Abstract
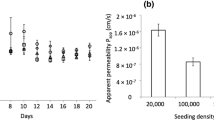
To develop inhaled medications, various cell culture models have been used to examine the transcellular transport or cellular uptake properties of small molecules. For the reproducible high throughput screening of the inhaled drug candidates, a further verification of cell architectures as drug transport barriers can contribute to establishing appropriate in vitro cell models. In the present study, side-by-side experiments were performed to compare the structure and transport function of three lung epithelial cells (Calu-3, normal human bronchial primary cells (NHBE), and NL-20). The cells were cultured on the nucleopore membranes in the air–liquid interface (ALI) culture conditions, with cell culture medium in the basolateral side only, starting from day 1. In transport assays, paracellular transport across all three types of cells appeared to be markedly different with the NHBE or Calu-3 cells, showing low paracellular permeability and high TEER values, while the NL-20 cells showed high paracellular permeability and low TEER. Quantitative image analysis of the confocal microscope sections further confirmed that the Calu-3 cells formed intact cell monolayers in contrast to the NHBE and NL-20 cells with multilayers. Among three lung epithelial cell types, the Calu-3 cell cultures under the ALI condition showed optimal cytometric features for mimicking the biophysical characteristics of in vivo airway epithelium. Therefore, the Calu-3 cell monolayers could be used as functional cell barriers for the lung-targeted drug transport studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agu RU, Ugwoke MI, Armand M, Kinget R, Verbeke N (2001) The lung as a route for systemic delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides. Respir Res 2:198–209
Astashkina A, Mann B, Grainger DW (2012) A critical evaluation of in vitro cell culture models for high-throughput drug screening and toxicity. Pharmacol Ther 134:82–106
Berube K, Prytherch Z, Job C, Hughes T (2010) Human primary bronchial lung cell constructs: the new respiratory models. Toxicology 278:311–318
Bhadriraju K, Chen CS (2002) Engineering cellular microenvironments to improve cell-based drug testing. Drug Discov Today 7:612–620
Borchard G, Cassara ML, Roemele PE, Florea BI, Junginger HE (2002) Transport and local metabolism of budesonide and fluticasone propionate in a human bronchial epithelial cell line (Calu-3). J Pharm Sci 91:1561–1567
Casartelli A, Bonato M, Cristofori P, Crivellente F, Dal Negro G, Masotto I, Mutinelli C, Valko K, Bonfante V (2003) A cell-based approach for the early assessment of the phospholipidogenic potential in pharmaceutical research and drug development. Cell Biol Toxicol 19:161–176
Cozens AL, Yezzi MJ, Yamaya M, Steiger D, Wagner JA, Garber SS, Chin L, Simon EM, Cutting GR, Gardner P, Friend DS, Basbaum CB, Gruenert DC (1992) A transformed human epithelial cell line that retains tight junctions post crisis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 28A:735–744
Dobson PD, Kell DB (2008) Carrier-mediated cellular uptake of pharmaceutical drugs: an exception or the rule? Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:205–220
Ehrhardt C, Forbes B, Kim K-J (2008) In vitro models of the tracheo-bronchial epithelium. In: Ehrhardt C, Kim K-J (eds) Drug absorption studies. Springer, New York, pp 235–257
Florea BI, Cassara ML, Junginger HE, Borchard G (2003) Drug transport and metabolism characteristics of the human airway epithelial cell line Calu-3. J Control Release 87:131–138
Forbes B, Ehrhardt C (2005) Human respiratory epithelial cell culture for drug delivery applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 60:193–205
Frixione E, Lagunes R, Ruiz L, Urban M, Porter RM (2001) Actin cytoskeleton role in the structural response of epithelial (MDCK) cells to low extracellular Ca2+. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 22:229–242
Gonda I (2006) Systemic delivery of drugs to humans via inhalation. J Aerosol Med 19:47–53
Grainger CI, Greenwell LL, Lockley DJ, Martin GP, Forbes B (2006) Culture of Calu-3 cells at the air interface provides a representative model of the airway epithelial barrier. Pharm Res 23:1482–1490
Gray TE, Guzman K, Davis CW, Abdullah LH, Nettesheim P (1996) Mucociliary differentiation of serially passaged normal human tracheobronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 14:104–112
Gruenert DC, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH (1995) Culture and transformation of human airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 268:L347–L360
Guzman K, Gray TE, Yoon JH, Nettesheim P (1996) Quantitation of mucin RNA by PCR reveals induction of both MUC2 and MUC5AC mRNA levels by retinoids. Am J Physiol 271:L1023–L1028
