Abstract
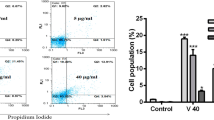
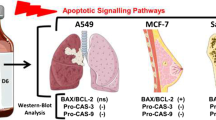
Snake venom toxin from Vipera lebetina turanica can induce apoptosis in many cancer cell lines, but there is no study about the apoptotic effect of snake venom toxin on human neuroblastoma cells. In this study, we investigated the apoptotic effect of snake venom toxin in human neuroblastoma SK-N-MC and SK-N-SH cells. Our result showed that cell detachment and apoptotic cell death were increased by snake venom toxin (1.25–10 µg/mL), but normal neuronal cells were not affected. Consistent with the induction of apoptosis, the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was increased, but mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was disrupted by treatment with snake venom toxin. However, the glutathione prevented snake venom toxin-induced cell growth inhibition. Snake venom toxin also increased the expression of pro-apoptotic protein Bax, but down-regulated anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Therefore, these results showed that snake venom toxin from Vipera lebetina turanica causes apoptotic cell death of neuroblastoma cells through ROS dependent MMP disruption, and suggested that snake venom toxin may be applicable as an anti-cancer agent for neuroblastoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ande, S. R., Kommoju, P. R., Draxl, S., Murkovic, M., Macheroux, P., Ghisla, S., and Ferrando-May, E., Mechanisms of cell death induction by L-amino acid oxidase, a major component of ophidian venom. Apoptosis, 11, 1439–1451 (2006).
Armstrong, J. S., Jones, D. P., Glutathione depletion enforces the mitochondrial permeability transition and causes cell death in Bcl-2 overexpressing HL60 cells. FASEB J., 16, 1263–1265 (2002).
Bennacef-Heffar N., Laraba-Djebari F., Evaluation of the effect of gamma rays on the venom of Vipera lebetina by biochemical study. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 81, 1110–1117 (2003).
Bertram, C. and Hass, R., Cellular responses to reactive oxygen species-induced DNA damage and aging. Biol. Chem., 389, 211–220 (2008).
Bras, M., Queenan, B., and Susin, S. A., Programmed cell death via mitochondria: different modes of dying. Biochemistry (Mosc)., 70, 231–239 (2005).
Cervia, D., Garcia-Gil, M., Simonetti, E., Di Giuseppe, G., Guella, G., Bagnoli, P., and Dini, F., Molecular mechanisms of euplotin C-induced apoptosis: involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and proteases. Apoptosis, 12, 1349–1363 (2007).
Choi, M. S., Yuk, D. Y., Oh, J. H., Jung, H. Y., Han, S. B., Moon, D. C., and Hong, J. T., Berberine inhibits human neuroblastoma cell growth through induction of p53-dependent apoptosis. Anticancer Res., 28, 3777–3784 (2008).
Combaret, V., Boyault, S., Iacono, I., Brejon, S., Rousseau, R., and Puisieux, A., Effect of bortezomib on human neuroblastoma: analysis of molecular mechanisms involved in cytotoxicity. Mol. Cancer, 7, 50 (2008).
Duan, H., Chai, J., Sheng, Z., Yao, Y., Yin, H., Liang, L., Shen, C., and Lin, J., Effect of burn injury on apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-related genes/proteins in skeletal muscles of rats. Apoptosis, 14, 52–65 (2009).
Galluzzi, L., Zamzami, N., de La Motte Rouge, T., Lemaire, C., Brenner, C., and Kroemer, G., Methods for the assessment of mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in apoptosis. Apoptosis, 12, 803–813 (2007).
Gasser, J. P., Hehl, M., Millward, T. A., A homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay for phosphatidylserine exposure on apoptotic cells. Anal. Biochem., 384, 49–55 (2009).
Ginkel, P. R., Sareen, D., Subramanian, L., Walker, Q., Darjatmoko, S. R., Lindstrom, M. J., Kulkarni, A., Albert, D. M., and Polans, A. S., Resveratrol inhibits tumor growth of human neuroblastoma and mediates apoptosis by directly targeting mitochondria. Clin. Cancer Res., 13, 5162–5169 (2007).
Gomes, A., Choudhury, S. R., Saha, A., Mishra, R., Giri, B., Biswas, A. K., Debnath, A., and Gomes, A., A heat stable protein toxin (drCT-I) from the Indian Viper (Daboia russelli russelli) venom having antiproliferative, cytotoxic and apoptotic activities. Toxicon, 49, 46–56 (2007).
