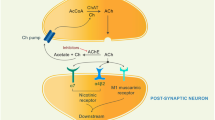
Abstract
The average human life span in developed countries has increased to more than 80 years following rapid breakthrough and developments in modern medicine and science, resulting in prolonged life expectancy and increase in the population counts of the geriatric age group. This translates into a dramatic increase in disease burden of elderly patients suffering from senile disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer’s disease (AD). AD is characterized by the death of nerve cells in the cerebral cortex and is the most common subtype of dementia that affected 25 million people worldwide in 2000 and is expected to increase to 114 million by 2050. Despite the exponential growth in the number of AD patients, only acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors are being currently used to treat AD. It is well known that AChE inhibitors can alleviate the symptoms of AD but not halt the disease progression. Consequently, therapeutic agents against AD acting at various pathologic levels are needed. In the recent decade, natural products with anti-AD properties have attracted much attention. But very few natural products have been investigated in a scientifically justifiable method for these biological activities. Following a detailed research process, it is certain that natural products have a strong potential to develop biologically active compounds with new chemical structures. Many studies have been carried out to identify the naturally occurring anti-AD agents. This review article describes the molecular targets aiming at developing the anti-AD agents including the inhibition of AChE, inhibition of Aβ production by enhancing α-secretase (non-amyloidogenic pathway) or inhibiting β- and γ-secretases (amyloidogenic pathway), alleviating Aβ-induced neurotoxicity or reducing Aβ-induced neuroinflammation. In addition, this paper summarizes the potential of some of the natural products that might inhibit specific molecular targets and slow the progression of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramov, A. Y., Canevari, L., and Duchen, M. R., Changes in intracellular calcium and glutathione in astrocytes as the primary mechanism of amyloid neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci., 23, 5088–5095 (2003).
Ahmad, A., Khan, K. A., Ahmad, V. U., and Qazi, S., Antibacterial Activity of Juliflorine Isolated from Prosopis juliflora. Planta Med., 52, 285–288 (1986).
Anderson, J. J., Holtz, G., Baskin, P. P., Turner, M., Rowe, B., Wang, B., Kounnas, M. Z., Lamb, B. T., Barten, D., Felsenstein, K., McDonald, I., Srinivasan, K., Munoz, B., Wagner, S. L., Reductions in beta-amyloid concentrations in vivo by the gamma-secretase inhibitors BMS-289948 and BMS-299897. Biochem. Pharmacol., 69, 689–698 (2005).
Ansari, M. A. and Scheff, S. W., Oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer disease in the frontal cortex. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 69, 155–167 (2010).
Barrow, C. J. and Zagorski, M. G., Solution structures of beta peptide and its constituent fragments: relation to amyloid deposition. Science, 253, 179–182 (1991).
Bastianetto, S., Ramassamy, C., Dore, S., Christen, Y., Poirier, J., and Quirion, R., The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by beta-amyloid. Eur. J. Neurosci., 12, 1882–1890 (2000a).
Bastianetto, S., Zheng, W. H., and Quirion, R., Neuroprotective abilities of resveratrol and other red wine constituents against nitric oxide-related toxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol., 131, 711–720 (2000b).
Benzi, G. and Moretti, A., Are reactive oxygen species involved in Alzheimer’s disease? Neurobiol. Aging, 16, 661–674 (1995).
Block, M. L. and Hong, J. S., Microglia and inflammationmediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog. Neurobiol., 76, 77–98 (2005).
Block, M. L., Zecca, L., and Hong, J. S., Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 8, 57–69 (2007).
Blumenthal, M., Asian ginseng: potential therapeutic uses. Adv. Nurse Pract., 9, 26–28, 33 (2001).
Borek, C., Garlic reduces dementia and heart-disease risk. J. Nutr., 136, 810S–812S (2006).
Brinker, A. M., Ma, J., Lipsky, P. E., and Raskin, I., Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium (Celastraceae). Phytochemistry, 68, 732–766 (2007).
Busciglio, J., Lorenzo, A., Yeh, J., and Yankner, B. A., betaamyloid fibrils induce tau phosphorylation and loss of microtubule binding. Neuron, 14, 879–888 (1995).
Cao, X. and Sudhof, T. C., Dissection of amyloid-beta precursor protein-dependent transcriptional transactivation. J. Biol. Chem., 279, 24601–24611 (2004).
Catalan, J., Moriguchi, T., Slotnick, B., Murthy, M., Greiner, R. S., and Salem, N., Jr., Cognitive deficits in docosahexaenoic acid-deficient rats. Behav. Neurosci., 116, 1022–1031 (2002).
Chang, Y. L., Shen, J. J., Wung, B. S., Cheng, J. J., and Wang, D. L., Chinese herbal remedy wogonin inhibits monocyte chemotactic protein-1 gene expression in human endothelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol., 60, 507–513 (2001).
Chauhan, N. B., Effect of aged garlic extract on APP processing and tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s transgenic model Tg2576. J. Ethnopharmacol., 108, 385–394 (2006).
Chauhan, N. B. and Sandoval, J., Amelioration of early cognitive deficits by aged garlic extract in Alzheimer’s transgenic mice. Phytother. Res., 21, 629–640 (2007).
