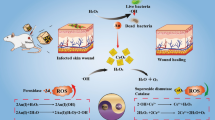
Abstract
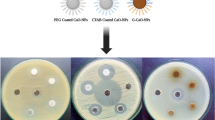
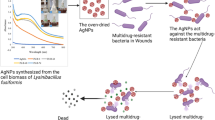
The mounting threat of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections has made it imperative to develop innovative antibacterial strategies. Here we propose a novel antibacterial nanoplatform of silver nanoparticles-decorated and mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes constructed via a N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ethylene diamine (TSD)-mediated method (SWCNTs@mSiO2-TSD@Ag). In this system, the outer mesoporous silica shells are able to improve the dispersibility of SWCNTs, which will increase their contact area with bacteria cell walls. Meanwhile, the large number of mesopores in silica layers act as microreactors for in situ synthesis of Ag NPs with controlled small size and uniform distribution, which induces an enhanced antibacterial activity. Compared with TSD modified mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs@mSiO2-TSD) and commercial Ag NPs, this combination nanosystem of SWCNTs@mSiO2-TSD@Ag exhibits much stronger antibacterial performance against multi-drug-resistant bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) in vitro through damaging the bacterial cell membranes and a fast release of silver ions. Furthermore, the in vivo rat skin infection model verifies that SWCNTs@mSiO2-TSD@Ag have remarkably improved abilities of bacterial clearance, wound healing promoting as well as outstanding biocompatibility. Therefore, this novel nanoplatform indicates promising potentials as a safe and powerful tool for the treatment of clinical drug-resistant infections.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Worthington, R.J.; Melander, C. Combination approaches to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Trends Biotechnol.2013, 31, 177–184.
Zhou, J.L.; Xiang, H.X.; Zabihi, F.; Yu, S. L.; Sun, B.; Zhu, M. F. Intriguing anti-superbug Cu2O@ZrP hybrid nanosheet with enhanced antibacterial performance and weak cytotoxicity. Nano Res.2019, 12, 1453–1460.
Bassetti, M.; Ginocchio, F.; Mikulska, M. New treatment options against gram-negative organisms. Crit Care2011, 15, 215.
Yang, X.L.; Zhang, L.M.; Jiang, X. Y. Aminosaccharide-gold nanoparticle assemblies as narrow-spectrum antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Nano Res.2018, 11, 6237–6243.
Conly, J.; Johnston, B. Where are all the new antibiotics? The new antibiotic paradox. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2005, 16, 159–160.
Sun, P.P.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, X.; Liu, C.Y.; Wang, Z.Z.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X. G. Phytochemical-encapsulated nanoplatform for “on-demand” synergistic treatment of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Nano Res.2018, 11, 3762–3770.
Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv.2014, 4, 3974–3983.
Huang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Cheng, T.J.; Ou, H.L.; Yang, L.J.; Liu, J.J.; Shi, L.Q.; Liu, J. F. Silver-decorated polymeric micelles combined with curcumin for enhanced antibacterial activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces2017, 9, 16880–16889.
Xiu, Z.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P. J. J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett.2012, 12, 4271–4275.
Samberg, M.E.; Orndorff, P.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N. A. Antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles of different sizes, surface conditions and synthesis methods. Nanotoxicology2011, 5, 244–253.
Chen, J.; Wang, F. Y. K.; Liu, Q.M.; Du, J. Z. Antibacterial polymeric nanostructures for biomedical applications. Chem Commun.2014, 50, 14482–14493.
Lok, C.N.; Ho, C.M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.Y.; Yu, W.Y.; Sun, H.Z.; Tam, P. K. H.; Chiu, J.F.; Che, C. M. Silver nanoparticles: Partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J Biol Inorg Chem.2007, 12, 527–534.
Qing, Y.A.; Cheng, L.; Li, R.Y.; Liu, G.C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Tang, X.F.; Wang, J.C.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. G. Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int J Nanomedicine2018, 13, 3311–3327.
Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H. L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11.