Huang TW, Chan YH, Cheng PW, Young YH, Lou PJ, Young TH (2010) Increased mucociliary differentiation of human respiratory epithelial cells on hyaluronan-derivative membranes. Acta Biomater 6:1191–1199
Irvine JD, Takahashi L, Lockhart K, Cheong J, Tolan JW, Selick HE, Grove JR (1999) MDCK (Madin–Darby canine kidney) cells: a tool for membrane permeability screening. J Pharm Sci 88:28–33
Li AP (2001) Screening for human ADME/Tox drug properties in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 6:357–366
Lin H, Li H, Cho HJ, Bian S, Roh HJ, Lee MK, Kim JS, Chung SJ, Shim CK, Kim DD (2007) Air–liquid interface (ALI) culture of human bronchial epithelial cell monolayers as an in vitro model for airway drug transport studies. J Pharm Sci 96:341–350
Louvard D, Kedinger M, Hauri HP (1992) The differentiating intestinal epithelial cell: establishment and maintenance of functions through interactions between cellular structures. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:157–195
O’Brien LE, Zegers MM, Mostov KE (2002) Opinion: building epithelial architecture: insights from three-dimensional culture models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:531–537
Patton JS, Byron PR (2007) Inhaling medicines: delivering drugs to the body through the lungs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:67–74
Sachs LA, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH (2003) Effects of media on differentiation of cultured human tracheal epithelium. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 39:56–62
Schiller JH, Bittner G, Oberley TD, Kao C, Harris C, Meisner LF (1992) Establishment and characterization of a SV40 T-antigen immortalized human bronchial epithelial cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 28A:461–464
Schiller J, Sabatini L, Bittner G, Pinkerman C, Mayotte J, Levitt M, Meisner L (1994) Phenotypic, molecular and genetic-characterization of transformed human bronchial epithelial-cell strains. Int J Oncol 4:461–470
Shah P, Jogani V, Bagchi T, Misra A (2006) Role of Caco-2 cell monolayers in prediction of intestinal drug absorption. Biotechnol Prog 22:186–198
Shen BQ, Finkbeiner WE, Wine JJ, Mrsny RJ, Widdicombe JH (1994) Calu-3: a human airway epithelial cell line that shows cAMP-dependent Cl− secretion. Am J Physiol 266:L493–L501
Stewart CE, Torr EE, Mohd Jamili NH, Bosquillon C, Sayers I (2012) Evaluation of differentiated human bronchial epithelial cell culture systems for asthma research. J Allergy 2012:943982
Suresh MV, Wagner MC, Rosania GR, Stringer KA, Min KA, Risler L, Shen DD, Georges GE, Reddy AT, Parkkinen J, Reddy RC (2012) Pulmonary administration of a water-soluble curcumin complex reduces severity of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 47:280–287
Szakacs G, Varadi A, Ozvegy-Laczka C, Sarkadi B (2008) The role of ABC transporters in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADME-Tox). Drug Discov Today 13:379–393
Szkotak AJ, Man SF, Duszyk M (2003) The role of the basolateral outwardly rectifying chloride channel in human airway epithelial anion secretion. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:710–720
Taub ME, Kristensen L, Frokjaer S (2002) Optimized conditions for MDCK permeability and turbidimetric solubility studies using compounds representative of BCS classes I-IV. Eur J Pharm Sci 15:331–340
Tsukazaki M, Satsu H, Mori A, Sugita-Konishi Y, Shimizu M (2004) Effects of tributyltin on barrier functions in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315:991–997
Volpe DA (2008) Variability in Caco-2 and MDCK cell-based intestinal permeability assays. J Pharm Sci 97:712–725
Vunjak-Novakovic G, Freed LE (1998) Culture of organized cell communities. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 33:15–30
Wu R, Zhao YH, Chang MM (1997) Growth and differentiation of conducting airway epithelial cells in culture. Eur Respir J 10:2398–2403
Yang J, Lan H, Huang X, Liu B, Tong Y (2012) MicroRNA-126 inhibits tumor cell growth and its expression level correlates with poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients. PLoS ONE 7:e42978
Yu JY, Zheng N, Mane G, Min KA, Hinestroza JP, Zhu H, Stringer KA, Rosania GR (2012) A cell-based computational modeling approach for developing site-directed molecular probes. PLoS Comput Biol 8:e1002378
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by grants from Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2015R1C1A1A02036781 to M. C. Shin and 2015R1A6A3A01020598 to K. A. Min). Part of this work was funded by NIH Grant R01GM078200 to G. R. Rosania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, K.A., Rosania, G.R., Kim, CK. et al. Functional and cytometric examination of different human lung epithelial cell types as drug transport barriers. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 359–369 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0704-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0704-6