Abstract
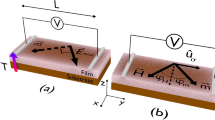
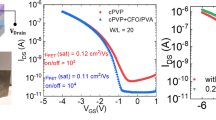
Flexible magnetoelectric (ME) materials have been studied for new applications such as memory, energy harvesters, and magnetic field sensors. Herein, with the widely studied and progressive advantages of ME phenomena in the multiferroic field, we demonstrate a new approach for utilizing flexible ME materials as gate dielectric layers in ME organic field-effect transistors (ME-OFET) that can be used for sensing a magnetic field and extracting the ME properties of the gate dielectric itself. The magnetoelectric nanohybrid gate dielectric layer comprises sandwiched stacks of magnetostrictive CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and a highly piezoelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) layer. While varying the magnetic field applied to the ME gate dielectric, the ME effect in the functional gate dielectric modulates the channel conductance of the ME-OFET owing to a change in the effective gate field. The clear separation of the ME responses in the gate dielectric layer of ME-OFET from those of the other parameters was demonstrated using the AC gate biasing method and enabled the extraction of the ME coefficient of ME materials. Additionally, the device shows high stability after cyclic bending of 10,000 cycles at a banding radius of 1.2 cm. The device has significant potential for not only the extraction of the intrinsic characterization of ME materials but also the sensing of a magnetic field in integrated flexible electronic systems.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong, S. X.; Li, J. F.; Viehland, D. Vortex magnetic field sensor based on ring-type magnetoelectric laminate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2307–2309.
Israel, C.; Mathur, N. D.; Scott, J. F. A one-cent roomtemperature magnetoelectric sensor. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 93–94.
Giang, D. T. H.; Duc, P. A.; Ngoc, N. T.; Duc, N. H. Geomagnetic sensors based on Metglas/PZT laminates. Sens. Act. A: Phys. 2012, 179, 78–82.
Giang, D. T. H.; Duc, N. H. Magnetoelectric sensor for microtesla magnetic-fields based on (Fe80Co20)78Si12B10/PZT laminates. Sens. Act. A: Phys. 2009, 149, 229–232.
Zhang, C. L.; Yang, J. S.; Chen. W. Q. Harvesting magnetic energy using extensional vibration of laminated magnetoelectric plates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 013511.
Patil, D. R.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, J. E.; Sharpes, N.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Kim, Y. D.; Kim, K. H.; Priya, S.; Ryu, J. Anisotropic selfbiased dual-phase low frequency magneto-mechano-electric energy harvesters with giant power densities. APL Mat. 2014, 2, 046102.
Bibes, M.; Barthélé my A. Multiferroics: Towards a magnetoelectric memory. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 425–426.
Wang, Z. G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. J.; Li, Y. X.; Luo, H. S.; Li, J. F.; Viehland, D. Magnetoelectric assisted 180° magnetization switching for electric field addressable writing in magnetoresistive random-access memory. ACS Nano. 2014, 8, 7793–7800.
Zavaliche, F.; Zheng, H.; Ardabili, L. M.; Yang, S. Y.; Zhan, Q.; Shafer, P.; Reilly, E.; Chopdekar, R.; Jia, Y.; Wright, P.; Schlom, D. G.; Suzuki, Y.; Ramesh, R. Electrically assisted magnetic recording in multiferroic nanostructures. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1793–1796.
Hur, N.; Park, S.; Sharma, P. A.; Ahn, J. S.; Guha, S.; Cheong, S-W. Electric polarization reversal and memory in a multiferroic material induced by magnetic fields. Nature. 2004, 429, 392–395.
Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, C. Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y. H.; Nan, C. W. Demonstration of magnetoelectric read head of multiferroic heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 152510.
Scott, J. F. Data storage: Multiferroic memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 256–257.
Martins, P.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Polymer-based magnetoelectric materials. Adv. Func. Mater. 2013, 23, 3371–3385.
Nan, C. W.; Bichurin, M. I.; Dong, S. X.; Viehland, D.; Srinivasan, G. Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: Historical perspective, status, and future directions. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 031101.
Zhai, J. Y.; Cai, N.; Shi, Z.; Lin, Y. H.; Nan, C. W. Magneticdielectric properties of NiFe2O4/PZT particulate composites. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 823–827.
Ryu, H.; Murugavel, P.; Lee, J. H.; Chae, S. C.; Noh, T. W.; Oh, Y. S.; Kim, K. H.; Jang, J. H.; Kim, M.; Bae, C. et al. Magnetoelectric effects of nanoparticulate Pb(Zr0.52Ti0.48)O3-NiFe2O4 composite films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 102907.
Wan, J. G.; Wang, X. W.; Wu, Y. J.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, W. Q.; Wang, G. H.; Liu, J. M. Magnetoelectric CoFe2O4 - Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 composite thin films derived by a sol-gel process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 122501.
Gao, X. S.; Rodriguez, B. J.; Liu, L. F.; Birajdar, B.; Pantel, D.; Ziese, M.; Alexe, M.; Hesse, D. Microstructure and properties of well ordered multiferroic Pb(Zr,Ti)O3/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. ACS Nano. 2010, 4, 1099–1107.