Choi, S. H., Hur, J. M., Yang, E. J., Jun, M., Park, H. J., Lee, K. B., Moon, E., and Song, K. S., Beta-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors from Perilla frutescens var. acuta. Arch. Pharm. Res., 31, 183–187 (2008a).
Choi, Y. H., Yon, G. H., Hong, K. S., Yoo, D. S., Choi, C. W., Park, W. K., Kong, J. Y., Kim, Y. S., and Ryu, S. Y., In vitro BACE-1 inhibitory phenolic components from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. Planta Med., 74, 1405–1408 (2008b).
Choi, Y. H., Yoo, M. Y., Choi, C. W., Cha, M. R., Yon, G. H., Kwon, D. Y., Kim, Y. S., Park, W. K., and Ryu, S. Y., A new specific BACE-1 inhibitor from the stembark extract of Vitis vinifera. Planta Med., 75, 537–540 (2009).
Chou, T. C., Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol., 139, 1146–1152 (2003).
Choudhary, M. I., Nawaz, S. A., ul-Haq, Z., Lodhi, M. A., Ghayur, M. N., Jalil, S., Riaz, N., Yousuf, S., Malik, A., Gilani, A. H., and ur-Rahman, A., Withanolides, a new class of natural cholinesterase inhibitors with calcium antagonistic properties. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 334, 276–287 (2005a).
Choudhary, M. I., Nawaz, S. A., Zaheerul, H., Azim, M. K., Ghayur, M. N., Lodhi, M. A., Jalil, S., Khalid, A., Ahmed, A., Rode, B. M., Attaur, R., Gilani, A. U., and Ahmad, V. U., Juliflorine: a potent natural peripheral anionic-sitebinding inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase with calciumchannel blocking potential, a leading candidate for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 332, 1171–1177 (2005b).
Colciaghi, F., Borroni, B., Zimmermann, M., Bellone, C., Longhi, A., Padovani, A., Cattabeni, F., Christen, Y., and Di Luca, M., Amyloid precursor protein metabolism is regulated toward alpha-secretase pathway by Ginkgo biloba extracts. Neurobiol. Dis., 16, 454–460 (2004).
Cummings, J. L., Vinters, H. V., Cole, G. M., and Khachaturian, Z. S., Alzheimer’s disease: etiologies, pathophysiology, cognitive reserve, and treatment opportunities. Neurology, 51, S2–17; discussion S65-17 (1998).
Dinamarca, M. C., Cerpa, W., Garrido, J., Hancke, J. L., and Inestrosa, N. C., Hyperforin prevents beta-amyloid neurotoxicity and spatial memory impairments by disaggregation of Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta-deposits. Mol. Psychiatry, 11, 1032–1048 (2006).
Dovey, H. F., John, V., Anderson, J. P., Chen, L. Z., de Saint Andrieu, P., Fang, L. Y., Freedman, S. B., Folmer, B., Goldbach, E., Holsztynska, E. J., Hu, K. L., Johnson-Wood, K. L., Kennedy, S. L., Kholodenko, D., Knops, J. E., Latimer, L. H., Lee, M., Liao, Z., Lieberburg, I. M., Motter, R. N., Mutter, L. C., Nietz, J., Quinn, K. P., Sacchi, K. L., Seubert, P. A., Shopp, G. M., Thorsett, E. D., Tung, J. S., Wu, J., Yang, S., Yin, C. T., Schenk, D. B., May, P. C., Altstiel, L. D., Bender, M. H., Boggs, L. N., Britton, T. C., Clemens, J. C., Czilli, D. L., Dieckman-McGinty, D. K., Droste, J. J., Fuson, K. S., Gitter, B. D., Hyslop, P. A., Johnstone, E. M., Li, W. Y., Little, S. P., Mabry, T. E., Miller, F. D., and Audia, J. E., Functional gamma-secretase inhibitors reduce beta-amyloid peptide levels in brain. J. Neurochem., 76, 173–181 (2001).
Drew, P. D., Storer, P. D., Xu, J., and Chavis, J. A., Hormone regulation of microglial cell activation: relevance to multiple sclerosis. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev., 48, 322–327 (2005).
Drieu, K., Preparation and definition of Ginkgo biloba extract. Presse Med., 15, 1455–1457 (1986).
Durairajan, S. S., Yuan, Q., Xie, L., Chan, W. S., Kum, W. F., Koo, I., Liu, C., Song, Y., Huang, J. D., Klein, W. L., and Li, M., Salvianolic acid B inhibits Abeta fibril formation and disaggregates preformed fibrils and protects against Abeta-induced cytotoxicty. Neurochem. Int., 52, 741–750 (2008).
Esch, F. S., Keim, P. S., Beattie, E. C., Blacher, R. W., Culwell, A. R., Oltersdorf, T., McClure, D., and Ward, P. J., Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science, 248, 1122–1124 (1990).
Ferris, S., Ihl, R., Robert, P., Winblad, B., Gatz, G., Tennigkeit, F., and Gauthier, S., Treatment effects of Memantine on language in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease patients. Alzheimers Dement., 5, 369–374 (2009).
Francis, P. T., Palmer, A. M., Snape, M., and Wilcock, G. K., The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a review of progress. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr., 66, 137–147 (1999).
