Abstract
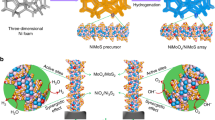
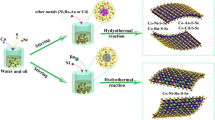
Size-controlled synthesis of two-dimensional (2D) catalysts with low stacking numbers and small nanoflake lengths is crucial for promoting the catalytic performance in diverse heterogeneous catalysis. Herein, we report a facile and general “surface curvature-confined synthesis” strategy to modulate the slab lengths and stacking numbers of 2D transition metal sulfides by controlling the strain induced by different surface curvature of supports. An efficient NiMo sulfide with shorter slab length (average 3.71 nm), less stacking number (1–2 layers) and more edge active sites is synthesized onto ZSM-5 zeolites with the average size of 100 nm, which shows superior kHDS value of dibenzothiophene (14.05 × 10−7 mol/(g·s)), enhanced stability up to 80 h, and high direct desulfurization selectivity (> 95%). This design concept is also proved to be generally applicable to modulate the slab lengths and stacking numbers of other 2D catalysts such as MoS2 and WS2 nanoflakes, which shows great potentials for developing more ultrasmall 2D catalysts with controlled sizes and excellent catalytic activities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boudart, M.; Betta, R. A. D.; Foger, K.; Löffler, D. G.; Samant, M. G. Study by synchrotron radiation of the structure of a working catalyst at high temperatures and pressures. Science1985, 228, 717–719.
Yang, R. T.; Hernández-Maldonado, A. J.; Yang, F. H. Desulfurization of transportation fuels with zeolites under ambient conditions. Science2003, 301, 79–81.
Li, Y.; Pan, D. H.; Yu, C. Z.; Fan, Y.; Bao, X. J. Synthesis and hydrodesulfurization properties of NiW catalyst supported on high-aluminum-content, highly ordered, and hydrothermally stable Al-SBA-15. J. Catal.2012, 286, 124–136.
Fu, W. Q.; Zhang, L.; Tang, T. D.; Ke, Q. P.; Wang, S.; Hu, J. B.; Fang, G. Y.; Li, J. X.; Xiao, F. S. Extraordinarily high activity in the hydrodesulfurization of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene over Pd supported on mesoporous zeolite Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2011, 133, 15346–15349.
Tang, T. D.; Zhang, L.; Fu, W. Q.; Ma, Y. L.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J.; Fang, G. Y.; Xiao, F. S. Design and synthesis of metal sulfide catalysts supported on zeolite nanofiber bundles with unprecedented hydrodesulfurization activities. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2013, 135, 11437–11440.
Zhou, W. W.; Liu, M. F.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Q.; Ding, S. J.; Zhou, Y. S. Synthesis of NiMo catalysts supported on gallium-containing mesoporous Y zeolites with different gallium contents and their high activities in the hydrodesulfurization of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene. ACS Catal.2017, 7, 7665–7679.
Liao, G. F.; Gong, Y.; Zhong, L.; Fang, J. S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. S.; Gao, H. Y.; Fang, B. Z. Unlocking the door to highly efficient Ag-based nanoparticles catalysts for NaBH4-assisted nitrophenol reduction. Nano Res.2019, 12, 2407–2436.
Bui, N. Q.; Geantet, C.; Berhault, G. Maleic acid, an efficient additive for the activation of regenerated CoMo/Al2O3 hydrotreating catalysts. J. Catal.2015, 330, 374–386.
Wang, H. T.; Yuan, H. T.; Sae Hong, S.; Li, Y. B.; Cui, Y. Physical and chemical tuning of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem. Soc. Rev.2015, 44, 2664–2680.
Singh, R.; Kunzru, D.; Sivakumar, S. Monodispersed ultrasmall NiMo metal oxide nanoclusters as hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2016, 185, 163–173.
Lauritsen, J. V.; Kibsgaard, J.; Helveg, S.; Topsøe, H.; Clausen, B. S.; Laegsgaard, E.; Besenbacher, F. Size-dependent structure of MoS2 nanocrystals. Nat. Nanotechnol.2007, 2, 53–58.
Liu, G. L.; Robertson, A. W.; Li, M. M. J.; Kuo, W. C. H.; Darby, M. T.; Muhieddine, M. H.; Lin, Y. C.; Suenaga, K.; Stamatakis, M.; Warner, J. H. et al. MoS2 monolayer catalyst doped with isolated Co atoms for the hydrodeoxygenation reaction. Nat. Chem.2017, 9, 810–816.
