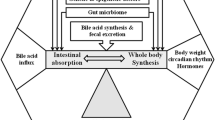
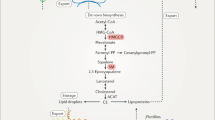
Abstract
We present here a brief description of the path that cholesterol covers from its intestinal absorption to its effects exerted on gene regulation. In particular, the relationship between cholesterol and the protein complexes involved in the intricate gene regulation mechanism implicated in cholesterol homeostasis will be discussed. In addition, a new target role for the pharmacological interventions of one of these factors, the insulin-induced gene (Insig) protein, will be introduced.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HMG-CoAR:
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase
- HMG-CoAS:
-
3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A synthase
- PGDH:
-
6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
- DHCR:
-
7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase
- ACC:
-
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- ACAT:
-
Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase
- aa:
-
Amino acid
- APP:
-
Amyloid peptide
- Apo:
-
Apoprotein
- ABC:
-
ATP binding cassette
- bHLH-Lzip:
-
Basic-helix–loop–helix-leucine zipper
- CMs:
-
Chylomicrons
- Cyp7α:
-
Cholesterol 7α hydroxylase
- CETP:
-
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein
- CBP:
-
CREB binding protein
- ADD1:
-
Determination and differentiation factor 1
- ERC:
-
Endocytic recycling compartment
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FPP:
-
Farnesyl diphosphate
- FAS:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- GPP:
-
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase
- GPAT:
-
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
- G6PD:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- Insig:
-
Insulin-induced gene
- CY51:
-
Lanosterol 14α-demethylase
- LPL:
-
Lipoprotein lipase
- LXR:
-
Liver X receptor
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- LDLr:
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptors
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ALLN:
-
N-Acetyl-l-leucyl-l-leucyl-norleucinal
- NPC1L1:
-
Nieman-Pick C1-like protein1
- nSREBP:
-
Nuclear SREBP
- PI(3)-kinase:
-
Phosphatidyl inositol (3) kinase
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
- PKB:
-
Protein kinase B
- PKCk:
-
Protein kinase Ck
- SR-B1:
-
Scavenger receptor class B type 1
- SCAP:
-
SREBP cleavage activating protein
- S1P:
-
Site 1 protease
- S2P:
-
Site 2 protease
- SUMO–1:
-
Small ubiquitin-related modifier-1
- SCD:
-
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase
- SSD:
-
Sterol sensing domain
- SRE:
-
Sterol regulatory element
- SREBPs:
-
Sterol regulatory binding proteins
- S f :
-
Svedberg flotation
- TG:
-
Triglyceride
- VLDL:
-
Very low-density lipoprotein
- DRIP:
-
Vitamin D receptor-integrating protein
- WAT:
-
White adipose tissue
References
Adams CM, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2003) Cholesterol induced conformational change in SCAP enhanced by Insig proteins and mimicked by cationic amphiphiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10647–10652
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002) Molecular biology of the cell. Garland Science, New York
Altmann SW, Davis HR Jr, Zhu LJ, Yao X, Hoos LM, Tetzloff G, Iyer SP, Maguire M, Golovko A, Zeng M, Wang L, Murgolo N, Graziano MP (2004) Niemann-Pick C1 like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science 303:1201–1204
Amemiya-Kudo M, Shimano H, Yoshikawa T, Yahagi N, Hasty AH, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Shionoiri F, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J, Harada K, Gotoda T, Sato R, Kimura S, Ishibashi S, Yamada N (2000) Promoter analysis of the mouse sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c gene. J Biol Chem 275:31078–31085
Antonny B, Schekman R (2001) ER export: public transportation by the COPII coach. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:438–443
Aridor M, Weissman J, Bannykh SI, Nuoffer C, Balch WE (1998) Cargo selection by the COPII budding machinery during export from the ER. J Cell Biol 141:61–70
Azzout-Marniche D, Becard D, Guichard C, Foretz M, Ferre P, Foufelle F (2000) Insulin effects on sterol regulatory-element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) transcriptional activity in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J 350(Pt. 2):389–393
Barlowe C (2002) COPII-dependent transport from the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:417–422
Bizeau ME, MacLean PS, Johnson GC, Wei Y (2003) Skeletal muscle sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c decreases with food deprivation and increases with feeding in rats. J Nutr 133:1787–1792
Bose C, Bhuvaneswaran C, Udupa KB (2005) Age-related alteration in hepatic acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase and its relation to LDL receptor and MAPK. Mech Ageing Dev 126:740–751