Fujiwara, H., Iwasaki, K., Furukawa, K., Seki, T., He, M., Maruyama, M., Tomita, N., Kudo, Y., Higuchi, M., Saido, T. C., Maeda, S., Takashima, A., Hara, M., Ohizumi, Y., and Arai, H., Uncaria rhynchophylla, a Chinese medicinal herb, has potent antiaggregation effects on Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid proteins. J. Neurosci. Res., 84, 427–433 (2006).
Fujiwara, H., Tabuchi, M., Yamaguchi, T., Iwasaki, K., Furukawa, K., Sekiguchi, K., Ikarashi, Y., Kudo, Y., Higuchi, M., Saido, T. C., Maeda, S., Takashima, A., Hara, M., Yaegashi, N., Kase, Y., and Arai, H., A traditional medicinal herb Paeonia suffruticosa and its active constituent 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucopyranose have potent anti-aggregation effects on Alzheimer’s amyloid beta proteins in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurochem., 109, 1648–1657 (2009).
Ganguli, M., Chandra, V., Kamboh, M. I., Johnston, J. M., Dodge, H. H., Thelma, B. K., Juyal, R. C., Pandav, R., Belle, S. H., and DeKosky, S. T., Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer disease: The Indo-US Cross-National Dementia Study. Arch. Neurol., 57, 824–830 (2000).
Gao, Y. G., Song, Y. M., Yang, Y. Y., Liu, W. F., and Tang, J. X., [Pharmacology of tanshinone (author’s transl)]. Yao Xue Xue Bao, 14, 75–82 (1979).
Giunta, B., Hou, H., Zhu, Y., Salemi, J., Ruscin, A., Shytle, R. D., and Tan, J., Fish oil enhances anti-amyloidogenic properties of green tea EGCG in Tg2576 mice. Neurosci. Lett., 471, 134–138 (2010).
Gong, Y., Xue, B., Jiao, J., Jing, L., and Wang, X., Triptolide inhibits COX-2 expression and PGE2 release by suppressing the activity of NF-kappaB and JNK in LPS-treated microglia. J. Neurochem., 107, 779–788 (2008).
Gonzalez-Scarano, F. and Baltuch, G., Microglia as mediators of inflammatory and degenerative diseases. Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 22, 219–240 (1999).
Greenberg, S. M. and Kosik, K. S., Secreted beta-APP stimulates MAP kinase and phosphorylation of tau in neurons. Neurobiol. Aging, 16, 403–407; discussion 407–408 (1995).
Gupta, V. B., Indi, S. S., and Rao, K. S., Garlic extract exhibits antiamyloidogenic activity on amyloid-beta fibrillogenesis: relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Phytother. Res., 23, 111–115 (2009).
Hanisch, U. K., Microglia as a source and target of cytokines. Glia, 40, 140–155 (2002).
Hebert, L. E., Scherr, P. A., Bienias, J. L., Bennett, D. A., and Evans, D. A., Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Arch. Neurol., 60, 1119–1122 (2003).
Heneka, M. T. and O’Banion, M. K., Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol., 184, 69–91 (2007).
Hsieh, L. T., Yang, H. H., and Chen, H. W., Ambient BTEX and MTBE in the neighborhoods of different industrial parks in Southern Taiwan. J. Hazard. Mater., 128, 106–115 (2006).
Ikemoto, A., Ohishi, M., Sato, Y., Hata, N., Misawa, Y., Fujii, Y., and Okuyama, H., Reversibility of n-3 fatty acid deficiency-induced alterations of learning behavior in the rat: level of n-6 fatty acids as another critical factor. J. Lipid Res., 42, 1655–1663 (2001).
Iqbal, K., Liu, F., Gong, C. X., Alonso Adel, C., and Grundke-Iqbal, I., Mechanisms of tau-induced neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol., 118, 53–69 (2009).
Jeon, S. Y., Bae, K., Seong, Y. H., and Song, K. S., Green tea catechins as a BACE1 (beta-secretase) inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 13, 3905–3908 (2003).
Jeon, S. Y., Kwon, S. H., Seong, Y. H., Bae, K., Hur, J. M., Lee, Y. Y., Suh, D. Y., and Song, K. S., Beta-secretase (BACE1)-inhibiting stilbenoids from Smilax Rhizoma. Phytomedicine, 14, 403–408 (2007).
Ji, Z. N., Dong, T. T., Ye, W. C., Choi, R. C., Lo, C. K., and Tsim, K. W., Ginsenoside Re attenuate beta-amyloid and serum-free induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol., 107, 48–52 (2006).
Jia, H., Jiang, Y., Ruan, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, X., Zhang, J., Beyreuther, K., Tu, P., and Zhang, D., Tenuigenin treatment decreases secretion of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-protein in cultured cells. Neurosci. Lett., 367, 123–128 (2004).
Jin, C. Y., Lee, J. D., Park, C., Choi, Y. H., and Kim, G. Y., Curcumin attenuates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 28, 1645–1651 (2007).
Jung, H. A., Min, B. S., Yokozawa, T., Lee, J. H., Kim, Y. S., and Choi, J. S., Anti-Alzheimer and antioxidant activities of Coptidis Rhizoma alkaloids. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 32, 1433–1438 (2009).