Yu, Y. F.; Nam, G. H.; He, Q. Y.; Wu, X. J.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Z. Z.; Chen, J. Z.; Ma, Q. L.; Zhao, M. T.; Liu, Z. Q. et al. High phase-purity 1T’-MoS2- and 1T’-MoSe2-layered crystals. Nat. Chem.2018, 10, 638–643.
Lau, T. H. M.; Lu, X. W.; Kulhavý, J.; Wu, S.; Lu, L. L.; Wu, T. S.; Kato, R.; Foord, J. S.; Soo, Y. L.; Suenaga, K. et al. Transition metal atom doping of the basal plane of MoS2 monolayer nanosheets for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Chem. Sci.2018, 9, 4769–4776.
Cheng, X. L.; Chai, X. Q.; Hu, W. G.; Li, S. G.; Zhu, Y. The on-and-off dynamics of thiophene on a nickel cluster enables efficient hydrodesulfurization and excellent stability at high temperatures. Nanoscale2019, 11, 4369–4375.
Naboulsi, I.; Aponte, C. F. L.; Lebeau, B.; Brunet, S.; Michelin, L.; Bonne, M.; Blin, J. L. An unexpected pathway for hydrodesulfurization of gazole over a CoMoS active phase supported on a mesoporous TiO2 catalyst. Chem. Commun.2017, 53, 2717–2720.
Chen, C. F.; Wu, A. P.; Yan, H. J.; Xiao, Y. L.; Tian, C. G.; Fu, H. G. Trapping [PMo12O40]3− clusters into pre-synthesized ZIF-67 toward MoxCoxC particles confined in uniform carbon polyhedrons for efficient overall water splitting. Chem. Sci.2018, 9, 4746–4755.
Wu, A. P.; Gu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Tian, C. G.; Yan, H. J.; Wang, D. X.; Zhang, X. M.; Cai, Z. Z.; Fu, H. G. Effective electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution in neutral medium based on 2D MoP/MoS2 heterostructure nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2019, 11, 25986–25995.
Toledo-Antonio, J. A.; Cortes-Jacome, M. A.; Escobar-Aguilar, J.; Angeles-Chavez, C.; Navarrete-Bolaños, J.; López-Salinas, E. Upgrading HDS activity of MoS2 catalysts by chelating thioglycolic acid to MoOx supported on alumina. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2017, 213, 106–117.
Wang, C. M.; Tsai, T. C.; Wang, I. Deep hydrodesulfurization over Co/Mo catalysts supported on oxides containing vanadium. J. Catal.2009, 262, 206–214.
Xu, J. D.; Guo, Y. F.; Huang, T. T.; Fan, Y. Decamethonium bromide-dispersed palladium nanoparticles on mesoporous HZSM-5 zeolites for deep hydrodesulfurization. Chem. Eng. J.2018, 333, 206–215.
Chhowalla, M.; Shin, H. S.; Eda, G.; Li, L. J.; Loh, K. P.; Zhang, H. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem.2013, 5, 263–275.
Shi, Y. M.; Li, H. N.; Li, L. J. Recent advances in controlled synthesis of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides via vapour deposition techniques. Chem. Soc. Rev.2015, 44, 2744–2756.
Tan, C. L.; Zhang, H. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheet-based composites. Chem. Soc. Rev.2015, 44, 2713–2731.
Cheng, X. S.; Wang, D. X.; Liu, J. C.; Kang, X.; Yan, H. J.; Wu, A. P.; Gu, Y.; Tian, C. G.; Fu, H. G. Ultra-small Mo2N on SBA-15 as a highly efficient promoter of low-loading Pd for catalytic hydrogenation. Nanoscale2018, 10, 22348–22356.
Yan, H. J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, A. P.; Cai, Z. C.; Wang, L.; Tian, C. G.; Zhang, X. M.; Fu, H. G. Anion-modulated HER and OER activities of 3D Ni-V-based interstitial compound heterojunctions for high-efficiency and stable overall water splitting. Adv. Mater.2019, 31, 1901174.
Yan, H. J.; Tian, C. G.; Sun, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Yin, J.; Wu, A. P.; Fu, H. G. Small-sized and high-dispersed WN from [SiO4(W3O9)4]4− clusters loading on GO-derived graphene as promising carriers for methanol electro-oxidation. Energy Environ. Sci.2014, 7, 1939–1949.