Dosunmu, E.; Chaudhari, A.A.; Singh, S.R.; Dennis, V.A.; Pillai, S. R. Silver-coated carbon nanotubes downregulate the expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes: A potential mechanism for their antimicrobial effect. Int J Nanomedicine2015, 10, 5025–5034.
Shao, W.; Liu, X.F.; Min, H.H.; Dong, G.H.; Feng, Q.Y.; Zuo, S. L. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanocomposite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces2015, 7, 6966–6973.
Tian, Y.; Qi, J.J.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, X. Y. Facile, one-pot synthesis, and antibacterial activity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles decorated with well-dispersed silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces2014, 6, 12038–12045.
Chen, H.Q.; Wang, B.; Gao, D.; Guan, M.; Zheng, L.N.; Ouyang, H.; Chai, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Feng, W. Y. Broad-spectrum antibacterial activity of carbon nanotubes to human gut bacteria. Small2013, 9, 2735–2746.
Hong, G.S.; Diao, S.; Antaris, A.L.; Dai, H. J. Carbon Nanomaterials for biological imaging and Nanomedicinal therapy. Chem Rev.2015, 115, 10816–10906.
Nie, C.X.; Cheng, C.; Peng, Z.H.; Ma, L.; He, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, C. S. Mussel-inspired coatings on Ag nanoparticle-conjugated carbon nanotubes: Bactericidal activity and mammal cell toxicity. J Mater Chem B2016, 4, 2749–2756.
Wang, N.; Pandit, S.; Ye, L.L.; Edwards, M.; Mokkapati, V. R. S. S.; Murugesan, M.; Kuzmenko, V.; Zhao, C.H.; Westerlund, F.; Mijakovic, I. et al. Efficient surface modification of carbon nanotubes for fabricating high performance CNT based hybrid nanostructures. Carbon2017, 111, 402–410.
Chaudhari, A.A.; Jasper, S.L.; Dosunmu, E.; Miller, M.E.; Arnold, R.D.; Singh, S.R.; Pillai, S. Novel pegylated silver coated carbon nanotubes kill Salmonella but they are non-toxic to eukaryotic cells. J Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 23.
Wang, Y.; Gu, H. C. Core-shell-type magnetic mesoporous silica nanocomposites for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Adv Mater.2015, 27, 576–585.
Wu, S.H.; Mou, C.Y.; Lin, H. P. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev.2013, 42, 3862–3875.
Qasim, M.; Singh, B.R.; Naqvi, A.H.; Paik, P.; Das, D. Silver nanoparticles embedded mesoporous SiO2 nanosphere: An effective anticandidal agent against Candida albicans 077. Nanotechnology2015, 26, 285102.
Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Yu, C.Z.; Gu, H. C. From helixes to mesos-tructures: Evolution of mesoporous silica shells on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Mat. 2016, 28, 936–942.
Liu, R.; Wang, X.D.; Ye, J.; Xue, X.M.; Zhang, F.R.; Zhang, H.C.; Hou, X.M.; Liu, X.L.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced antibacterial activity of silver-decorated sandwich-like mesoporous silica/reduced graphene oxide nanosheets through photothermal effect. Nanotechnology2018, 29, 105704.
Wang, Y.; Ding, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.K.; Gu, H. C. Antibiotic-loaded, silver core-embedded mesoporous silica nanovehicles as a synergistic antibacterial agent for the treatment of drug-resistant infections. Biomaterials2016, 101, 207–216.
Ruparelia, J. P.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Duttagupta, S.P.; Mukherji, S. Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nano-particles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 707–716.
Kirchhoff, C.; Cypionka, H. Boosted membrane potential as Bioenergetic response to anoxia in Dinoroseobacter shibae Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 695.
Novo, D.; Perlmutter, N.G.; Hunt, R.H.; Shapiro, H. M. Accurate flow cytometric membrane potential measurement in bacteria using diethyloxacarbocyanine and a ratiometric technique. Cytometry1999, 35, 55–63.
Kugelberg, E.; Norström, T.; Petersen, T.K.; Duvold, T.; Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Establishment of a superficial skin infection model in mice by using Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3435–3441.
