. X.; Wang, F. Micro electrostatic energy harvester with both broad bandwidth and high normalized power density. Appl. Energ.2018, 212, 362–371.
Zhou, T.; Zhang, L. M.; Xue, F.; Tang, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z. L. Multilayered electret films based triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1442–1451.
Fan, K. Q.; Tan, Q. X.; Zhang, Y. W.; Liu, S. H.; Cai, M. L.; Zhu, Y. M. A monostable piezoelectric energy harvester for broadband low-level excitations. Appl. Phys. Lett.2018, 112, 123901.
Shan, X. B.; Li, H. L.; Yang, Y. C.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. C.; Xie, T. Enhancing the performance of an underwater piezoelectric energy harvester based on flow-induced vibration. Energy2019, 172, 134–140.
Wang, J. L.; Zhou, S. X.; Zhang, Z. E.; Yurchenko, D. Highperformance piezoelectric wind energy harvester with Y-shaped attachments. Energy Convers. Manage.2019, 181, 645–652.
Zhang, X. Q.; Pondrom, P.; Sessler, G. M.; Ma, X. C. Ferroelectret nanogenerator with large transverse piezoelectric activity. Nano Energy2018, 50, 52–61.
Ueno, T. Performance of improved magnetostrictive vibrational power generator, simple and high power output for practical applications. J. Appl. Phys.2015, 117, 17A740.
Yang, Z. S.; Tang, L. H.; Tao, K.; Aw, K. A broadband electret-based vibrational energy harvester using soft magneto-sensitive elastomer with asymmetrical frequency response profile. Smart Mater. Struct.2019, 28, 10LT02.
Zou, H. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L. T.; Wang, P. H.; He, X.; Dai, G. Z.; Zheng, H. W.; Chen, C. Y.; Wang, A. C.; Xu, C. et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun.2019, 10, 1427.
Lin, Z. M.; Zhang, B. B.; Guo, H. Y.; Wu, Z. Y.; Zou, H. Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z. L. Super-robust and frequency-multiplied triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting water and wind energy. Nano Energy2019, 64, 103908
Wang, Z. L.; Wang, A. C. On the origin of contact-electrification. Mater. Today2019, 30, 34–51.
Niu, S. M.; Wang, S. H.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. S.; Hu, Y. F.; Wang, Z. L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci.2013, 6, 3576–3583.
Qin, K.; Chen, C.; Pu, X. J.; Tang, Q.; He, W. C.; Liu, Y. K.; Zeng, Q. X.; Liu, G. L.; Guo, H. Y.; Hu, C. G. Magnetic array assisted triboelectric nanogenerator sensor for real-time gesture interaction. Nano-Micro Lett.2021, 13, 51.
Liu, G. L.; Xiao, L. F.; Chen, C. Y.; Liu, W. L.; Pu, X. J.; Wu, Z. Y.; Hu, C. G.; Wang, Z. L. Power cables for triboelectric nanogenerator networks for large-scale blue energy harvesting. Nano Energy2020, 75, 104975.
Tang, Q.; Guo, H. Y.; Yan, P.; Hu, C. G. Recent progresses on paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator for portable self-powered sensing systems. EcoMat2020, 2, e12060.
Xia, K. Q.; Zhang, H. Z.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Xu, Z. W. Folding triboelectric nanogenerator on paper based on conductive ink and teflon tape. Sensor. Actuat. A-Phys.2018, 272, 28–32.
An, J.; Wang, Z. M.; Jiang, T.; Liang, X.; Wang, Z. L. Whirling-folded triboelectric nanogenerator with high average power for water wave energy harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater.2019, 29, 1904867.
Tao, K.; Yi, H. P.; Yang, Y.; Chang, H. L.; Wu, J.; Tang, L. H.; Yang, Z. S.; Wang, N.; Hu, L. X.; Fu, Y. Q. et al. Origami-inspired electret-based triboelectric generator for biomechanical and ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy2020, 67, 104197.
Yang, H. M.; Deng, M. M.; Tang, Q.; He, W. C.; Hu, C. G.; Xi, Y.; Liu, R. C.; Wang, Z. L. A nonencapsulative pendulum-like paper-based hybrid nanogenerator for energy harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater.2019, 9, 1901149.