Kalmijn, S., van Boxtel, M. P., Ocke, M., Verschuren, W. M., Kromhout, D., and Launer, L. J., Dietary intake of fatty acids and fish in relation to cognitive performance at middle age. Neurology, 62, 275–280 (2004).
Kang, G., Kong, P. J., Yuh, Y. J., Lim, S. Y., Yim, S. V., Chun, W., and Kim, S. S., Curcumin suppresses lipopolysaccharideinduced cyclooxygenase-2 expression by inhibiting activator protein 1 and nuclear factor kappab bindings in BV2 microglial cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci., 94, 325–328 (2004).
Kelloff, G. J., Crowell, J. A., Steele, V. E., Lubet, R. A., Malone, W. A., Boone, C. W., Kopelovich, L., Hawk, E. T., Lieberman, R., Lawrence, J. A., Ali, I., Viner, J. L., and Sigman, C. C., Progress in cancer chemoprevention: development of diet-derived chemopreventive agents. J. Nutr., 130, 467S–471S (2000).
Kim, D. H., Jeon, S. J., Jung, J. W., Lee, S., Yoon, B. H., Shin, B. Y., Son, K. H., Cheong, J. H., Kim, Y. S., Kang, S. S., Ko, K. H., and Ryu, J. H., Tanshinone congeners improve memory impairments induced by scopolamine on passive avoidance tasks in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 574, 140–147 (2007).
Kim, H., Kim, Y. S., Kim, S. Y., and Suk, K., The plant flavonoid wogonin suppresses death of activated C6 rat glial cells by inhibiting nitric oxide production. Neurosci. Lett., 309, 67–71 (2001).
Kimura, Y., Matsushita, N., Yokoi-Hayashi, K., and Okuda, H., Effects of baicalein isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis Radix on adhesion molecule expression induced by thrombin and thrombin receptor agonist peptide in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Planta Med., 67, 331–334 (2001).
Klein, W. L., Krafft, G. A., and Finch, C. E., Targeting small Abeta oligomers: the solution to an Alzheimer’s disease conundrum? Trends Neurosci., 24, 219–224 (2001).
Kuboyama, T., Tohda, C., and Komatsu, K., Neuritic regeneration and synaptic reconstruction induced by withanolide A. Br. J. Pharmacol., 144, 961–971 (2005).
Lanz, T. A., Hosley, J. D., Adams, W. J., and Merchant, K. M., Studies of Abeta pharmacodynamics in the brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma in young (plaque-free) Tg2576 mice using the gamma-secretase inhibitor N2-[(2S)-2-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxyethanoyl]-N1-[(7S)-5-methyl-6-oxo -6,7-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,d]azepin-7-yl]-L-alaninamide (LY-411575). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 309, 49–55 (2004).
Lee, H., Kim, Y. O., Kim, H., Kim, S. Y., Noh, H. S., Kang, S. S., Cho, G. J., Choi, W. S., and Suk, K., Flavonoid wogonin from medicinal herb is neuroprotective by inhibiting inflammatory activation of microglia. FASEB J., 17, 1943–1944 (2003).
Lee, H. S., Jung, K. K., Cho, J. Y., Rhee, M. H., Hong, S., Kwon, M., Kim, S. H., and Kang, S. Y., Neuroprotective effect of curcumin is mainly mediated by blockade of microglial cell activation. Pharmazie, 62, 937–942 (2007).
Lee, J. W., Lee, Y. K., Ban, J. O., Ha, T. Y., Yun, Y. P., Han, S. B., Oh, K. W., and Hong, J. T., Green tea (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits beta-amyloid-induced cognitive dysfunction through modification of secretase activity via inhibition of ERK and NF-kappaB pathways in mice. J. Nutr., 139, 1987–1993 (2009).
Lee, J. W., Lee, Y. K., Lee, B. J., Nam, S. Y., Lee, S. I., Kim, Y. H., Kim, K. H., Oh, K. W., and Hong, J. T., Inhibitory effect of ethanol extract of Magnolia officinalis and 4-Omethylhonokiol on memory impairment and neuronal toxicity induced by beta-amyloid. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 95, 31–40 (2010).
Lesne, S. and Kotilinek, L., Amyloid plaques and amyloidbeta oligomers: an ongoing debate. J. Neurosci., 25, 9319–9320 (2005).
Letenneur, L., Dartigues, J. F., and Orgogozo, J. M., Wine consumption in the elderly. Ann. Intern. Med., 118, 317–318 (1993).
Li, F. Q., Wang, T., Pei, Z., Liu, B., and Hong, J. S., Inhibition of microglial activation by the herbal flavonoid baicalein attenuates inflammation-mediated degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. J. Neural Transm., 112, 331–347 (2005).
Li, L., Tsai, H. J., and Wang, X. M., Icariin inhibits the increased inward calcium currents induced by amyloidbeta( 25–35) peptide in CA1 pyramidal neurons of neonatal rat hippocampal slice. Am. J. Chin. Med., 38, 113–125 (2010).
Li, N., Liu, B., Dluzen, D. E., and Jin, Y., Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg2 against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol., 111, 458–463 (2007).
