Abstract
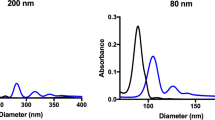
A thorough understanding of how proteins induce nanoparticle (NP) aggregation is crucial when designing in vitro and in vivo assays and interpreting experimental results. This knowledge is also crucial when developing nano-applications and formulation for drug delivery systems. In this study, we found that extraction of immunoglobulin G (IgG) from cow serum results in lower polystyrene NPs aggregation. Moreover, addition of isolated IgG or fibrinogen to fetal cow serum enhanced this aggregation, thus demonstrating that these factors are major drivers of NP aggregation in serum. Counter-intuitively, NP aggregation was inversely dependent on protein concentration; i.e., low protein concentrations induced large aggregates, whereas high protein concentrations induced small aggregates. Protein-induced NP aggregation and aggregate size were monitored by absorbance at 400 nm and dynamic light scattering, respectively. Here, we propose a mechanism behind the protein concentration dependent aggregation; this mechanism involves the effects of multiple protein interactions on the NP surface, surface area limitations, aggregation kinetics, and the influence of other serum proteins.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sund, J.; Alenius, H.; Vippola, M.; Savolainen, K.; Puustinen, A. Proteomic characterization of engineered nanomaterialprotein interactions in relation to surface reactivity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4300–4309.
Maiorano, G.; Sabella, S.; Sorce, B.; Brunetti, V.; Malvindi, M. A.; Cingolani, R.; Pompa, P. P. Effects of cell culture media on the dynamic formation of protein-nanoparticle complexes and influence on the cellular response. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7481–7491.
Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K. A. Nanoparticle size and surface properties determine the protein corona with possible implications for biological impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270.
Ferreira, S. A.; Oslakovic, C.; Cukalevski, R.; Frohm, B.; Dahlback, B.; Linse, S.; Gama, F. M.; Cedervall, T. Biocompatibility of mannan nanogel-safe interaction with plasma proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1043–1051.
Dobrovolskaia, M. A.; Patri, A. K.; Zheng, J.; Clogston, J. D.; Ayub, N.; Aggarwal, P.; Neun, B. W.; Hall, J. B.; McNeil, S. E. Interaction of colloidal gold nanoparticles with human blood: Effects on particle size and analysis of plasma protein binding profiles. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine 2009, 5, 106–117.
Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggard, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K. A.; Linse, S. Understanding the nanoparticle-protein corona using methods to quantify exchange rates and affinities of proteins for nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055.
Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Foy, M.; Berggard, T.; Donnelly, S. C.; Cagney, G.; Linse, S.; Dawson, K. A. Detailed identification of plasma proteins adsorbed on copolymer nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5754–5756.
Walkey, C. D.; Olsen, J. B.; Guo, H.; Emili, A.; Chan, W. C. Nanoparticle size and surface chemistry determine serum protein adsorption and macrophage uptake. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2139–2147.
Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Rosfa, S.; Wlodarski, A.; Kuharev, J.; Rekik, A.; Knauer, S. K.; Bantz, C.; Nawroth, T.; Bier, C.; Sirirattanapan, J. et al. Nanoparticle size is a critical physicochemical determinant of the human blood plasma corona: A comprehensive quantitative proteomic analysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7155–7167.
Dell’Orco, D.; Lundqvist, M.; Oslakovic, C.; Cedervall, T.; Linse, S. Modeling the time evolution of the nanoparticleprotein corona in a body fluid. PloS One 2010, 5, e10949.
Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G. J.; Puntes, V. Time evolution of the nanoparticle protein corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632.
Monopoli, M. P.; Walczyk, D.; Campbell, A.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Bombelli, F. B.; Dawson, K. A. Physical-chemical aspects of protein corona: Relevance to in vitro and in vivo biological impacts of nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2525–2534.
Shang, W.; Nuffer, J. H.; Muniz-Papandrea, V. A.; Colon, W.; Siegel, R. W.; Dordick, J. S. Cytochrome C on silica nanoparticles: Influence of nanoparticle size on protein structure, stability, and activity. Small 2009, 5, 470–476.
Shang, W.; Nuffer, J. H.; Dordick, J. S.; Siegel, R. W. Unfolding of ribonuclease A on silica nanoparticle surfaces. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1991–1995.
Lundqvist, M.; Sethson, I.; Jonsson, B. H. Protein adsorption onto silica nanoparticles: Conformational changes depend on the particles’ curvature and the protein stability. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10639–10647.
