Abstract
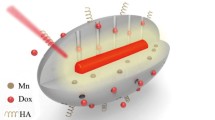
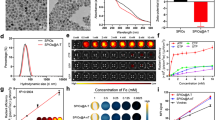
A universal platform with Mn doping and hyaluronic acid (HA) modification, based on mesoporous silica (mSiO2), was designed and used as a basic multifunctional material with magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. Furthermore, we added flexible functions through the addition of functional molecules. Specially, two typical compounds, hydrophobic perfluorooctyl bromide (PFOB) and hydrophilic doxorubicin (DOX), were loaded into the channels to obtain PFOB@Mn@mSiO2@HA (PMMH) or DOX@Mn@mSiO2@HA (DMMH) nanoparticles for dual-mode imaging or imaging and therapy, respectively. The PMMH and DMMH nanoparticles were highly targeted to the lymph system in vitro and in vivo. MR and ultrasound imaging of PMMH nanoparticles were performed in the lymph system, while MR imaging and chemotherapy of DMMH nanoparticles was used to detect cancer. These results showed that both PMMH and DMMH nanoparticles can be designed with high lymph targeting efficiency. PMMH nanoparticles are a dual-mode contrast agent for both ultrasound and MR imaging for the lymph system and DMMH nanoparticles are powerful agents for the combined diagnosis and therapy of cancer in vivo.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin, Y. D.; Gao, X. H. Plasmonic fluorescent quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 571–576.
Hu, S. H.; Gao, X. H. Nanocomposites with spatially separated functionalities for combined imaging and magnetolytic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7234–7237.
Fan, W. P.; Shen, B.; Bu, W. B.; Chen, F.; Zhao, K. L.; Zhang, S. J.; Zhou, L. P.; Peng, W. J.; Xiao, Q. F.; Xing, H. Y. et al. Rattle-structured multifunctional nanotheranostics for synergetic chemo-/radiotherapy and simultaneous magnetic/luminescent dual-mode imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6494–6503.
Passuello, T.; Pedroni, M.; Piccinelli, F.; Polizzi, S.; Marzola, P.; Tambalo, S.; Conti, G.; Benati, D.; Vetrone, F.; Bettinelli, M. et al. PEG-capped, lanthanide doped GdF3 nanoparticles: Luminescent and T2 contrast agents for optical and MRI multimodal imaging. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7682–7689.
Pellegatti, L.; Zhang, J.; Drahos, B.; Villette, S.; Suzenet, F.; Guillaumet, G.; Petoud, S.; Tóth, E. Pyridine-based lanthanide complexes: Towards bimodal agents operating as near infrared luminescent and MRI reporters. Chem. Commun. 2008, 6591–6593.
Nishioka, T.; Shiga, T.; Shirato, H.; Tsukamoto, E.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kato, T.; Ohmori, K.; Yamazaki, A.; Aoyama, H.; Hashimoto, S. et al. Image fusion between 18FDG-PET and MRI/CT for radiotherapy planning of oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2002, 53, 1051–1057.
Wen, S. H.; Li, K. G.; Cai, H. D.; Chen, Q.; Shen, M. W.; Huang, Y. P.; Peng, C.; Hou, W. X.; Zhu, M. F.; Zhang, G. X. et al. Multifunctional dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles for dual mode CT/MR imaging applications. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1570–1580.
Kubota, K.; Yokoyama, J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ono, S.; Qureshy, A.; Itoh, M.; Fukuda, H. FDG-PET delayed imaging for the detection of head and neck cancer recurrence after radiochemotherapy: Comparison with MRI/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imag. 2004, 31, 590–595.
Cheng, S. H.; Lee, C. H.; Chen, M. C.; Souris, J. S.; Tseng, F. G.; Yang, C. S.; Mou, C. Y.; Chen, C. T.; Lo, L. W. Trifunctionalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for comprehensive cancer theranostics-the trio of imaging, targeting and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6149–6157.
Cho, H. J.; Yoon, H. Y.; Koo, H.; Ko, S. H.; Shim, J. S.; Cho, J. H.; Park, J. H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, D. D. Hyaluronic acid-ceramide-based optical/MR dual imaging nanoprobe for cancer diagnosis. J. Controlled Release 2012, 162, 111–118.
Yang, K.; Hu, L. L.; Ma, X. X.; Ye, S. Q.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X. Z.; Li, C. H.; Li, Y. G.; Liu, Z. Multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy using functionalized graphene nanosheets anchored with magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1868–1872.