Wang, D. X.; Liu, J. C.; Cheng, X. S.; Kang, X.; Wu, A. P.; Tian, C. G.; Fu, H. G. Trace Pt clusters dispersed on SAPO-11 promoting the synergy of metal sites with acid sites for high-effective hydroisomerization of n-alkanes. Small Methods2019, 3, 1800510.
Wang, D.; Zhu, Y. J.; Tian, C. G.; Wang, L.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Y. L.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y. F.; Yuan, F. L.; Fu, H. G. Synergistic effect of Mo2N and Pt for promoted selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde over Pt-Mo2N/SBA-15. Catal. Sci. Technol.2016, 6, 2403–2412.
Fan, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, H. Y.; Bao, X. J. Morphology tuning of supported MoS2 slabs for selectivity enhancement of fluid catalytic cracking gasoline hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2009, 91, 73–82.
Li, L. J.; Zhang, Y. Controlling the luminescence of monolayer MoS2 based on the piezoelectric effect. Nano Res.2017, 10, 2527–2534.
Liu, J. C.; Wang, N.; Yu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H. Y.; Li, J. Y.; Yu, J. H. Carbon dots in zeolites: A new class of thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials with ultralong lifetimes. Sci. Adv.2017, 3, e1603171.
Nix, W. D. Mechanical properties of thin films. Metall. Trans. A1989, 20, 2217–2245.
Lloyd, D.; Liu, X. H.; Christopher, J. W.; Cantley, L.; Wadehra, A.; Kim, B. L.; Goldberg, B. B.; Swan, A. K.; Bunch, J. S. Band gap engineering with ultralarge biaxial strains in suspended monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett.2016, 16, 5836–5841.
Brune, H.; Bromann, K.; Röder, H.; Kern, K.; Jacobsen, J.; Stoltze, P.; Jacobsen, K.; No/rskov, J. Effect of strain on surface diffusion and nucleation. Phys. Rev. B1995, 52, R14380.
Liu, L. C.; Lopez-Haro, M.; Lopes, C. W.; Li, C. G.; Concepcion, P.; Simonelli, L.; Calvino, J. J.; Corma, A. Regioselective generation and reactivity control of subnanometric platinum clusters in zeolites for high-temperature catalysis. Nat. Mater.2019, 18, 866–873.
Wang, N.; Sun, Q. M.; Yu, J. H. Ultrasmall metal nanoparticles confined within crystalline nanoporous materials: A fascinating class of nanocatalysts. Adv. Mater.2019, 31, 1803966.
Méndez, F. J.; Franco-López, O. E.; Bokhimi, X.; Solís-Casados, D. A.; Escobar-Alarcón, L.; Klimova, T. E. Dibenzothiophene hydrodesulfurization with NiMo and CoMo catalysts supported on niobium-modified MCM-41. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2017, 219, 479–491.
Gao, D. W.; Duan, A. J.; Zhang, X.; Chi, K. B.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J. M.; Qin, Y. C.; Wang, X. L.; Xu, C. M. Self-assembly of monodispersed hierarchically porous beta-SBA-15 with different morphologies and its hydro-upgrading performances for FCC gasoline. J. Mater. Chem. A2015, 3, 16501–16512.
Jiao, F.; Guo, H. L.; Chai, Y. M.; Awala, H.; Mintova, S.; Liu, C. G. Synergy between a sulfur-tolerant Pt/Al2O3@sodalite core-shell catalyst and a CoMo/Al2O3 catalyst. J. Catal.2018, 368, 89–97.
Han, W.; Yuan, P.; Fan, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, H. Y.; Bai, D. J.; Bao, X. J. Preparation of supported hydrodesulfurization catalysts with enhanced performance using Mo-based inorganic-organic hybrid nanocrystals as a superior precursor. J. Mater. Chem.2012, 22, 25340–25353.
Ke, W. Y.; Cui, T. L.; Yu, Q. Y.; Wang, M. Y.; Lv, L. B.; Wang, H. H.; Jiang, Z. D.; Li, X. H.; Chen, J. S. Mesoporous H-ZSM-5 nanocrystals with programmable number of acid sites as “solid ligands” to activate Pd nanoparticles for C-C coupling reactions. Nano Res.2018, 11, 874–881.
