Abstract
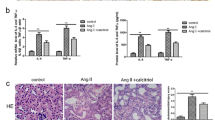
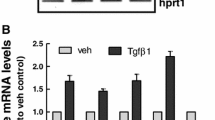
Angiotensin II (ATII), a physiologically active mediator of the renin-angiotensin system, has been shown to be associated with renal fibrosis pathophysiology. In our current study with murine renal epithelial TCMK-1 cells, ATII inhibited the expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-target antioxidant genes such as NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase-1 and γ-glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL). In accord to the reduced expression of GCL, a GSH biosynthesis enzyme, ATII treatment reduced intracellular GSH content and increased the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). While, there was no significant changes in nuclear protein levels of Nrf2 following ATII treatment, implying the potential alterations in the expression of partner proteins of Nrf2. Our measurement of Nrf2 partner bZIP transcription factors, including Bach1, small Maf proteins, and activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) showed that the expression level for ATF3 was enhanced in ATII-treated TCMK cells. Presumably through ATII-induced oxidative stress, ATII treatment was found to enhance the inducible level of TGFβ-mediated α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression, which is one of molecular markers of renal fibrosis. In conclusion, our results indicate that ATII suppresses Nrf2-GSH signaling in murine renal epithelial cells. Elevated ROS levels in ATII exposed epithelial cells might be a causing factor contributing to renal fibrosis pathology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, S. L., Sekhar, K. R., Rachakonda, G., Sasi, S., and Freeman, M. L., Activating transcription factor 3 is a novel repressor of the nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-regulated stress pathway. Cancer Res., 68, 364–368 (2008).
Carvajal, G., Rodríguez-Vita, J., Rodrigues-Díez, R., Sánchez-López, E., Rupérez, M., Cartier, C., Esteban, V., Ortiz, A., Egido, J., Mezzano, S. A., and Ruiz-Ortega, M., Angiotensin II activates the Smad pathway during epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Kidney Int., 74, 585–595 (2008).
Chan, Y. C. and Leung, P. S., Angiotensin II type 1 receptordependent nuclear factor-kappaB activation-mediated proinflammatory actions in a rat model of obstructive acute pancreatitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 323, 10–18 (2007).
Chen, Y. X., Li, Y., Wang, W. M., Zhang, W., Chen, X. N., Xie, Y. Y., Lu, J., Huang, Q. H., and Chen, N., Phosphoproteomic study of human tubular epithelial cell in response to transforming growth factor-beta-1-induced epithelial-tomesenchymal transition. Am. J. Nephrol., 31, 24–35 (2009).
Choi, H. K., Pokharel, Y. R., Lim, S. C., Han, H. K., Ryu, C. S., Kim S. K., Kwak, M. K., and Kang, K. W., Inhibition of liver fibrosis by solubilized coenzyme Q10: Role of Nrf2 activation in inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1 expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 240, 377–384 (2009).
Daniel, C., Blocking of angiotensin II is more than blocking of transforming growth factor-beta. Kidney Int., 74, 551–553 (2008).
Djamali, S., Reese, J., Yracheta, J., Oberley, T., Hullett, D., and Becker, B., Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and oxidative stress in chronic allograft nephropathy. Am. J. Transplant., 5, 500–509 (2005).
Griffith, O. W., Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal. Biochem., 106, 207–212 (1980).
Hagen, T. M., Liu, J., Lykkesfeldt, J., Wehr, C. M., Ingersoll, R. T., Vinarsky, V., Bartholomew, J. C., and Ames, B. N., Feeding acetyl-L-carnitine and lipoic acid to old rats significantly improves metabolic function while decreasing oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 99, 1870–1875 (2002).
Itoh, K., Ishii, T., Wakabayashi, N., and Yamamoto, M., Regulatory mechanisms of cellular response to oxidative stress. Free Radic. Res., 31, 319–324 (1999).
Iwano, M., Plieth, D., Danoff, T. M., Xue, C., Okada, H., and Neilson, E. G., Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest., 110, 341–350 (2002).
Kalluri, R. and Neilson, E. G., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest., 112, 1776–1784 (2003).