Zha, Z. B.; Wang, J. R.; Zhang, S. H.; Wang, S. M.; Qu, E. Z.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Dai, Z. F. Engineering of perfluorooctylbromide polypyrrole nano-/microcapsules for simultaneous contrast enhanced ultrasound imaging and photothermal treatment of cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 287–293.
Bhang, S. H.; Won, N.; Lee, T. J.; Jin, H.; Nam, J.; Park, J.; Chung, H.; Park, H. S.; Sung, Y. E.; Hahn, S. K. et al. Hyaluronic acid-quantum dot conjugates for in vivo lymphatic vessel imaging. Acs Nano 2009, 3, 1389–1398.
Jaggupilli, A.; Elkord, E. Significance of CD44 and CD24 as cancer stem cell markers: An enduring ambiguity. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 708036.
Kim, J. H.; Glant, T. T.; Lesley, J.; Hyman, R.; Mikecz, K. Adhesion of lymphoid cells to CD44-specific substrata: The consequences of attachment depend on the ligand. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 256, 445–453.
Banerji, S.; Ni, J.; Wang, S. X.; Clasper, S.; Su, J.; Tammi, R.; Jones, M.; Jackson, D. G. LYVE-1, a new homologue of the CD44 glycoprotein, is a lymph-specific receptor for hyaluronan. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 789–801.
Jackson, D. G.; Prevo, R.; Clasper, S.; Banerji, S. LYVE-1, the lymphatic system and tumor lymphangiogenesis. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 317–321.
Mizrahy, S.; Raz, S. R.; Hasgaard, M.; Liu, H.; Soffer-Tsur, N.; Cohen, K.; Dvash, R.; Landsman-Milo, D.; Bremer, M. G. E. G.; Moghimi, S. M. et al. Hyaluronan-coated nanoparticles: The influence of the molecular weight on CD44- hyaluronan interactions and on the immune response. J. Controlled Release 2011, 156, 231–238.
Wu, G. Y.; Zhang, H. J.; Zhan, Z. F.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, J. J.; Xu, J. R.; Zhu, J. Hyaluronic acid-gadolinium complex nanospheres as lymphatic system-specific contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Chinese J. Chem. 2015, 33, 1153–1158.
Ma, M.; Xu, H. X.; Chen, H. R.; Jia, X. Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, S. G.; Wu, R.; Yao, M. H.; Cai, X. J. et al. A drug-perfluorocarbon nanoemulsion with an ultrathin silica coating for the synergistic effect of chemotherapy and ablation by high-intensity focused ultrasound. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7378–7385.
Choi, K. Y.; Yoon, H. Y.; Kim, J. H.; Bae, S. M.; Park, R. W.; Kang, Y. M.; Kim, I. S.; Kwon, I. C.; Choi, K.; Jeong, S. Y. et al. Smart nanocarrier based on PEGylated hyaluronic acid for cancer therapy. Acs Nano 2011, 5, 8591–8599.
Choi, K. Y.; Min, K. H.; Yoon, H. Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J. H.; Kwon, I. C.; Choi, K.; Jeong, S. Y. PEGylation of hyaluronic acid nanoparticles improves tumor targetability in vivo. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1880–1889.
Park, S. J.; Park, W.; Na, K. Photo-activatable ternary complex based on a multifunctional shielding material for targeted shRNA delivery in cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8991–8999.
He, Q. J.; Shi, J. L. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based nano drug delivery systems: Synthesis, controlled drug release and delivery, pharmacokinetics and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5845–5855.
Sim, L. N.; Majid, S. R.; Arof, A. K. FTIR studies of PEMA/ PVdF-HFP blend polymer electrolyte system incorporated with LiCF3SO3 salt. Vib. Spectrosc. 2012, 58, 57–66.
Sim, L. N.; Majid, S. R.; Arof, A. K. Effects of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate ionic liquid in poly(ethyl methacrylate)/poly(vinylidenefluoride-cohexafluoropropylene) blend based polymer electrolyte system. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 123, 190–197.
Guillet-Nicolas, R.; Laprise-Pelletier, M.; Nair, M. M.; Chevallier, P.; Lagueux, J.; Gossuin, Y.; Laurent, S.; Kleitz, F.; Fortin, M. A. Manganese-impregnated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for signal enhancement in MRI cell labelling studies. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11499–11511.
Bejar, A.; Ben Chaabene, S.; Jaber, M.; Lambert, J. F.; Bergaoui, L. Mn-analcime: Synthesis, characterization and application to cyclohexene oxidation. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2014, 196, 158–164.
Liu, Y.; Shen, J. M.; Chen, Z. L.; Liu, Y. Degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene in drinking water by manganese silicate catalyzed ozonation. Desalination 2011, 279, 219–224.