Chen, Y. J.; Hsieh, Y. H.; Liao, S. C.; Hu, Z. W.; Huang, M. J.; Kuo, W. C.; Chin, Y. Y.; Uen, T. M.; Juang, J. Y.; Lai, C. H. et al. Strong magnetic enhancement in self-assembled multiferroic-ferrimagnetic nanostructures. Nanoscale. 2013, 5, 4449–4453.
Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Lofland, S. E.; Ma, Z.; Mohaddes- Ardabili, L.; Zhao, T.; Salamanca-Riba, L.; Shinde, S. R.; Ogale, S. B.; Bai, F. et al. Multiferroic BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 nanostructures. Science. 2004, 303, 661–663.
Imai, A.; Cheng, X.; Xin, H. L.; Eliseev, E. A.; Morozovska, A. N.; Kalinin, S. V.; Takahashi, R.; Lippmaa, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nagarajan, V. Epitaxial Bi5Ti3FeO15-CoFe2O4 pillar-matrix multiferroic nanostructures. ACS Nano. 2013, 7, 11079–11086.
Zavaliche, F.; Zheng, H.; Mohaddes-Ardabili, L.; Yang, S. Y.; Zhan, Q.; Shafer, P.; Reilly, E.; Chopdekar, R.; Jia, Y.; Wright, P. et al. Electric field-induced magnetization switching in epitaxial columnar nanostructures. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1793–1796.
Hu, J.-M.; Yang, T. N.; Wang, J. J.; Huang, H. B.; Zhang, J. X.; Chen, L. Q.; Nan, C. W. Purely electric-field-driven perpendicular magnetization reversal. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 616–622.
Liu, X. H.; Liu, S. Y.; Han, M. G.; Zhao, L.; Deng, H. M.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y. M.; Krusin-Elbaum, L.; O’Brien, S. Magnetoelectricity in CoFe2O4 nanocrystal-P(VDF-HFP) thin films. Nano. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 374.
Srinivasan, G.; Rasmussen, E. T.; Hayes, R. Magnetoelectric effects in ferrites-lead zirconate titanate layered composites: The influence of zinc substitution in ferrites. Phys. Rev. B. 2003, 67, 014418.
Wang, Y. J.; Gray, D.; Gao, J. Q.; Berry, D.; Li, M. H.; Li, J. F.; Viehland, D.; Luo, H. Improvement of magnetoelectric properties in Metglas/Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 laminates by poling optimization, J. Alloys Comp. 2012, 519, 1–3.
Molegraaf, H. J. A.; Hoffman, J.; Vaz, C. A. F.; Gariglio, S.; van der Marel, D.; Ahn, C. H.; Triscone, J. M. Magnetoelectric effects in complex oxides with competing ground states. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3470–3474.
Silva, M.; Reis, S.; Lehmann, C. S.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Lasheras, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Barandiarán, J. M. Optimization of the magnetoelectric response of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/epoxy/vitrovac laminates. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 10912–10919.
Zhang, S. T.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Z. L.; Lu, M. H.; Gu, Z. B.; Chen, Y. F. Multiferroic properties of Bi0.8La0.2FeO3/CoFe2O4 multilayer thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 5092–5095.
Wang, Y.; Hu, J. M.; Lin, Y. H.; Nan, C. W. Multiferroic magnetoelectric composite nanostructures. NPG Asia Mater. 2010, 2, 61–68.
Vaz, C. A. F.; Hoffman, J.; Ahn, C. H.; Ramesh, R. Magnetoelectric coupling effects in multiferroic complex oxide composite structures. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2900–2918.
Cui, N. Y.; Wu, W. W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, S.; Meng, L. X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Magnetic force driven nanogenerators as a noncontact energy harvester and sensor. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3701–3705.
Yang, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Q. S.; Hou, T. C.; Wang, Z. L. Self-powered magnetic sensor based on a triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano. 2012, 6, 10378–10383.
Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S. K.; Ceylan, A. Synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. Mag. Mag. Mater. 2007, 308, 289–295.
Tien, N. T.; Jeon, S.; Kim, D. I.; Trung, T. Q.; Jang, M.; Hwang, B. U.; Byun, K. E.; Bae, J.; Lee, E.; Tok, J. B. H.; Bao, Z. N.; Lee, N. E.; Park, J. J. A flexible bimodal sensor array for simultaneous sensing of pressure and temperature. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 796–804.
Tien, N. T.; Trung, T. Q.; Seol, Y. G.; Kim, D. I.; Lee, N. E. Physically responsive field-effect transistors with giant electromechanical coupling induced by nanocomposite gate dielectrics. ACS Nano. 2011, 5, 7069–7076.
Trung, T. Q.; Tien, N. T.; Seol, Y. G.; Lee. N. E. Transparent and flexible organic field-effect transistor for multi-modal sensing. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 533–540.
Tien, N. T.; Seol, Y. G.; Dao, L. H. A.; Noh, H. Y.; Lee, N. E. Utilizing highly crystalline pyroelectric material as functional gate dielectric in organic thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 910–915.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triet, N.M., Trung, T.Q., Hien, N.T.D. et al. A flexible magnetoelectric field-effect transistor with magnetically responsive nanohybrid gate dielectric layer. Nano Res. 8, 3421–3429 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0843-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0843-6