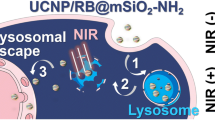
Abstract
Endo/lysosomal escape and gene release are two critical bottlenecks in gene delivery. Herein, a novel photo-controllable metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) nanoswitch is rationally designed for enhancing small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery. One single laser triggers the “off-to-on” switching of MOFs nanocomplexes, inducing significant siRNA release accompanied by rapid MOFs dissociation into protonatable 2-methylimidazalo and osmotic rupturing Zn2+ ions, which cooperatively contribute to remarkable endo/lysosomal rupture (∼ 90%). The simultaneous endo/lysosomal rupture and release enable a high spatio-temporal control on RNA interference for effective cancer therapy. Notably, the “off-to-on” switching also activates fluorescence recovery for real-time monitoring siRNA delivery. The nanoswitch could easily be extended to deliver other therapeutic agents (e.g., DNA, protein, anticancer drug) for overcoming endo/lysosomal entrapment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mintzer, M. A.; Simanek, E. E. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem. Rev.2009, 109, 259–302.
Lächelt, U.; Wagner, E. Nucleic acid therapeutics using polyplexes: A journey of 50 years (and beyond). Chem. Rev.2015, 115, 11043–11078.
Wang, J. Q.; Mi, P.; Lin, G.; Wang, Y. X. J.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Y. Imaging-guided delivery of RNAi for anticancer treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev.2016, 104, 44–60.
Whitehead, K. A.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. Knocking down barriers: Advances in siRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.2009, 8, 129–138.
Varkouhi, A. K.; Scholte, M.; Storm, G.; Haisma, H. J. Endosomal escape pathways for delivery of biologicals. J. Control. Release2011, 151, 220–228.
Ma, D. Enhancing endosomal escape for nanoparticle mediated siRNA delivery. Nanoscale2014, 6, 6415–6425.
Dominska, M.; Dykxhoorn, D. M. Breaking down the barriers: siRNA delivery and endosome escape. J. Cell Sci.2010, 123, 1183–1189.
Gilleron, J.; Querbes, W.; Zeigerer, A.; Borodovsky, A.; Marsico, G.; Schubert, U.; Manygoats, K.; Seifert, S.; Andree, C.; Stöter, M. et al. Image-based analysis of lipid nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery, intracellular trafficking and endosomal escape. Nat. Biotechnol.2013, 31, 638–646.
Shi, J. J.; Kantoff, P. W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O. C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer2016, 17, 20–37.
Shim, M. S.; Kwon, Y. J. Controlled delivery of plasmid DNA and siRNA to intracellular targets using ketalized polyethylenimine. Biomacromolecules2008, 9, 444–455.
Shim, M. S.; Kwon, Y. J. Acid-responsive linear polyethylenimine for efficient, specific, and biocompatible siRNA delivery. Bioconjugate Chem.2009, 20, 488–499.
Lin, G.; Zhu, W. C.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Lin, B. B.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, Z. Z.; Xia, C. C.; Gong, Q. Y.; Song, B. et al. Delivery of siRNA by MRI-visible nanovehicles to overcome drug resistance in MCF-7/ADR human breast cancer cells. Biomaterials2014, 35, 9495–9507.
Hunter, A. C. Molecular hurdles in polyfectin design and mechanistic background to polycation induced cytotoxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev.2006, 58, 1523–1531.
Chen, H. B.; Xiao, L.; Anraku, Y.; Mi, P.; Liu, X. Y.; Cabral, H.; Inoue, A.; Nomoto, T.; Kishimura, A.; Nishiyama, N. et al. Polyion complex vesicles for photoinduced intracellular delivery of amphiphilic photosensitizer. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2014, 136, 157–163.
Yuan, Y. Y.; Zhang, C. J.; Liu, B. A photoactivatable AIE polymer for light-controlled gene delivery: Concurrent Endo/Lysosomal escape and DNA unpacking. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2015, 54, 11419–11423.
Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, C.; Kim, W. J. Synergistic nanomedicine by combined gene and photothermal therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev.2016, 98, 99–112.
Lin, G.; Mi, P.; Chu, C. C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G. Inorganic nanocarriers overcoming multidrug resistance for cancer theranostics. Adv. Sci.2016, 3, 1600134.
Feng, L. Z.; Yang, X. Z.; Shi, X. Z.; Tan, X. F.; Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Polyethylene glycol and polyethylenimine dual-functionalized nano-graphene oxide for photothermally enhanced gene delivery. Small2013, 9, 1989–1997.
