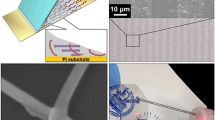
Abstract
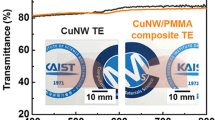
Copper nanowires (Cu NWs) have attracted increasing attention as building blocks for electronics due to their outstanding electrical properties and low cost. However, organic residues and oxide layers ubiquitously existing on the surface of Cu NWs impede good inter-wire contact. Commonly used methods such as thermal annealing and acid treatment often lead to nanowire damage. Herein, hydrogen plasma treatment at room temperature has been demonstrated to be effective for simultaneous surface cleaning and selective welding of Cu NWs at junctions. Transparent electrodes with excellent optical-electrical performance (19 O·sq–1 @ 90% T) and enhanced stability have been fabricated and integrated into organic solar cells. Besides, Cu NW conductors with superior stretchability and cycling stability under stretching speeds of up to 400 mm·min–1 can also be produced by the nanowelding process, and the feasibility of their application in stretchable LED circuits has been demonstrated.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, J.; Yun, J. H.; Kim, H.; Cho, Y.; Park, H. H.; Kumar, M. M. D.; Yi, J.; Anderson, W. A.; Kim, D. W. Transparent conductor-embedding nanocones for selective emitters: Optical and electrical improvements of Si solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9256.
Yao, S. S.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled stretchable conductors: Strategies, materials and devices. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1480–1511.
Chang, J. H.; Chiang, K. M.; Kang, H. W.; Chi, W. J.; Chang, J. H.; Wu, C. I.; Lin, H. W. A solution-processed molybdenum oxide treated silver nanowire network: A highly conductive transparent conducting electrode with superior mechanical and hole injection properties. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4572–4579.
Jin, Y. X.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y. R.; Kong, L. Q.; Pei, Q. B.; Xiao, F. Cohesively enhanced conductivity and adhesion of flexible silver nanowire networks by biocompatible polymer sol–gel transition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1581–1587.
Kholmanov, I. N.; Magnuson, C. W.; Piner, R.; Kim, J. Y.; Aliev, A. E.; Tan, C.; Kim, T. Y.; Zakhidov, A. A.; Sberveglieri, G.; Baughman, R. H. et al. Optical, electrical, and electromechanical properties of hybrid graphene/carbon nanotube films. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3053–3059.
Lin, Y.; Kim, J. W.; Connell, J. W.; Lebrón-Colón, M.; Siochi, E. J. Purification of carbon nanotube sheets. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2015, 17, 674–688.
Jurewicz, I.; Fahimi, A.; Lyons, P. E.; Smith, R. J.; Cann, M.; Large, M. L.; Tian, M. W.; Coleman, J. N.; Dalton, A. B. Insulator-conductor type transitions in graphene-modified silver nanowire networks: A route to inexpensive transparent conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 7580–7587.
Rahimi, S.; Tao, L.; Chowdhury, S. F.; Park, S.; Jouvray, A.; Buttress, S.; Rupesinghe, N.; Teo, K.; Akinwande, D. Toward 300 mm wafer-scalable high-performance polycrystalline chemical vapor deposited graphene transistors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10471–10479.
Guo, C. F.; Ren, Z. F. Flexible transparent conductors based on metal nanowire networks. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 143–154.
Song, J. Z.; Li, J. H.; Xu, J. Y.; Zeng, H. B. Superstable transparent conductive Cu@Cu4Ni nanowire elastomer composites against oxidation, bending, stretching, and twisting for flexible and stretchable optoelectronics. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6298–6305.
Ye, S. R.; Rathmell, A. R.; Chen, Z. F.; Stewart, I. E.; Wiley, B. J. Metal nanowire networks: The next generation of transparent conductors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6670–6687.
Lee, D.; Paeng, D.; Park, H. K.; Grigoropoulos, C. P. Vacuum-free, maskless patterning of Ni electrodes by laser reductive sintering of NiO nanoparticle ink and its application to transparent conductors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9807–9814.
Mehta, R.; Chugh, S.; Chen, Z. H. Enhanced electrical and thermal conduction in graphene-encapsulated copper nanowires. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 2024–2030.
Rathmell, A. R.; Wiley, B. J. The synthesis and coating of long, thin copper nanowires to make flexible, transparent conducting films on plastic substrates. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4798–4803.
Rathmell, A. R.; Bergin, S. M.; Hua, Y. L.; Li, Z. Y.; Wiley, B. J. The growth mechanism of copper nanowires and their properties in flexible, transparent conducting films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3558–3563.
Zhang, D. Q.; Wang, R. R.; Wen, M. C.; Weng, D.; Cui, X.; Sun, J.; Li, H. X.; Lu, Y. F. Synthesis of ultralong copper nanowires for high-performance transparent electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14283–14286.
Guo, H. Z.; Lin, N.; Chen, Y. Z.; Wang, Z. W.; Xie, Q. S.; Zheng, T. C.; Gao, N.; Li, S. P.; Kang, J. Y.; Cai, D. J. et al. Copper nanowires as fully transparent conductive electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 9256.