Pitek, A. S.; O’Connell, D.; Mahon, E.; Monopoli, M. P.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Dawson, K. A. Transferrin coated nanoparticles: Study of the bionano interface in human plasma. PloS One 2012, 7, e40685.
Cukalevski, R.; Lundqvist, M.; Oslakovic, C.; Dahlback, B.; Linse, S.; Cedervall, T. Structural changes in apolipoproteins bound to nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 14360–14369.
Jiang, X.; Jiang, J. G.; Jin, Y. D.; Wang, E.; Dong, S. J. Effect of colloidal gold size on the conformational changes of adsorbed cytochrome C: Probing by circular dichroism, UV-visible, and infrared spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 46–53.
Goy-Lopez, S.; Juarez, J.; Alatorre-Meda, M.; Casals, E.; Puntes, V. F.; Taboada, P.; Mosquera, V. Physicochemical characteristics of protein-NP bioconjugates: The role of particle curvature and solution conditions on human serum albumin conformation and fibrillogenesis inhibition. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9113–9126.
Dominguez-Medina, S.; McDonough, S.; Swanglap, P.; Landes, C. F.; Link, S. In situ measurement of bovine serum albumin interaction with gold nanospheres. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9131–9139.
Glomm, W. R.; Halskau, Ø.; Hanneseth, A. M.; Volden, S. Adsorption behavior of acidic and basic proteins onto citrate-coated Au surfaces correlated to their native fold, stability, and pI. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 14329–14345.
Zhang, D. M.; Neumann, O.; Wang, H.; Yuwono, V. M.; Barhoumi, A.; Perham, M.; Hartgerink, J. D.; Wittung-Stafshede, P.; Halas, N. J. Gold nanoparticles can induce the formation of protein-based aggregates at physiological pH. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 666–671.
Kumar, S.; Aswal, V. K.; Kohlbrecher, J. SANS and UV-vis spectroscopy studies of resultant structure from lysozyme adsorption on silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10167–10173.
Gagner, J. E.; Lopez, M. D.; Dordick, J. S.; Siegel, R. W. Effect of gold nanoparticle morphology on adsorbed protein structure and function. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7241–7252.
Bharti, B.; Meissner, J.; Findenegg, G. H. Aggregation of silica nanoparticles directed by adsorption of lysozyme. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9823–9833.
Kendall, M.; Ding, P.; Kendall, K. Particle and nanoparticle interactions with fibrinogen: The importance of aggregation in nanotoxicology. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 55–65.
Deng, Z. J.; Liang, M.; Toth, I.; Monteiro, M. J.; Minchin, R. F. Molecular interaction of poly(acrylic acid) gold nanoparticles with human fibrinogen. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8962–8969.
Wells, M. A.; Abid, A.; Kennedy, I. M.; Barakat, A. I. Serum proteins prevent aggregation of Fe2O3 and ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 837–846.
Wiogo, H. T.; Lim, M.; Bulmus, V.; Yun, J.; Amal, R. Stabilization of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in biological media by fetal bovine serum (FBS). Langmuir 2011, 27, 843–850.
Wiogo, H. T.; Lim, M.; Bulmus, V.; Gutierrez, L.; Woodward, R. C.; Amal, R. Insight into serum protein interactions with functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in biological media. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4346–4356.
Zook, J. M.; Maccuspie, R. I.; Locascio, L. E.; Halter, M. D.; Elliott, J. T. Stable nanoparticle aggregates/agglomerates of different sizes and the effect of their size on hemolytic cytotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 517–530.
Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G. J.; Puntes, V. F. Hardening of the nanoparticle-protein corona in metal (Au, Ag) and oxide (Fe3O4, CoO, and CeO2) nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 3479–3486.
Oslakovic, C.; Cedervall, T.; Linse, S.; Dahlback, B. Polystyrene nanoparticles affecting blood coagulation. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine 2012, 8, 981–986.
Ferreira, S. A.; Pereira, P.; Sampaio, P.; Coutinho, P. J. G.; Gama, F. M. Supramolecular assembled nanogel made of mannan. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2011, 361, 97–108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cukalevski, R., Ferreira, S.A., Dunning, C.J. et al. IgG and fibrinogen driven nanoparticle aggregation. Nano Res. 8, 2733–2743 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0780-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0780-4