Bosner MS, Lange LG, Stenson WF, Ostlund RE Jr (1999) Percent cholesterol absorption in normal women and men quantified with dual stable isotopic tracers and negative ion mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res 40:302–308
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1986) A receptor mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 232:24–47
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 89:331–340
Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1999) A proteolytic pathway that controls the cholesterol content of membranes, cells, and blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11041–11048
Brown MS, Ye J, Rawson RB, Goldstein JL (2000) Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: a control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell 100:391–398
Buhman KK, Accad M, Novak S, Choi RS, Wong JS, Hamilton RL, Turley S, Farese RV Jr (2000) Resistance to diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and gallstone formation in ACAT2-deficient mice. Nat Med 6:1341–1347
Chen IS, Hotta SS, Ikeda I, Cassidy MM, Sheppard AJ, Vahouny GV (1987) Digestion, absorption and effects on cholesterol absorption of menhaden oil, fish oil concentrate and corn oil by rats. J Nutr 117:1676–1680
Commerford SR, Peng L, Dube JJ, O’Doherty RM (2004) In vivo regulation of SREBP-1c in skeletal muscle: effects of nutritional status, glucose, insulin, and leptin. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R218–R227
Dietschy JM, Turley SD, Spady DK (1993) Role of liver in the maintenance of cholesterol and low density lipoprotein homeostasis in different animal species, including humans. J Lipid Res 34:1637–1659
Distefano E, Marino M, Gillette JA, Hanstein B, Pallottini V, Bruning J, Krone W, Trentalance A (2002) Role of tyrosine kinase signaling in estrogen-induced LDL receptor gene expression in HepG2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1580:145–149
Duncan EA, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Sakai J (1997) Cleavage site for sterol-regulated protease localized to a leu-Ser bond in the luminal loop of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. J Biol Chem 272:12778–12785
Duncan EA, Dave UP, Sakai J, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1998) Second-site cleavage in sterol regulatory element-binding protein occurs at transmembrane junction as determined by cysteine panning. J Biol Chem 273:17801–17809
Eckhardt ER, Wang DQ, Donovan JM, Carey MC (2002) Dietary sphingomyelin suppresses intestinal cholesterol absorption by decreasing thermodynamic activity of cholesterol monomers. Gastroenterology 122:948–956
Einarsson K, Nilsell K, Leijd B, Angelin B (1985) Influence of age on secretion of cholesterol and synthesis of bile acids by the liver. N Engl J Med 313:277–282
Epand RM (2006) Cholesterol and the interaction of proteins with membrane domains. Prog Lipid Res 45:279–294
Espenshade PJ, Cheng D, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1999) Autocatalytic processing of site-1 protease removes propeptide and permits cleavage of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 274:22795–22804
Espenshade PJ, Li WP, Yabe D (2002) Sterols block binding of COPII proteins to SCAP, thereby controlling SCAP sorting in ER. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11694–11699
Feramisco JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2004) Membrane topology of human insig-1, a protein regulator of lipid synthesis. J Biol Chem 279:8487–8496
Fleischmann M, Iynedjian PB (2000) Regulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 gene expression in liver: role of insulin and protein kinase B/cAkt. Biochem J 349:13–17
Foretz M, Guichard C, Ferre P, Foufelle F (1999a) Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12737–12774
Foretz M, Pacot C, Dugail I, Lemarchand P, Guichard C, Le Liepvre X, Berthelier-Lubrano C, Spiegelman B, Kim JB, Ferre P, Foufelle F (1999b) ADD1/SREBP-1c is required in the activation of hepatic lipogenic gene expression by glucose. Mol Cell Biol 19:3760–3768
Fulop T, Larbi A, Douziech N (2003) Insulin receptor and ageing. Pathol Biol (Paris) 51:574–580
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1990) Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 343:425–430
Goldstein JL, DeBose-Boyd RA, Brown MS (2006) Protein sensors for membrane sterols. Cell 124:35–46
Gong Y, Lee JN, Lee PCW, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Ye J (2006) Sterol-regulated ubiquitination and degradation of Insig-1 creates a convergent mechanism for feedback control of cholesterol synthesis and uptake. Cell Metab 3:15–24
Hegarty BD, Bobard A, Hainault I, Ferre P, Bossard P, Foufelle F (2005) Distinct roles of insulin and liver X receptor in the induction and cleavage of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:791–796