Mayousse, C.; Celle, C.; Carella, A.; Simonato, J.-P. Synthesis and purification of long copper nanowires. Application to high performance flexible transparent electrodes with and without PEDOT: PSS. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 315–324.
Stewart, I. E.; Rathmell, A. R.; Yan, L.; Ye, S. R.; Flowers, P. F.; You, W.; Wiley, B. J. Solution-processed coppernickel nanowire anodes for organic solar cells. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5980–5988.
Won, Y.; Kim, A.; Lee, D.; Yang, W.; Woo, K.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J. Annealing-free fabrication of highly oxidationresistive copper nanowire composite conductors for photovoltaics. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e105.
Oh, J. S.; Oh, J. S.; Shin, J. H.; Yeom, G. Y.; Kim, K. N. Nano-welding of Ag nanowires using rapid thermal annealing for transparent conductive films. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 8647–8651.
Song, T.-B.; Chen, Y.; Chung, C.-H.; Yang, Y.; Bob, B.; Duan, H.-S.; Li, G.; Tu, K.-N.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y. Nanoscale joule heating and electromigration enhanced ripening of silver nanowire contacts. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2804–2811.
Lu, Y.; Huang, J. Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. H.; Lou, J. Cold welding of ultrathin gold nanowires. Nat. Nanotech. 2010, 5, 218–224.
Garnett, E. C.; Cai, W. S.; Cha, J. J.; Mahmood, F.; Connor, S. T.; Christoforo, M. G.; Cui, Y.; McGehee, M. D.; Brongersma, M. L. Self-limited plasmonic welding of silver nanowire junctions. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 241–249.
Han, S.; Hong, S.; Ham, J.; Yeo, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, B.; Lee, P.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S. S.; Yang, M.-Y. et al. Fast plasmonic laser nanowelding for a Cu-nanowire percolation network for flexible transparent conductors and stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5808–5814.
Cheng, Y.; Wang, S. L.; Wang, R. R.; Sun, J.; Gao, L. Copper nanowire based transparent conductive films with high stability and superior stretchability. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 5309–5316.
Cao, L. Y.; Barsic, D. N.; Guichard, A. R.; Brongersma, M. L. Plasmon-assisted local temperature control to pattern individual semiconductor nanowires and carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3523–3527.
Govorov, A. O.; Zhang, W.; Skeini, T.; Richardson, H.; Lee, J.; Kotov, N. A. Gold nanoparticle ensembles as heaters and actuators: Melting and collective plasmon resonances. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2006, 1, 84–90.
Dunaev, A. V. Survey of emission spectra of the plasma of chlorine, hydrogen chloride, argon, and hydrogen. Russ. Microelectronics 2015, 44, 173–177.
Klement, P.; Feser, C.; Hanke, B.; von Maydell, K.; Agert, C. Correlation between optical emission spectroscopy of hydrogen/germane plasma and the Raman crystallinity factor of germanium layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 152109.
Wu, M. Z.; Huang, T. Y.; Jin, C. G.; Zhuge, L. J.; Han, Q.; Wu, X. M. Effect of multiple frequency H2/Ar plasma treatment on the optical, electrical, and structural properties of AZO films. IEEE T. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 3687–3690.
van Huis, M. A.; Kunneman, L. T.; Overgaag, K.; Xu, Q.; Pandraud, G.; Zandbergen, H. W.; Vanmaekelbergh, D. Low-temperature nanocrystal unification through rotations and relaxations probed by in situ transmission electron microscopy. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3959–3963.
Cho, K. S.; Talapin, D. V.; Gaschler, W.; Murray, C. B. Designing PbSe nanowires and nanorings through oriented attachment of nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7140–7147.
Schriver, M.; Regan, W.; Gannett, W. J.; Zaniewski, A. M.; Crommie, M. F.; Zettl, A. Graphene as a long-term metal oxidation barrier: Worse than nothing. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5763–5768.
Zhou, F.; Li, Z. T.; Shenoy, G. J.; Li, L.; Liu, H. T. Enhanced room-temperature corrosion of copper in the presence of graphene. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6939–6947.
Shi, L. J.; Wang, R. R.; Zhai, H. T.; Liu, Y. Q.; Gao, L.; Sun, J. A long-term oxidation barrier for copper nanowires: Graphene says yes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 4231–4236.
Hu, W. L.; Niu, X. F.; Li, L.; Yun, S.; Yu, Z. B.; Pei, Q. B. Intrinsically stretchable transparent electrodes based on silver-nanowire-crosslinked-polyacrylate composites. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 344002.
Hu, W. L.; Wang, R. R.; Lu, Y. F.; Pei, Q. B. An elastomeric transparent composite electrode based on copper nanowires and polyurethane. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1298–1305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Zhai, H., Wang, T. et al. Plasma-induced nanowelding of a copper nanowire network and its application in transparent electrodes and stretchable conductors. Nano Res. 9, 2138–2148 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1103-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1103-0