Wang, H. M.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Xing, C.; Wang, M.; Bai, S. M.; Lu, C. H.; Yang, H. H. A black phosphorus nanosheet-based siRNA delivery system for synergistic photothermal and gene therapy. Chem. Commun.2018, 54, 3142–3145.
Wang, H.; Agarwal, P.; Zhao, S. T.; Yu, J. H.; Lu, X. B.; He, X. M. A near-infrared laser-activated “nanobomb” for breaking the barriers to microRNA delivery. Adv. Mat.2016, 28, 347–355.
Midoux, P.; Pichon, C.; Yaouanc, J. J.; Jaffrès, P. A. Chemical vectors for gene delivery: A current review on polymers, peptides and lipids containing histidine or imidazole as nucleic acids carriers. Br. J. Pharmacol.2009, 157, 166–178.
Mishra, S.; Heidel, J. D.; Webster, P.; Davis, M. E. Imidazole groups on a linear, cyclodextrin-containing polycation produce enhanced gene delivery via multiple processes. J. Control. Release2006, 116, 179–191.
Sun, C. Y.; Qin, C.; Wang, X. L.; Yang, G. S.; Shao, K. Z.; Lan, Y. Q.; Su, Z. M.; Huang, P.; Wang, C. G.; Wang, E. B. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as efficient pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicle. Dalton Trans.2012, 41, 6906–6909.
Zhuang, J.; Kuo, C. H.; Chou, L. Y.; Liu, D. Y.; Weerapana, E.; Tsung, C. K. Optimized metal-organic-framework nanospheres for drug delivery: Evaluation of small-molecule encapsulation. ACS Nano2014, 8, 2812–2819.
Alsaiari, S. K.; Patil, S.; Alyami, M.; Alamoudi, K. O.; Aleisa, F. A.; Merzaban, J. S.; Li, M.; Khashab, N. M. Endosomal escape and delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing machinery enabled by nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2018, 140, 143–146.
Bus, T.; Traeger, A.; Schubert, U. S. The great escape: How cationic polyplexes overcome the endosomal barrier. J. Mater. Chem. B2018, 6, 6904–6918.
Chu, C. C.; Ren, E.; Zhang, Y. M.; Yu, J. W.; Lin, H. R.; Pang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Qin, Z. N.; Cheng, Y. et al. Zinc(II)-dipicolylamine coordination nanotheranostics: Toward synergistic nanomedicine by combined photo/gene therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2019, 58, 269–272.
Altieri, D. C. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer2008, 8, 61–70.
Park, D. H.; Cho, J.; Kwon, O. J.; Yun, C. O.; Choy, J. H. Biodegradable inorganic nanovector: Passive versus active tumor targeting in siRNA transportation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2016, 55, 4582–4586.
Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C. Q.; Chu, C. C.; Shi, Y. S.; Pang, X.; Ren, E.; Wu, Y.Y.; Mi, P.; Xia, H. P. et al. Photo-excitable hybrid nanocomposites for image-guided photo/TRAIL synergistic cancer therapy. Biomaterials2018, 176, 60–70.
Mi, P.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K. Ligand-installed nanocarriers toward precision therapy. Adv. Mat.2019, 1902604.
Chen, T. T.; Yi, J. T.; Zhao, Y. Y.; Chu, X. Biomineralized metal-organic framework nanoparticles enable intracellular delivery and Endo-Lysosomal release of native active proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2018, 140, 9912–9920.
Li, S. D.; Huang, L. Targeted delivery of antisense oigodeoxynucleotide and small interference RNA into lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharm.2006, 3, 579–588.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Jingru Huang and Baoying Xie from Central Laboratory in School of Medicine, Xiamen University for assistance with inductively coupled plasma experiment, laser scanning confocal microscope and data analysis. This work was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (No. 2017YFA0205201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81925019, 81422023, U1705281, and U1505221), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 20720190088), and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, China (No. NCET-13-0502). All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Management and Ethics Committee of the Xiamen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2019_2606_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Metal-organic frameworks nanoswitch: Toward photo-controllable endo/lysosomal rupture and release for enhanced cancer RNA interference
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, G., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Metal-organic frameworks nanoswitch: Toward photo-controllable endo/lysosomal rupture and release for enhanced cancer RNA interference. Nano Res. 13, 238–245 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2606-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2606-2