Abstract
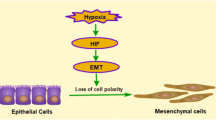
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a phenotype conversion of epithelial cells to myofibroblasts, is closely related with pathogenesis of renal fibrosis. Although it has been known that angiotensin II (ATII) stimulates EMT process in various cell types, the precise molecular mechanisms had not been clearly demonstrated. In this issue, Kang et al. show that AII suppresses NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling and enhances transforming growth factor-β1’s activity to induce EMT in renal epithelial cells (Kang et al., 2011). They suggest that ATII-mediated EMT stimulating effect may result from the increased oxidative stress via defect in Nrf2-antioxidant system. This report proposes a possible mechanism of ATII-mediated renal fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daniel, C., Blocking of angiotensin II is more than blocking of transforming growth factor-beta. Kidney Int., 74, 551–553 (2008).
Galichon, P. and Hertig, A., Epithelial to mesenchymal transition as a biomarker in renal fibrosis: are we ready for the bedside? Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, 6, 4–11 (2011).
Kalluri, R. and Neilson, E. G., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest., 112, 1776–1784 (2003).
Kalluri, R. and Weinberg, R. A., The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Invest., 119, 1420–1428 (2009).
Kang, K. W., Lee, S. J., and Kim, S. G., Molecular mechanism of Nrf2 activation by oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal., 7, 1664–1673 (2005).
Kang, S. J., You, A., and Kwak, M.-K., Suppression of Nrf2 Signaling by Angiotensin II in Murine Renal Epithelial Cells. Arch. Pharm. Res., 34, 829–836 (2011).
Kolesnyk, I., Struijk, D. G., Dekker, F. W., and Krediet, R. T., Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers in patients with chronic kidney disease. Neth. J. Med., 68, 15–23 (2010).
Leehey, D. J., Isreb, M. A., Marcic, S., Singh, A. K., and Singh, R., Effect of high glucose on superoxide in human mesangial cells: role of angiotensin II. Nephron Exp. Nephrol., 100, e46–e53 (2005).
Lewis, E., Hunsicker, L., Bain, R., and Rhode, R., The effects of angiotensin converting enzyme initiation on diabetic nepropathy. N. Engl. J. Med., 329, 1456–1462 (1993).
Liu, Y., New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 21, 212–222 (2010).
Onozato, M. L., Tojo, A., Goto, A., Fujita, T., and Wilcox, C. S., Oxidative stress and nitric oxide synthase in rat diabetic nephropathy: Effects of ACEI and ARB. Kidney Int., 61, 186–194 (2002).
Remuzzi, G., Perico, N., Macia, M., and Ruggenenti, P., The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl., S57–S65 (2005).
Rhyu, D. Y., Yang, Y., Ha, H., Lee, G. T., Song, J. S., Uh, S. T., and Lee, H. B., Role of reactive oxygen species in TGFbeta1-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 16, 667–675 (2005).
Ushio-Fukai, M., Zafari, A. M., Fukui, T., Ishizawa, N., and Grindling, K. K., p22Phox is a critical component of the superoxide-generating NADH/NADPH oxidase system and regulates angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23317–23321 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, K.W. Angiotensin II-mediated Nrf2 down-regulation: a potential causing factor for renal fibrosis?. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 695–697 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0500-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0500-x