Xiao, F.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Q.; Lei, C.; Han, S.; Zhu, Q.; Maurer, S.; Dai, D.; Parvulescu, A. N.; Mueller, U. et al. An efficient, rapid, and non-centrifugation synthesis of nanosized zeolites by accelerating the nucleation rate. J. Mater. Chem. A2018, 6, 21156–21161.
Kuechl, D. E.; Benin, A. I.; Knight, L. M.; Abrevaya, H.; Wilson, S. T.; Sinkler, W.; Mezza, T. M.; Willis, R. R. Multiple paths to nanocrystalline high silica beta zeolite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater.2010, 127, 104–118.
Li, B.; Hu, Z. J.; Kong, B.; Wang, J. X.; Li, W.; Sun, Z. K.; Qian, X. F.; Yang, Y. S.; Shen, W.; Xu, H. L. et al. Hierarchically tetramodal-porous zeolite ZSM-5 monoliths with template-free-derived intracrystalline mesopores. Chem. Sci.2014, 5, 1565–1573.
Xu, J. Q.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y. Q.; Xie, J. Q. Highly hydrothermal stable mesoporous molecular sieves (TZM) prepared by the self assembly of zeolitic subunits from ZSM-5 desilication and their catalytic performance for CO2 reforming of CH4. New J. Chem.2018, 42, 19000–19007.
Beale, A. M.; Gao, F.; Lezcano-Gonzalez, I.; Peden, C. H. F.; Szanyi, J. Recent advances in automotive catalysis for NOx emission control by small-pore microporous materials. Chem. Soc. Rev.2015, 44, 7371–7405.
Hou, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, X. W.; Liu, G. Z. Effects of regeneration of ZSM-5 based catalysts on light olefins production in n-pentane catalytic cracking. Chem. Eng. J.2017, 321, 572–583.
Wang, X. L.; Mei, J. L.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z. T.; Gao, D. W.; Fu, J. Y.; Fan, J. Y.; Duan, A. J.; Xu, C. M. Self-assembly of hierarchically porous ZSM-5/SBA-16 with different morphologies and its high isomerization performance for hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene. ACS Catal.2018, 8, 1891–1902.
Afanasiev, P. On the interpretation of temperature programmed reduction patterns of transition metals sulphides. Appl. Catal. A Gen.2006, 303, 110–115.
Jiao, J. Q.; Fu, J. Y.; Wei, Y. C.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, A. J.; Xu, C. M.; Li, J. M.; Song, H.; Zheng, P.; Wang, X. L. et al. Al-modified dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres-supported NiMo catalysts for the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene: Efficient accessibility of active sites and suitable metal-support interaction. J. Catal.2017, 356, 269–282.
Xu, J. D.; Huang, T. T.; Fan, Y. Highly efficient NiMo/SiO2-Al2O3 hydrodesulfurization catalyst prepared from gemini surfactant-dispersed Mo precursor. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2017, 203, 839–850.
Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C. C. R.; Tay, B. K.; Edwin, T. H. T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From bulk to monolayer MoS2: Evolution of Raman scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater.2012, 22, 1385–1390.
Xu, J. D.; Guo, Y. F.; Huang, T. T.; Fan, Y. Hexamethonium bromide-assisted synthesis of CoMo/graphene catalysts for selective hydrodesulfurization. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2019, 244, 385–395.
Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Liu, X. Y.; Liu, T. F.; Jiang, Z. X.; Li, C. Morphology-performance relation of (Co)MoS2 catalysts in the hydrodesulfurization of FCC gasoline. Appl. Catal. A Gen.2018, 556, 20–28.
Salavati, H.; Rasouli, N. Synthesis and characterization of supported heteropolymolybdate nanoparticles between silicate layers of bentonite with enhanced catalytic activity for epoxidation of alkenes. Mater. Res. Bull.2011, 46, 1853–1859.
Zhu, C. R.; Wang, G.; Liu, B. L.; Marie, X.; Qiao, X. F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X. X.; Fan, H.; Tan, P. H.; Amand, T. et al. Strain tuning of optical emission energy and polarization in monolayer and bilayer MoS2. Phys. Rev. B2013, 88, 121301.
Li, Z.; Jiang, K. R.; Khan, F.; Goswami, A.; Liu, J.; Passian, A.; Thundat, T. Anomalous interfacial stress generation during sodium intercalation/extraction in MoS2 thin-film anodes. Sci. Adv.2019, 5, eaav2820.