Samy, R.P.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Houghton, P.; Ignacimuthu, S. Purification of antibacterial agents from Tragia involucrata—A popular tribal medicine for wound healing. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 107, 99–106.
Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Jia, Y.C.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y. M. Roxadustat promotes angiogenesis through HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling and accelerates cutaneous wound healing in diabetic rats. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 324–334.
Liong, M.; France, B.; Bradley, K.A.; Zink, J. I. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanocrystals encapsulated in mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv Mater.2009, 21, 1684–1689.
Song, J.; Kang, H.; Lee, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Jang, J. Aqueous synthesis of silver nanoparticle embedded cationic polymer nanofibers and their antibacterial activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces2012, 4, 460–465.
Cui, G.J.; Sun, Z.B.; Li, H.Z.; Liu, X.N.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.X.; Yan, S. Q. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic elongated hollow mesoporous silica nanocapsules with silver nanoparticles. J Mater Chem A2016, 4, 1771–1783.
Song, Z.L.; Ma, Y.J.; Xia, G.G.; Wang, Y.; Kapadia, W.; Sun, Z.Y.; Wu, W.; Gu, H.C.; Cui, W.G.; Huang, X. Y. In vitro and in vivo combined antibacterial effect of levofloxacin/silver co-loaded elec-trospun fibrous membranes. J Mat Chem B2017, 5, 7632–7643.
Shi, X.H.; Kong, Y.; Gao, H. J. Coarse grained molecular dynamics and theoretical studies of carbon nanotubes entering cell membrane. Acta Mech Sin. 2008, 24, 161–169.
Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle release, transformation and toxicity: A critical review of current knowledge and recommendations for future studies and applications. Materials2013, 6, 2295–2350.
Holt, K.B.; Bard, A. J. Interaction of silver(I) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: An electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micromolar Ag+. Biochemistry2005, 44, 13214–13223.
Long, Y.M.; Hu, L.G.; Yan, X.T.; Zhao, X.C.; Zhou, Q.F.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, G. B. Surface ligand controls silver ion release of nanosilver and its antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli Int J Nano-medicine2017, 12, 3193–3206.
Seong, M.J.; Lee, D. G. Silver Nanoparticles against Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium: Role of inner membrane dysfunction. Curr Microbiol. 2017, 74, 661–670.
Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Sullivan, N.; Chen, Y. S. Modeling the primary size effects of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles on their ion release kinetics. Environ Sci Technol. 2011, 45, 4422–4428.
Moran, G.J.; Krishnadasan, A.; Gorwitz, R.J.; Fosheim, G.E.; McDougal, L.K.; Carey, R.B.; Talan, D. A. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med. 2006, 355, 666–674.
Edwards, R.; Harding, K. G. Bacteria and wound healing. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2004, 17, 91–96.
Siddiqui, A.R.; Bernstein, J. M. Chronic wound infection: Facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010, 28, 519–526.
Kingsley, A. The wound infection continuum and its application to clinical practice. Ostomy Wound Manage2003, 49, 1–7.
Park, S. Y.; Lee, H.U.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, G.H.; Park, E.C.; Han, S.H.; Lee, J.G.; Choi, S.; Heo, N.S.; Kim, D. L. et al. Wound healing potential of antibacterial microneedles loaded with green tea extracts. Mater Sci Eng C2014, 42, 757–762.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51802192, 81802156, and 81772338), the Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (No. YG2017ZD05), Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 19ZR1474800), Shanghai Sailing Program (No. 18YF1410700), and Innovation Research Plan supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. ZXWF082101). The authors would like to acknowledge the Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the characterization of materials, and Juanxi Gu of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for her graphic assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2020_2621_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Silver nanoparticles-decorated and mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes with an enhanced antibacterial activity for killing drug-resistant bacteria
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Xu, J., Wang, Y. et al. Silver nanoparticles-decorated and mesoporous silica coated single-walled carbon nanotubes with an enhanced antibacterial activity for killing drug-resistant bacteria. Nano Res. 13, 389–400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2621-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2621-3