Li, S. L. Double-folding paper-based generator for mechanical energy harvesting. Front. Optoelectron.2017, 10, 38–43.
Chen, C.; Howard, D.; Zhang, S. L.; Do, Y.; Sun, S.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z. L.; Abowd, G. D.; Oh, H. SPIN (Self-powered paper interfaces): Bridging triboelectric nanogenerator with folding paper creases. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2020, pp 431–442.
Zhou, C. J.; Yang, Y. Q.; Sun, N.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, P.; Xie, X. K.; Shao, H. Y.; Shen, Q. Q.; Chen, X. P.; Liu, Y. N. et al. Flexible self-charging power units for portable electronics based on folded carbon paper. Nano Res.2018, 11, 4313–4322.
Niu, S. M.; Zhou, Y. S.; Wang, S. H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Bando, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Simulation method for optimizing the performance of an integrated triboelectric nanogenerator energy harvesting system. Nano Energy2014, 8, 150–156.
Niu, S. M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. S.; Wang, S. H.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z. L. Optimization of triboelectric nanogenerator charging systems for efficient energy harvesting and storage. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev.2015, 62, 641–647.
Schenk, M.; Guest, S. D. Geometry of miura-folded metamaterials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA2013, 110, 3276–3281.
Silverberg, J. L.; Evans, A. A.; McLeod, L.; Hayward, R. C.; Hull, T.; Santangelo, C. D.; Cohen, I. Using origami design principles to fold reprogrammable mechanical metamaterials. Science2014, 345, 647–650.
Song, Z. M.; Ma, T.; Tang, R.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, X.; Krishnaraju, D.; Panat, R.; Chan, C. K.; Yu, H. Y.; Jiang, H. P. Origami lithium-ion batteries. Nat. Commun.2014, 5, 3140.
Yasuda, H.; Yang, J. Reentrant origami-based metamaterials with negative poisson’s ratio and bistability. Phys. Rev. Lett.2015, 114, 185502.
Tao, K.; Yi, H. P.; Yang, Y.; Tang, L. H.; Yang, Z. S.; Wu, J.; Chang, H. L.; Yuan, W. Z. Miura-origami-inspired electret/triboelectric power generator for wearable energy harvesting with water-proof capability. Microsyst. Nanoeng.2020, 6, 56.
Liu, W. L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, G. L.; Chen, J.; Pu, X. J.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H. Y.; Hu, C. G. et al. Integrated charge excitation triboelectric nanogenerator. Nat. Commun.2019, 10, 1426.
He, W. C.; Liu, W. L.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. K.; Pu, X. J.; Yang, H. M.; Tang, Q.; Yang, H. K.; Guo, H. Y. et al. Boosting output performance of sliding mode triboelectric nanogenerator by charge space-accumulation effect. Nat. Commun.2020, 11, 4277.
Wang, Z.; Liu, W. L.; Hu, J. L.; He, W. C.; Yang, H. K.; Ling, C.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, A. P.; Hu, C. G. Two voltages in contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator: From asymmetry to symmetry for maximum output. Nano Energy2020, 69, 104452.
Liu, Y. K.; Liu, W. L.; Wang, Z.; He, W. C.; Tang, Q.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, H. Y.; Hu, C. G. Quantifying contact status and the air-breakdown model of charge-excitation triboelectric nanogenerators to maximize charge density. Nat. Commun.2020, 11, 1599.
Wang, Z.; Liu, W. L.; He, W. C.; Guo, H. Y.; Long, L.; Xi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, A. P.; Hu, C. G. Ultrahigh electricity generation from low-frequency mechanical energy by efficient energy management. Joule2021, 5, 441–455.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52073037), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2019CDXZWL001) and Chongqing graduate tutor team construction project (No. ydstd1832).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary material, approximately 4.16 MB.
Supplementary material, approximately 13.8 MB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Liu, G., He, W. et al. Miura folding based charge-excitation triboelectric nanogenerator for portable power supply. Nano Res. 14, 4204–4210 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3401-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3401-4