Kalluri, R. and Weinberg, R. A., The basics of epithelialmesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Invest., 119, 1420–1428 (2009).
Kang, Y., Chen, C. R., and Massagué, J., A self-enabling TGF-β response coupled to stress signaling: Smad engages stress response factor ATF3 for Id1 repression in epithelial cells. Mol. Cell, 11, 915–926 (2003).
Kensler, T. W., Wakabayashi, N., and Biswal, S., Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 47, 89–116 (2007).
Kim, J., Seok, Y. M., Jung, K. J., and Park, K. M., Reactive oxygen species/oxidative stress contributes to progression of kidney fibrosis following transient ischemic injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol., 297, F461–F470(2009).
Kobayashi, A., Kang, M. I., Okawa, H., Ohtsuji, M., Zenke, Y., Chiba, T., Igarashi, K., and Yamamoto, M., Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell. Biol., 24, 7130–7139 (2004).
Kobayashi, M. and Yamamoto, M., Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal., 7, 385–394 (2005).
Kwak, M. K., Wakabayashi, N., and Kensler, T. W., Chemoprevention through the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway by phase 2 enzyme inducers. Mutat. Res., 555, 133–148 (2004).
Lee, J. M., Dedhar, S., Kalluri, R., and Thompson, E. W., The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell Biol., 172, 973–981 (2006).
Liu, R. and Choi, J., Age-associated decline in gammaglutamylcysteine synthetase gene expression in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 28, 566–574 (2000).
McMahon, M., Itoh, K., Yamamoto, M., and Hayes, J. D., Keap1-dependent proteasomal degradation of transcription factor Nrf2 contributes to the negative regulation of antioxidant response element-driven gene expression. J. Biol. Chem., 278, 21592–21600 (2003).
Mezzano, S. A., Ruiz-Ortega, M., and Egido, J., Angiotensin II and renal fibrosis. Hypertension, 38, 635–638 (2001).
Onozato, M. L., Tojo, A., Kobayashi, N., Goto, A., Matsuoka, H., and Fujita, T., Dual blockade of aldosterone and angiotensin II additively suppresses TGF-b and NADPH oxidase in the hypertensive kidney. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant., 22, 1314–1322 (2007).
Rhyu, D. Y., Yang, Y., Ha, H., Lee, G. T., Song, J. S., Uh, S. T., and Lee, H. B., Role of reactive oxygen species in TGFbeta1-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 16, 667–675 (2005).
Takenaka, H., Kihara, Y., Iwanaga, Y., Onozawa, Y., Toyokuni, S., and Kita, T., Angiotensin II, oxidative stress, and extracellular matrix degradation during transition to LV failure in rats with hypertension. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 41, 989–997 (2006).
Touyz, R. M., Yao, G., Quinn, M. T., Pagano, P. J., and Schiffrin, E. L., p47phox associates with the cytoskeleton through cortactin in human vascular smooth muscle cells: Role in NAD(P)H oxidase regulation by angiotensin II. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 25, 512–518 (2005).
Tsai, M. K., Lin, Y. L., and Huang, Y. T., Effects of salvianolic acids on oxidative stress and hepatic fibrosis in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 242, 155–164 (2010).
Uejima, Y., Fukuchi, Y., Teramoto, S., Tabata, R., and Orimo, H., Age changes in visceral content of glutathione in the senescence accelerated mouse (SAM). Mech. Ageing Dev., 67, 129–139 (1993).
Ushio-Fukai, M., Zafari, A. M., Fukui, T., Ishizaka, N., and Griendling, K. K., p22phox is a critical component of the superoxide-generating NADH/NADPH oxidase system and regulates angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem., 271, 23317–23321 (1996).
Wynn, T. A., Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol., 214, 199–210 (2008).
Yang, J. and Liu, Y., Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol., 159, 1465–1475 (2001).
Zhao, W., Chen, S. S., Chen, Y., Ahokas, R. A., and Sun, Y., Kidney fibrosis in hypertensive rats: role of oxidative stress. Am. J. Nephrol., 28, 548–554 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S.J., You, A. & Kwak, MK. Suppression of Nrf2 signaling by angiotensin II in murine renal epithelial cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 829–836 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0517-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0517-1