Abstract
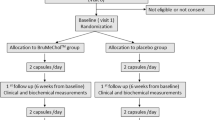
The tocotrienol vitamin E has potent antioxidant property, however absorption is low due to high lipid solubility. A self emulsifying preparation of tocotrienol rich vitamin E (SF-TRE) had been reported to increase their bioavailability. This randomized, placebo controlled, blinded end point clinical study aimed to determine the effects of 50, 100 and 200 mg daily of SF-TRE and placebo for two months on arterial compliance and vitamin E blood levels. Assessment of arterial compliance by carotid femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) and augmentation index (AI), plasma vitamin E, serum total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol were taken before and after 2 months’ treatment in 36 healthy males. Un-supplemented tocotrienol levels were low, after treatment, all SF-TRE treated groups had significantly higher plasma α, δ and δ tocotrienol concentrations compared to placebo. Augmentation index change from baseline to end of treatment for groups placebo, 50, 100, and 200 mg were 2.22±1.54, −6.59±2.84, −8.72±3.77, and −6.27±2.67% respectively (p=0.049, 0.049, and 0.047 respectively). Groups 100 and 200 mg showed significant improvement after treatment with pulse wave velocity reductions of 0.77 m/s and 0.65 m/s respectively (p=0.007 and p=0.002). There was no effect of SF-TRE on serum lipids. We conclude that there was a trend towards improvement in arterial compliance with 2 months’ of SF-TRE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, C. K., Effects of vitamin E [palm vitee] supplementation on exercise induced lipid peroxidation and endurance performance in the heat. PhD thesis, Universiti Sains Malaysia (2004).
Cruickshank, K., Riste L., Anderson, S. G., Wright, J., Dunn, G., and Gosling, R. G., Aortic pulse wave velocity and its relationship to mortality in diabetes and glucose intolerance; and integrated index of vascular function. Circulation. 106, 2085–2090 (2002).
Florey, C. V., Sample size for beginners. BMJ. 306, 1181–1184 (1993).
Ikeda, I., Imasato, Y., Sasaki, E., and Sugano, M., Lymphatic transport of alpha, gamma and delta tocotrienols and alpha tocopherol in rats. Int. J. Vit. Nutr. Res., 66, 217–221 (1996).
Khor, H. T. and Chieng, D. Y., Effect of dietary supplementation of tocotrienols and tocopherols on serum lipids in the hamster. Nutr. Res., 16, 1393–1401 (1996).
Khor, H. T., Chieng, D. Y., and Ong, K. K., Tocotrienols inhibit liver HMG CoA Reductase activity in the guinea pig. Nutrition Research, 15, 537–544 (1995).
Kritchevsky, S. B., Shimakawa, T., Tell, G. S., Dennis, B., Carpenter, M., Eckfeldt, J. H., Peacher-Ryan, H., and Heiss, G., Dietary antioxidants and carotid artery wall thickness. The ARIC study. Circulation, 92, 2142–2150 (1995).
Laurent, S., Boutouyrie, P., Asmar, R., Gautier, I., Laloux, B., Guize, L., Ducimetiere, P., and Benetos, A., Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all cause and cardiovasular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 37, 1236–1241 (2001).
Newaz, M. A., Yousefipour, Z., Nawal, N., and Adeeb, N., Nitric oxide synthase activity in blood vessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats: antioxidant protection by gamma-tocotrienol. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 54, 319–327 (2003).
O’Byrne, D., Grundy, S., Packer, L., Devaraj, S., Baldenius, K., Hoppe, P., Kramer, K., Jialal, I., and Traber, M. G., Studies of LDL oxidation following alpha, gamma or delta tocotrienol acetate supplementation of hypercholesterolemic humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 29, 834–845 (2000).
O’Rourke, M. and Gallagher, D. E., Pulse wave analysis. J. Hypertens, 14, S147–S157 (1996).
Parker, R. A., Pearce, B. C., Clark, R. W. D., Gordon, A., and Wright, J. J., Tocotrienols regulate cholesterol production in mammalian cells by post transcriptional suppression of 3 hydroxy-3methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J. Biol. Chem., 268, 11230–11238 (1993).