Li, Q., Zhao, H. F., Zhang, Z. F., Liu, Z. G., Pei, X. R., Wang, J. B., and Li, Y., Long-term green tea catechin administration prevents spatial learning and memory impairment in senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 mice by decreasing Abeta1–42 oligomers and upregulating synaptic plasticity-related proteins in the hippocampus. Neuroscience, 163, 741–749 (2009).
Lim, G. P., Chu, T., Yang, F., Beech, W., Frautschy, S. A., and Cole, G. M., The curry spice curcumin reduces oxidative damage and amyloid pathology in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse. J. Neurosci., 21, 8370–8377 (2001).
Lim, G. P., Calon, F., Morihara, T., Yang, F., Teter, B., Ubeda, O., Salem, N., Jr., Frautschy, S. A., and Cole, G. M., A diet enriched with the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid burden in an aged Alzheimer mouse model. J. Neurosci., 25, 3032–3040 (2005).
Lim, J. Y., Won, T. J., Hwang, B. Y., Kim, H. R., Hwang, K. W., Sul, D., and Park, S. Y., The new diterpene isodojaponin D inhibited LPS-induced microglial activation through NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 642, 10–18 (2010).
Lin, H. C., Ding, H. Y., Ko, F. N., Teng, C. M., and Wu, Y. C., Aggregation inhibitory activity of minor acetophenones from Paeonia species. Planta Med., 65, 595–599 (1999).
Lin, L. C., Wang, M. N., Tseng, T. Y., Sung, J. S., and Tsai, T. H., Pharmacokinetics of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in conscious and freely moving rats and its brain regional distribution. J. Agric. Food Chem., 55, 1517–1524 (2007).
Lin, Y. H., Liu, A. H., Wu, H. L., Westenbroek, C., Song, Q. L., Yu, H. M., Ter Horst, G. J., and Li, X. J., Salvianolic acid B, an antioxidant from Salvia miltiorrhiza, prevents Abeta(25–35)-induced reduction in BPRP in PC12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 348, 593–599 (2006).
Lipton, S. A., Pathologically-activated therapeutics for neuroprotection: mechanism of NMDA receptor block by memantine and S-nitrosylation. Curr. Drug Targets, 8, 621–632 (2007).
Lleo, A., Greenberg, S. M., and Growdon, J. H., Current pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Med., 57, 513–533 (2006).
Lue, L. F., Kuo, Y. M., Roher, A. E., Brachova, L., Shen, Y., Sue, L., Beach, T., Kurth, J. H., Rydel, R. E., and Rogers, J., Soluble amyloid beta peptide concentration as a predictor of synaptic change in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol., 155, 853–862 (1999).
Lv, J., Jia, H., Jiang, Y., Ruan, Y., Liu, Z., Yue, W., Beyreuther, K., Tu, P., and Zhang, D., Tenuifolin, an extract derived from tenuigenin, inhibits amyloid-beta secretion in vitro. Acta Physiol. (Oxf), 196, 419–425 (2009).
Marco, L. and do Carmo Carreiras, M., Galanthamine, a natural product for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov., 1, 105–111 (2006).
Marumoto, S. and Miyazawa, M., beta-secretase inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica. Phytother. Res., 24, 510–513 (2010).
Mecocci, P., Bladstrom, A., and Stender, K., Effects of memantine on cognition in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: post-hoc analyses of ADAScog and SIB total and single-item scores from six randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry, 24, 532–538 (2009).
Mei, Z., Zhang, F., Tao, L., Zheng, W., Cao, Y., Wang, Z., Tang, S., Le, K., Chen, S., Pi, R., and Liu, P., Cryptotanshinone, a compound from Salvia miltiorrhiza modulates amyloid precursor protein metabolism and attenuates beta-amyloid deposition through upregulating alphasecretase in vivo and in vitro. Neurosci. Lett., 452, 90–95 (2009).
Minghetti, L. and Levi, G., Microglia as effector cells in brain damage and repair: focus on prostanoids and nitric oxide. Prog. Neurobiol., 54, 99–125 (1998).
Montine, T. J., Neely, M. D., Quinn, J. F., Beal, M. F., Markesbery, W. R., Roberts, L. J., and Morrow, J. D., Lipid peroxidation in aging brain and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 33, 620–626 (2002).
Morris, M. C., Evans, D. A., Bienias, J. L., Tangney, C. C., Bennett, D. A., Wilson, R. S., Aggarwal, N., and Schneider, J., Consumption of fish and n-3 fatty acids and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol., 60, 940–946 (2003).
Newman, D. J. and Cragg, G. M., Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod., 70, 461–477 (2007).
Nunan, J. and Small, D. H., Regulation of APP cleavage by alpha-, beta- and gamma-secretases. FEBS Lett., 483, 6–10 (2000).
Oberpichler, H., Beck, T., Abdel-Rahman, M. M., Bielenberg, G. W., and Krieglstein, J., Effects of Ginkgo biloba constituents related to protection against brain damage caused by hypoxia. Pharmacol. Res. Commun., 20, 349–368 (1988).
Ono, K., Hasegawa, K., Naiki, H., and Yamada, M., Antiamyloidogenic activity of tannic acid and its activity to destabilize Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid fibrils in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1690, 193–202 (2004a).
Ono, K., Hasegawa, K., Naiki, H., and Yamada, M., Curcumin has potent anti-amyloidogenic effects for Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid fibrils in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res., 75, 742–750 (2004b).