Gustafsson, A. B. and Gottlieb, R. A., Bcl-2 family members and apoptosis, taken to heart. Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol., 292, 45–51 (2007).
Hengartner, M. O., The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature, 407, 770–777 (2000).
Henkels, K. M. and Turchi, J. J., Cisplatin-induced apoptosis proceeds by caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways in cisplatin-resistant and -sensitive human ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Res., 59, 3077–3083 (1999).
Itahana, K. and Zhang, Y., Mitochondrial p32 is a critical mediator of ARF-induced apoptosis. Cancer Cell, 13, 542–553 (2008).
Johnson, T. M., Yu, Z. X., Ferrans, V. J., Lowenstein, R. A., and Finkel, T., Reactive oxygen species are downstream mediators of p53-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 11848–11852 (1996).
Kang, M. H. and Reynolds, C. P., Bcl-2 inhibitors: targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res., 15, 1126–1132 (2009).
Kayanoki, Y., Fujii, J., Islam, K. N., Suzuki, K., Kawata, S., Matsuzawa, Y., and Taniguchi, N., The protective role of glutathione peroxidase in apoptosis induced by reactive oxygen species. J. Biochem., 119, 817–822 (1996).
Knudson, C. M. and Brown, N. M., Mitochondria potential, bax “activation,” and programmed cell death. Methods Mol. Biol., 414, 95–108 (2008).
Koniaras, K., Cuddihy, A. R., Christopoulos, H., Hogg A., and O’Connell, M. J., Inhibition of Chk1-dependent G2 DNA damage checkpoint radiosensitizes p53 mutant human cells. Oncogene, 20, 7453–7463 (2001).
Leber, B., Lin, J., and Andrews, D. W., Embedded together: the life and death consequences of interaction of the Bcl-2 family with membranes. Apoptosis, 12, 897–911(2007).
Maris, J. M. and Matthay, K. K., Molecular biology of neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol., 17, 2264–2279 (1999).
Martínez-Pastor, F., Aisen, E., Fernández-Santos, M. R., Esteso, M. C., Maroto-Morales, A., GarcÍa-Alvarez, O., and Garde, J. J., Reactive oxygen species generators affect quality parameters and apoptosis markers differently in red deer spermatozoa. Reproduction, 137, 225–135 (2009).
Michalet, S., Teixeira, F., and Gilquin, B., Relative spatial position of a snake neurotoxin and the reduced disulfide bond alpha (Cys192–Cys193) at the alpha gamma interface of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Biol. Chem., 33, 25608–25615 (2000).
Miller, T. J., Phelka, A. D., Tjalkens, R. B., Dethloff, L. A., and Philbert, M. A., CI-1010 induced opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore precedes oxidative stress and apoptosis in SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res., 963, 43–56 (2003).
Mühlethaler-Mottet, A., Meier, R., Flahaut, M., Bourloud, K. B., Nardou, K., Joseph, J. M., and Gross N., Complex molecular mechanisms cooperate to mediate histone deacetylase inhibitors anti-tumour activity in neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cancer, 55 (2008).
Murphy, E., Imahashi, K., and Steenbergen, C., Bcl-2 regulation of mitochondrial energetics. Trends Cardiovasc. Med., 15, 283–290 (2005).
Nandakumar, V., Singh, T., and Katiyar, S. K., Multi-targeted prevention and therapy of cancer by proanthocyanidins. Cancer Lett., 269, 378–387 (2008).
Orrenius, S., Gogvadze, V., and Zhivotovsky, B., Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 47, 143–183 (2007).
Ott, M., Gogvadze, V., Orrenius, S., and Zhivotovsky, B., Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis, 12, 913–922 (2007).
Pagnan, G., Di Paolo, D., Carosio, R., Pastorino, F., Marimpietri, D., Brignole, C., Pezzolo, A., Loi, M., Galietta, L. J., Piccardi, F., Cilli, M., Nico, B., Ribatti, D., Pistoia, V., and Ponzoni, M., The combined therapeutic effects of bortezomib and fenretinide on neuroblastoma cells involve endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Clin. Cancer Res., 15, 1199–1209 (2009).
Park, H. J., Lee, S. H., Son, D. J., Oh, K. W., Kim, K. H., Song, H. S., Kim, G. J., Oh, G. T., Yoon, D. Y., and Hong, J. T., Antiarthritic effect of bee venom: Inhibition of inflammation mediator generation by suppression of NFkappaB through interaction with the p50 subunit. Arthritis Rheum., 50, 3504–3515 (2004).