Päll, T.; Pink, A.; Kasak, L.; Turkina, M.; Anderson, W.; Valkna, A.; Kogerman, P. Soluble CD44 interacts with intermediate filament protein vimentin on endothelial cell surface. PLoS One 2011, 6, e29305.
Jones, M.; Tussey, L.; Athanasou, N.; Jackson, D. G. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan isoforms of the CD44 hyaluronan receptor induced in human inflammatory macrophages can function as paracrine regulators of fibroblast growth factor action. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7964–7974.
Appaturi, J. N.; Adam, F. A facile and efficient synthesis of styrene carbonate via cycloaddition of CO2 to styrene oxide over ordered mesoporous MCM-41-Imi/Br catalyst. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 136–137, 150–159.
Banerji, S.; Hide, B. R. S.; James, J. R.; Noble, M. E. M.; Jackson, D. G. Distinctive properties of the hyaluronanbinding domain in the lymphatic endothelial receptor lyve-1 and their implications for receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10724–10735.
Faul, C.; Donnelly, M.; Merscher-Gomez, S.; Chang, Y. H.; Franz, S.; Delfgaauw, J.; Chang, J. M.; Choi, H. Y.; Campbell, K. N.; Kim, K. et al. The actin cytoskeleton of kidney podocytes is a direct target of the antiproteinuric effect of cyclosporine A. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 931–938.
Stanisz, G. J.; Henkelman, R. M. Gd-DTPA relaxivity depends on macromolecular content. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 44, 665–667.
Muharnmad, F.; Guo, M. Y.; Qi, W. X.; Sun, F. X.; Wang, A. F.; Guo, Y. J.; Zhu, G. S. pH-triggered controlled drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles via intracelluar dissolution of ZnO nanolids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8778–8781.
Zhao, W. W.; Cui, B.; Peng, H. X.; Qiu, H. J.; Wang, Y. Y. Novel method to investigate the interaction force between etoposide and APTES-functionalized Fe3O4@nSiO2@mSiO2 nanocarrier for drug loading and release processes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 4379–4386.
Mathew, A.; Parambadath, S.; Park, S. S.; Ha, C. S. Hydrophobically modified spherical MCM-41 as nanovalve system for controlled drug delivery. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2014, 200, 124–131.
de la Torre, C.; Casanova, I.; Acosta, G.; Coll, C.; Moreno, M. J.; Albericio, F.; Aznar, E.; Mangues, R.; Royo, M.; Sancenon, F. et al. Gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles using a double-role circular peptide for the controlled and target-preferential release of doxorubicin in CXCR4-expresing lymphoma cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 687–695.
Niu, C. C.; Wang, Z. G.; Lu, G. M.; Krupka, T. M.; Sun, Y.; You, Y. F.; Song, W. X.; Ran, H. T.; Li, P.; Zheng, Y. Y. Doxorubicin loaded superparamagnetic PLGA-iron oxide multifunctional microbubbles for dual-mode US/MR imaging and therapy of metastasis in lymph nodes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2307–2317.
Yang, X. Y.; Wang, Y. S.; Huang, X.; Ma, Y. F.; Huang, Y.; Yang, R. C.; Duan, H. Q.; Chen, Y. S. Multi-functionalized graphene oxide based anticancer drug-carrier with dualtargeting function and pH-sensitivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3448–3454.
Chen, Z. W.; Li, Z. H.; Lin, Y. H.; Yin, M. L.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Biomineralization inspired surface engineering of nanocarriers for pH-responsive, targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1364–1371.
Sun, J. S.; Xianyu, Y. L.; Li, M. M.; Liu, W. W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D. B.; Liu, C.; Hu, G. Q.; Jiang, X. Y. A microfluidic origami chip for synthesis of functionalized polymeric nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5262–5265.
Yu, L. L.; Bi, H. Facile synthesis and magnetic property of iron oxide/MCM-41 mesoporous silica nanospheres for targeted drug delivery. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07B514.
Lankveld, D. P. K.; Oomen, A. G.; Krystek, P.; Neigh, A.; Troost-de Jong, A.; Noorlander, C. W.; Van Eijkeren, J. C. H.; Geertsma, R. E.; De Jong, W. H. The kinetics of the tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8350–8361.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Wu, G., Cheng, J. et al. Multifunctional lymph-targeted platform based on Mn@mSiO2 nanocomposites: Combining PFOB for dual-mode imaging and DOX for cancer diagnose and treatment. Nano Res. 9, 473–489 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0929-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0929-1