Orgogozo, J. M., Dartigues, J. F., Lafont, S., Letenneur, L., Commenges, D., Salamon, R., Renaud, S., and Breteler, M. B., Wine consumption and dementia in the elderly: a prospective community study in the Bordeaux area. Rev. Neurol. (Paris), 153, 185–192 (1997).
Ortega, M. G., Agnese, A. M., and Cabrera, J. L., Anticholinesterase activity in an alkaloid extract of Huperzia saururus. Phytomedicine, 11, 539–543 (2004).
Panegyres, P. K., The functions of the amyloid precursor protein gene. Rev. Neurosci., 12, 1–39 (2001).
Park, B. K., Heo, M. Y., Park, H., and Kim, H. P., Inhibition of TPA-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and skin inflammation in mice by wogonin, a plant flavone from Scutellaria radix. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 425, 153–157 (2001).
Park, C. H., Choi, S. H., Koo, J. W., Seo, J. H., Kim, H. S., Jeong, S. J., and Suh, Y. H., Novel cognitive improving and neuroprotective activities of Polygala tenuifolia Willdenow extract, BT-11. J. Neurosci. Res., 70, 484–492 (2002).
Park, E. K., Choo, M. K., Oh, J. K., Ryu, J. H., and Kim, D. H., Ginsenoside Rh2 reduces ischemic brain injury in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 27, 433–436 (2004).
Park, J. S., Park, E. M., Kim, D. H., Jung, K., Jung, J. S., Lee, E. J., Hyun, J. W., Kang, J. L., and Kim, H. S., Antiinflammatory mechanism of ginseng saponins in activated microglia. J. Neuroimmunol., 209, 40–49 (2009).
Park, S. Y., Kim, H. S., Cho, E. K., Kwon, B. Y., Phark, S., Hwang, K. W., and Sul, D., Curcumin protected PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity through the inhibition of oxidative damage and tau hyperphosphorylation. Food Chem. Toxicol., 46, 2881–2887 (2008).
Park, S. Y., Neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of isorosmanol. Z. Naturforsch. C, 64, 395–398 (2009).
Park, S. Y., Lim, J. Y., Jeong, W., Hong, S. S., Yang, Y. T., Hwang, B. Y., and Lee, D., C-methylflavonoids isolated from Callistemon lanceolatus protect PC12 cells against Abeta-induced toxicity. Planta Med., 76, 863–868 (2010).
Peng, Y., Xing, C., Lemere, C. A., Chen, G., Wang, L., Feng, Y., and Wang, X., l-3-n-Butylphthalide ameliorates betaamyloid-induced neuronal toxicity in cultured neuronal cells. Neurosci. Lett., 434, 224–229 (2008).
Peng, Y., Xing, C., Xu, S., Lemere, C. A., Chen, G., Liu, B., Wang, L., Feng, Y., and Wang, X., L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment induced by intracerebroventricular infusion of amyloid-beta peptide in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 621, 38–45 (2009).
Peng, Y., Sun, J., Hon, S., Nylander, A. N., Xia, W., Feng, Y., Wang, X., and Lemere, C. A., L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment and reduces amyloid-beta in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci., 30, 8180–8189 (2010).
Pike, C. J., Ramezan-Arab, N., and Cotman, C. W., Betaamyloid neurotoxicity in vitro: evidence of oxidative stress but not protection by antioxidants. J. Neurochem., 69, 1601–1611 (1997).
Qian, Y. H., Han, H., Hu, X. D., and Shi, L. L., Protective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on beta-amyloid protein(1–42)-induced neurotoxicity in cortical neurons. Neurol. Res., 31, 663–667 (2009).
Qiu, D. and Kao, P. N., Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of triptolide, the principal active diterpenoid from the Chinese medicinal herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. Drugs R D, 4, 1–18 (2003).
Radad, K., Gille, G., Liu, L., and Rausch, W. D., Use of ginseng in medicine with emphasis on neurodegenerative disorders. J. Pharmacol. Sci., 100, 175–186 (2006).
Rai, G. S., Shovlin, C., and Wesnes, K. A., A double-blind, placebo controlled study of Ginkgo biloba extract (’tanakan’) in elderly outpatients with mild to moderate memory impairment. Curr. Med. Res. Opin., 12, 350–355 (1991).
Rank, K. B., Pauley, A. M., Bhattacharya, K., Wang, Z., Evans, D. B., Fleck, T. J., Johnston, J. A., and Sharma, S. K., Direct interaction of soluble human recombinant tau protein with Abeta 1–42 results in tau aggregation and hyperphosphorylation by tau protein kinase II. FEBS Lett., 514, 263–268 (2002).
Rapoport, M., Dawson, H. N., Binder, L. I., Vitek, M. P., and Ferreira, A., Tau is essential to beta -amyloid-induced neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 99, 6364–6369 (2002).
Rezai-Zadeh, K., Shytle, D., Sun, N., Mori, T., Hou, H., Jeanniton, D., Ehrhart, J., Townsend, K., Zeng, J., Morgan, D., Hardy, J., Town, T., and Tan, J., Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) modulates amyloid precursor protein cleavage and reduces cerebral amyloidosis in Alzheimer transgenic mice. J. Neurosci., 25, 8807–8814 (2005).