Zhou, W. W.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, Y. S.; Liu, M. F.; Ding, S. J.; Yang, Q. Hydrodesulfurization of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene over NiMo sulfide catalysts supported on meso-microporous Y zeolite with different mesopore sizes. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2018, 238, 212–224.
Li, Y.; Li, G. C.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Li, X. B.; Huang, X. Size-dependent activity of unsupported Co-Mo sulfide catalysts for the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Appl. Catal. A Gen.2016, 512, 85–92.
Biswas, P.; Narayanasarma, P.; Kotikalapudi, C. M.; Dalai, A. K.; Adjaye, J. Characterization and activity of ZrO2 doped SBA-15 supported NiMo catalysts for HDS and HDN of bitumen derived heavy gas oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.2011, 50, 7882–7895.
Duan, A. J.; Li, T. S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, B. J.; Zhou, X. F.; Jiang, G. Y.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y. C.; Pan, H. F. Synthesis of hierarchically porous L-KIT-6 silica-alumina material and the super catalytic performances for hydrodesulfurization of benzothiophene. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2015, 165, 763–773.
Zhu, D. D.; Liu, J. L.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S. Z. Engineering 2D metal-organic framework/MoS2 interface for enhanced alkaline hydrogen evolution. Small2019, 15, 1805511.
Wu, A. P.; Tian, C. G.; Yan, H. J.; Jiao, Y. Q.; Yan, Q.; Yang, G. Y.; Fu, H. G. Hierarchical MoS2/CdS core-shell heterojunction electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction over a broad pH range. Nanoscale2016, 8, 11052–11059.
Ninh, T. K. T.; Massin, L.; Laurenti, D.; Vrinat, M. A new approach in the evaluation of the support effect for NiMo hydrodesulfurization catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen.2011, 407, 29–39.
Wu, A. P.; Tian, C. G.; Jiao, Y. Q.; Yan, Q.; Yang, G. Y.; Fu, H. G. Sequential two-step hydrothermal growth of MoS2/CdS core-shell heterojunctions for efficient visible light-driven photocatalytic H2 evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ.2017, 203, 955–963.
Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Chai, Y. M.; Zhao, J. C.; Li, Y. P.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y. Q.; Liu, C. G. Effect of sulfiding conditions on the hydrodesulfurization performance of the ex-situ presulfided CoMoS/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Fuel2018, 234, 1144–1153.
Yan, H. J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, A. P.; Cai, Z. C.; Wang, L.; Tian, C. G.; Zhang, X. M.; Fu, H. G. Anion-modulated HER and OER activities of 3D Ni-V-based interstitial compound heterojunctions for high-efficiency and stable overall water splitting. Adv. Mater.2019, 31, 1901174.
López-Benítez, A.; Guevara-Lara, A.; Berhault, G. Nickel-containing polyoxotungstates based on [PW9O34]9− and [PW10O39]13− Keggin lacunary anions supported on Al2O3 for dibenzothiophene hydrodesulfurization application. ACS Catal.2019, 9, 6711–6727.
Jalilov, A. S.; Tanimu, A.; Ganiyu, S. A.; Alhooshani, K. Kinetic and mechanistic analysis of dibenzothiophene hydrodesulfurization on Ti-SBA-15-NiMo catalysts. Energy Fuels2018, 32, 11383–11389.
Salazar, N.; Schmidt, S. B.; Lauritsen, J. V. Adsorption of nitrogenous inhibitor molecules on MoS2 and CoMoS hydrodesulfurization catalysts particles investigated by scanning tunneling microscopy. J. Catal.2019, 370, 232–240.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFE0201704), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21631004, 21801069, 21571054, and 21901064), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (Nos. 3072019CFJ1502 and RCYJTD201801), the University Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (No. UNPYSCT-2018013), Heilongjiang Provincial Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. LBH-Z18232) and the Heilongjiang University Excellent Youth Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2020_2716_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Surface curvature-confined strategy to ultrasmall nickel-molybdenum sulfide nanoflakes for highly efficient deep hydrodesulfurization
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, X., Liu, J., Tian, C. et al. Surface curvature-confined strategy to ultrasmall nickel-molybdenum sulfide nanoflakes for highly efficient deep hydrodesulfurization. Nano Res. 13, 882–890 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2716-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2716-x