Park, M. H., Song, H. S., Kim, K. H., Son, D. J., Lee, S. H., Yoon, D. Y., Kim, Y., Park, I. Y., Song, S., Hwang, B. Y., Jung, J. K., and Hong, J. T., Cobrotoxin inhibits NFkappa B activation and target gene expression through reaction with NF-kappa B signal molecules. Biochemistry, 44, 8326–8336 (2005).
Pasquier, E., Carré, M., Pourroy, B., Camoin, L., Rebaï, O., Briand, C., and Braguer, D., Antiangiogenic activity of paclitaxel is associated with its cytostatic effect, mediated by the initiation but not completion of a mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Ther., 3, 1301–1310 (2004).
Polyak, K., Xia, Y., Zweier, J. L., and Kinzler, K. W., Vogelstein B., A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature, 389, 300–305 (1997).
Raha, S. and Robinson, B. H., Mitochondria, oxygen free radicals, and apoptosis. Am. J. Med. Genet., 106, 62–70 (2001).
Reed, J. C., Proapoptotic multidomain Bcl-2/Bax-family proteins: mechanisms, physiological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Differ., 13, 1378–1386 (2006).
Saleem, M., Maddodi, N., Abu Zaid, M., Khan, N., bin Hafeez, B., Asim, M., Suh, Y., Yun, J. M., Setaluri, V., and Mukhtar, H., Lupeol inhibits growth of highly aggressive human metastatic melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo by inducing apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res., 14, 2119–2127 (2008).
Salganik, R. I., The benefits and hazards of antioxidants: controlling apoptosis and other protective mechanisms in cancer patients and the human population. J. Am. Coll. Nutr., 20, 464S–472S (2001).
Sasnauskiene, A., Kadziauskas, J., Vezelyte, N., Jonusiene, V., and Kirveliene, V., Apoptosis, autophagy and cell cycle arrest following photodamage to mitochondrial interior. Apoptosis, 14, 276–286 (2009).
Schwartz, P. S. and Waxman, D. J., Cyclophosphamide induces caspase 9-dependent apoptosis in 9L tumor cells. Mol. Pharmacol., 60, 1268–1279 (2001).
Servent, D., Winckler-Dietrich, V., and Hu, H. Y., Only snake curaremimetic toxins with a fifth disulfide bond have high affinity for the neuronal alpha7 nicotinic receptor. J. Biol. Chem., 39, 24279–24286 (1997).
Son, D. J., Park, M. H., Chae, S. J., Moon, S. O., Lee, J. W., Song, H. S., Moon, D. C., Kang, S. S., Kwon, Y. E., and Hong, J. T., Inhibitory effect of snake venom toxin from Vipera lebetina turanica on hormone-refractory human prostate cancer cell growth: induction of apoptosis through inactivation of nuclear factor kappaB. Mol. Cancer Ther., 6, 675–683 (2007).
Torkin, R., Lavoie, J. F., Kaplan, D. R., Yeger, H., Induction of caspase-dependent, p53-mediated apoptosis by apigenin in human neuroblastoma. Mol. Cancer Ther., 4, 1–11 (2005).
Wachowicz, B., Rywaniak, J. Z., and Nowak, P., Apoptotic markers in human blood platelets treated with peroxynitrite. Platelets, 19, 624–635 (2008).
Wang, L., Zhang, Q., Liu, B., Han, M., and Shan, B., Challenge and promise: roles for Livin in progression and therapy of cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther., 7, 3661–3669 (2008).
Wolbers, F., Buijtenhuijs, P., Haanen, C., and Vermes, I., Apoptotic cell death kinetics in vitro depend on the cell types and the inducers used. Apoptosis, 9, 385–392 (2004).
Yang, J., Amiri, K. I., Burke, J. R., Schmid, J. A., and Richmond, A., BMS-345541 targets inhibitor of kappaB kinase and induces apoptosis in melanoma: involvement of nuclear factor kappaB and mitochondria pathways. Clin. Cancer Res., 12, 950–960 (2006).
Yang, S. H., Tsai, C. H., Lu, M. C., Yang, Y. N., Chien, C. M., Lin, S. F., and Lin, S. R., Effects of cardiotoxin III on expression of genes and proteins related to G2/M arrest and apoptosis in K562 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 300, 185–190 (2007).
Yin, C., Knudson, C. M., Korsmeyer, S. J., and Van Dyke, T., Bax suppresses tumorigenesis and stimulates apoptosis in vivo. Nature, 385, 637–640 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, M.H., Son, D.J., Kwak, D.H. et al. Snake venom toxin inhibits cell growth through induction of apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 1545–1554 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-2106-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-2106-0