Rezai-Zadeh, K., Arendash, G. W., Hou, H., Fernandez, F., Jensen, M., Runfeldt, M., Shytle, R. D., and Tan, J., Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces betaamyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice. Brain Res., 1214, 177–187 (2008).
Roberson, E. D. and Mucke, L., 100 years and counting: prospects for defeating Alzheimer’s disease. Science, 314, 781–784 (2006).
Roberson, E. D., Scearce-Levie, K., Palop, J. J., Yan, F., Cheng, I. H., Wu, T., Gerstein, H., Yu, G. Q., and Mucke, L., Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid betainduced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Science, 316, 750–754 (2007).
Rojo, L. E., Fernandez, J. A., Maccioni, A. A., Jimenez, J. M., and Maccioni, R. B., Neuroinflammation: implications for the pathogenesis and molecular diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Med. Res., 39, 1–16 (2008).
Rosen, D. R., Martin-Morris, L., Luo, L. Q., and White, K., A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human beta-amyloid protein precursor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 86, 2478–2482 (1989).
Rovira, C., Arbez, N., and Mariani, J., Abeta(25–35) and Abeta(1–40) act on different calcium channels in CA1 hippocampal neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 296, 1317–1321 (2002).
Rudakewich, M., Ba, F., and Benishin, C. G., Neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions of ginsenosides Rb(1) and Rg(1). Planta Med., 67, 533–537 (2001).
Selkoe, D. J., The cell biology of beta-amyloid precursor protein and presenilin in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Cell Biol., 8, 447–453 (1998).
Selkoe, D. J., Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev., 81, 741–766 (2001).
Selkoe, D. J., Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science, 298, 789–791 (2002).
Seubert, P., Oltersdorf, T., Lee, M. G., Barbour, R., Blomquist, C., Davis, D. L., Bryant, K., Fritz, L. C., Galasko, D., and Thal, L. J., Secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein cleaved at the amino terminus of the beta-amyloid peptide. Nature, 361, 260–263 (1993).
Sha, D., Li, L., Ye, L., Liu, R., and Xu, Y., Icariin inhibits neurotoxicity of beta-amyloid by upregulating cocaine-regulated and amphetamine-regulated transcripts. Neuroreport, 20, 1564–1567 (2009).
Shi, C., Zhao, L., Zhu, B., Li, Q., Yew, D. T., Yao, Z., and Xu, J., Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) and its constituents quercetin and ginkgolide B against beta-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem. Biol. Interact., 181, 115–123 (2009).
Shimada, Y., Goto, H., Itoh, T., Sakakibara, I., Kubo, M., Sasaki, H., and Terasawa, K., Evaluation of the protective effects of alkaloids isolated from the hooks and stems of Uncaria sinensis on glutamate-induced neuronal death in cultured cerebellar granule cells from rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 51, 715–722 (1999).
Shytle, R. D., Bickford, P. C., Rezai-zadeh, K., Hou, L., Zeng, J., Tan, J., Sanberg, P. R., Sanberg, C. D., Roschek, B., Jr., Fink, R. C., and Alberte, R. S., Optimized turmeric extracts have potent anti-amyloidogenic effects. Curr. Alzheimer Res., 6, 564–571 (2009).
Smith, W. W., Gorospe, M., and Kusiak, J. W., Signaling mechanisms underlying Abeta toxicity: potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets, 5, 355–361 (2006).
Sonkusare, S. K., Kaul, C. L., and Ramarao, P., Dementia of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders-memantine, a new hope. Pharmacol. Res., 51, 1–17 (2005).
Sramek, J. J., Frackiewicz, E. J., and Cutler, N. R., Review of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor galanthamine. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs, 9, 2393–2402 (2000).
Sreejayan and Rao, M. N., Nitric oxide scavenging by curcuminoids. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 49, 105–107 (1997).
St George-Hyslop, P. H. and Petit, A., Molecular biology and genetics of Alzheimer’s disease. C. R. Biol., 328, 119–130 (2005).
Suk, K., Lee, H., Kang, S. S., Cho, G. J., and Choi, W. S., Flavonoid baicalein attenuates activation-induced cell death of brain microglia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 305, 638–645 (2003).
Szabo, M. E., Droy-Lefaix, M. T., and Doly, M., Direct measurement of free radicals in ischemic/reperfused diabetic rat retina. Clin. Neurosci., 4, 240–245 (1997).
Takahashi, Y., Fuwa, H., Kaneko, A., Sasaki, M., Yokoshima, S., Koizumi, H., Takebe, T., Kan, T., Iwatsubo, T., Tomita, T., Natsugari, H., and Fukuyama, T., Novel gamma-secretase inhibitors discovered by library screening of in-house synthetic natural product intermediates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 16, 3813–3816 (2006).
Takashima, A., Honda, T., Yasutake, K., Michel, G., Murayama, O., Murayama, M., Ishiguro, K., and Yamaguchi, H., Activation of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta by amyloid beta peptide (25–35) enhances phosphorylation of tau in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Res., 31, 317–323 (1998).
Tanzi, R. E. and Bertram, L., Twenty years of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid hypothesis: a genetic perspective. Cell, 120, 545–555 (2005).