Pearce, B. C., Parker, R. A., Deason, M. E., Qureshi, A. A., and Wright, J. J., Hypocholesterolemic activity of synthetic and natural tocotrienols. J. Med. Chem., 35, 3595–3606 (1992).
Qureshi, A. A., Sami, S. A., Salser, W. A., and Khan, F. A., Dose-dependent suppression of serum cholesterol by tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF25) of rice bran in hyperchol-esterolemic humans. Atherosclerosis, 161, 199–207 (2002).
Rasool, A. H., Yuen, K. H., Khalid, Y., Wong, A. R., and Rahman, A. R. A., Dose dependent elevation of plasma tocotrienol levels and its effect on arterial compliance, plasma total antioxidant status and lipid profile in healthy humans supplemented with tocotrienol rich vitamin E. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol., 52, 473–478 (2006).
Reaven, P. D., Khouw, A., Beltz, W. F., Parthasarathy, S., and Witzturo, J. L., Effect of antioxidant combinations inhumans; protection of LDL by vitamin E but not by Beta Carotene. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol., 13, 590–600 (1993).
Rubanyi, G. M. and Vanhoutte, P. M., Superoxide anion and hyperoxia inactivate endothelial derived relaxing factor. Am. J. Physiol., 25, 822H–827H (1986).
Serbinova, E., Kagan, V., Han, D., and Packer, L., Free radical recycling and intramembrane mobility in the antioxidant properties of alpha tocopherol and alpha-tocotrienol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 10, 263–275 (1991).
Serbinova, E., Khwaja, S., Catudioc, J., Ericson, J., Torres, Z., Gapor, A., Kagan, V., and Packer, L., Palm oil vitamin E protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in the isolated perfused Langendorff heart. Nutr. Res., 12, S203–S215 (1992).
Stephens, N. G., Parsons, A., Schofield, P. M., Kelly, F., Cheeseman, K., Mitchinson, M. J., and Brown, M. J., Randomised controlled trial of vitamin E in patients with coronary disease: Cambridge Heart Antioxidant Study (CHAOS). Lancet, 347, 781–786 (1996).
Tomeo, A. C., Geller, M., Watkins, T. R., Gapor, A., and Bierenbaum, M. L., Antioxidant effects of tocotrienols in patients with hyperlipidemia and carotid stenosis. Lipids, 30, 1179–1183 (1995).
Vlachopoulos, C., Aznaouridis, K., Alexopoulos, N., Economou, E., Andreadou, I., and Stefanadis, C., Effect of dark chocolate on arterial function in healthy individuals. Am. J. Hypertens, 18, 785–791 (2005).
Wilkinson, A. B., Megson, I. L., MacCallum, H., Sogo, N., Cockroft, J. R., and Webb, D. J., Oral vitamin C reduces arterial stiffness and platelet aggregation in humans. J. Cardiovasc Pharmacol., 34, 690–693 (1999).
Wilkinson, I. B., Qasem, A., McEniery, C. M., Webb, D. J., Avolio, A. P., and Cockroft, J. R., Nitric oxide regulates local arterial distensibility in vivo. Circulation, 105, 213–217 (2002).
Willum-Hansen, T., Staessen, J. A., Torp-Pedersen, C., Rasmussen, S., Thijs, L., Ibsen, H., and Jeppesen, J., Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation, 113, 601–603 (2006).
Yap, S. P., Julianto, T., Wong, J. W., and Yuen, K. H., Simple high performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of tocotrienols in human plasma. Journal of Chromatography, 735, 279–283 (1999).
Yap, S. P. and K. Yuen, H., Influence of lipolysis and droplet size on tocotrienol absorption from self-emulsifying formulations. Int. J. Pharm., 281, 67–78 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasool, A.H.G., Rahman, A.R.A., Yuen, K.H. et al. Arterial compliance and vitamin E blood levels with a self emulsifying preparation of tocotrienol rich vitamin E. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 1212–1217 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1291-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1291-5