Tian, J., Fu, F., Geng, M., Jiang, Y., Yang, J., Jiang, W., Wang, C., and Liu, K., Neuroprotective effect of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 on cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Lett., 374, 92–97 (2005).
Tierney, M. C., Fisher, R. H., Lewis, A. J., Zorzitto, M. L., Snow, W. G., Reid, D. W., and Nieuwstraten, P., The NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer’s disease: a clinicopathologic study of 57 cases. Neurology, 38, 359–364 (1988).
Um, M. Y., Ahn, J. Y., Kim, S., Kim, M. K., and Ha, T. Y., Sesaminol glucosides protect beta-amyloid peptide-induced cognitive deficits in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 32, 1516–1520 (2009).
Van Marum, R. J., Current and future therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 22, 265–274 (2008).
Virgili, M. and Contestabile, A., Partial neuroprotection of in vivo excitotoxic brain damage by chronic administration of the red wine antioxidant agent, trans-resveratrol in rats. Neurosci. Lett., 281, 123–126 (2000).
Wakabayashi, I., Inhibitory effects of baicalein and wogonin on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in macrophages. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 84, 288–291 (1999).
Wallin, A. K., Blennow, K., Andreasen, N., and Minthon, L., CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: levels of betaamyloid, tau, phosphorylated tau relate to clinical symptoms and survival. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord., 21, 131–138 (2006).
Walsh, D. M. and Selkoe, D. J., A beta oligomers — a decade of discovery. J. Neurochem., 101, 1172–1184 (2007).
Wang, L. C., Wang, B., Ng, S. Y., and Lee, T. F., Effects of ginseng saponins on beta-amyloid-induced amnesia in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol., 103, 103–108 (2006a).
Wang, R., Zhang, H. Y., and Tang, X. C., Huperzine A attenuates cognitive dysfunction and neuronal degeneration caused by beta-amyloid protein-(1–40) in rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 421, 149–156 (2001).
Wang, R., Yan, H., and Tang, X. C., Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 27, 1–26 (2006b).
Wimo, A., Winblad, B., Aguero-Torres, H., and von Strauss, E., The magnitude of dementia occurrence in the world. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord., 17, 63–67 (2003).
Wirths, O., Multhaup, G., and Bayer, T. A., A modified betaamyloid hypothesis: intraneuronal accumulation of the beta-amyloid peptide—the first step of a fatal cascade. J. Neurochem., 91, 513–520 (2004).
Xiao, X. Q., Wang, R., Han, Y. F., and Tang, X. C., Protective effects of huperzine A on beta-amyloid (25–35) induced oxidative injury in rat pheochromocytoma cells. Neurosci. Lett., 286, 155–158 (2000).
Yan, H., Zhang, H. Y., and Tang, X. C., Involvement of M1-muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase in the effect of huperzine A on secretory amyloid precursor protein-alpha. Neuroreport, 18, 689–692 (2007).
Yan, R., Bienkowski, M. J., Shuck, M. E., Miao, H., Tory, M. C., Pauley, A. M., Brashier, J. R., Stratman, N. C., Mathews, W. R., Buhl, A. E., Carter, D. B., Tomasselli, A. G., Parodi, L. A., Heinrikson, R. L., and Gurney, M. E., Membraneanchored aspartyl protease with Alzheimer’s disease betasecretase activity. Nature, 402, 533–537 (1999).
Yurko-Mauro, K., Cognitive and cardiovascular benefits of docosahexaenoic acid in aging and cognitive decline. Curr. Alzheimer Res., 7, 190–196 (2010).
Zaveri, N. T., Green tea and its polyphenolic catechins: medicinal uses in cancer and noncancer applications. Life Sci., 78, 2073–2080 (2006).
Zhang, D., Zhang, Y., Liu, G., and Zhang, J., Dactylorhin B reduces toxic effects of beta-amyloid fragment (25–35) on neuron cells and isolated rat brain mitochondria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol., 374, 117–125 (2006).
Zhang, J., Cheng, Y., and Zhang, J. T., Protective effect of (−) clausenamide against neurotoxicity induced by okadaic acid and beta-amyloid peptide25–35. Yao Xue Xue Bao, 42, 935–942 (2007).
Zhao, B. L., Li, X. J., He, R. G., Cheng, S. J., and Xin, W. J., Scavenging effect of extracts of green tea and natural antioxidants on active oxygen radicals. Cell Biophys., 14, 175–185 (1989).
Zheng, W. H., Bastianetto, S., Mennicken, F., Ma, W., and Kar, S., Amyloid beta peptide induces tau phosphorylation and loss of cholinergic neurons in rat primary septal cultures. Neuroscience, 115, 201–211 (2002).
Zhou, H. F., Liu, X. Y., Niu, D. B., Li, F. Q., He, Q. H., and Wang, X. M., Triptolide protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-mediated damage induced by lipopolysaccharide intranigral injection. Neurobiol. Dis., 18, 441–449 (2005).
Zipp, F. and Aktas, O., The brain as a target of inflammation: common pathways link inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci., 29, 518–527 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SY. Potential therapeutic agents against Alzheimer’s disease from natural sources. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1589–1609 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1010-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-1010-y