Heider JG, Pickens CE, Kelly LA (1983) Role of acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase in cholesterol absorption and its inhibition by 57–118 in the rabbit. J Lipid Res 24:1127–1134
Henriksson P, Einarsson K, Eriksson A, Kelter U, Angelin B (1989) Estrogen-induced gallstone formation in males. Relation to changes in serum and biliary lipids during hormonal treatment of prostatic carcinoma. J Clin Invest 84:811–816
Hirano Y, Murata S, Tanaka K, Shimizu M, Sato R (2003) Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins are negatively regulated through SUMO-1 modification independent of the ubiquitin/26 S proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 278:16809–16819
Hirano Y, Yoshida M, Shimizu M, Sato R (2001) Direct demonstration of rapid degradation of nuclear sterol regulatory element-binding proteins by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 276:36431–36437
Hoffmann AF, Borgstrom B (1963) Hydrolysis of long-chain monoglycerides in micellar solution by pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta 70:317–331
Horton JD, Bashmakov Y, Shimomura I, Shimano H (1998) Regulation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins in livers of fasted and refed mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5987–5992
Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2002) SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest 109:1125–1131
Horton JD, Shah NA, Warrington JA, Anderson NN, Park SW, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2003a) Combined analysis of oligonucleotide microarray data from transgenic and knockout mice identifies direct SREBP target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12027–12032
Horton JD, Shimomura I, Ikemoto S, Bashmakov Y, Hammer RE (2003b) Overexpression of SREBP-1a in mouse adipose tissue produces adipocyte hypertrophy, increased fatty acid secretion, and fatty liver. J Biol Chem 278:36652–36660
Hua X, Nohturfft A, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1996) Sterol resistance in CHO cells traced to point mutation in SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP). Cell 87:415–426
Hua X, Sakai J, Ho YK, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1995) Hairpin orientation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 in cell membranes as determined by protease protection. J Biol Chem 270:29422–29427
Hua X, Wu J, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Hobbs HH (1995) Structure of the human gene encoding sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 (SREBF1) and localization of SREBF1 and SREBF2 to chromosomes 17p11.2 and 22q13. Genomics 25:667–673
Hussain MM (2000) A proposed model for the assembly of chylomicrons. Atherosclerosis 148:1–15
Ikeda I, Tanaka K, Sugano M, Vahouny GV, Gallo LL (1988) Inhibition of cholesterol absorption in rats by plant sterols. J Lipid Res 29:1573–1582
Iynedjian PB, Roth RA, Fleischmann M, Gjinovci A (2000) Activation of protein kinase B/cAkt in hepatocytes is sufficient for the induction of expression of the gene encoding glucokinase. Biochem J 351(Pt. 3):621–627
Janowski BA (2002) The hypocholesterolemic agent LY295427 upregulates INSIG-1, identifying the INSIG-1 protein as a mediator of cholesterol homeostasis through SREBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12675–12680
Janowski BA, Grogan MJ, Jones SA, Wisely GB, Kliewer SA, Corey EJ, Mangelsdorf DJ (1999) Structural requirements of ligands for the oxysterol liver X receptors LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:266–271
Kam NT, Albright E, Mathur S, Field FJ (1990) Effect of lovastatin on acyl-CoA: cholesterol O-acyltransferase (ACAT) activity and the basolateral-membrane secretion of newly synthesized lipids by CaCo-2 cells. Biochem J 272:427–433
Kam NT, Albright E, Mathur SN, Field FJ (1989) Inhibition of acylcoenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase activity in CaCo-2 cells results in intracellular triglyceride accumulation. J Lipid Res 30:371–377
Kim JB, Sarraf P, Wright M, Yao KM, Mueller E, Solanes G, Lowell BB, Spiegelman BM (1998) Nutritional and insulin regulation of fatty acid synthetase and leptin gene expression through ADD1/SREBP1. J Clin Invest 101:1–9
Kim JB, Spotts GD, Halvorsen YD, Shih HM, Ellenberger T, Towle HC, Spiegelman BM (1995) Dual DNA binding specificity of ADD1/SREBP1 controlled by a single amino acid in the basic helix–loop–helix domain. Mol Cell Biol 15:2582–2588
Kotzka J, Lehr S, Roth G, Avci H, Knebel B, Muller-Wieland D (2004) Insulin-activated Erk-mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 at serine residues 432 and 455 in vivo. J Biol Chem 279:22404–22411
Lammert F, Wang DQ (2005) New insights into the genetic regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption. Gastroenterology 129:718–734
Lee YS, Lee HH, Park J, Yoo EJ, Glackin CA, Choi YI, Jeon SH, Seong RH, Park SD, Kim JB (2003) Twist2, a novel ADD1/SREBP1c interacting protein, represses the transcriptional activity of ADD1/SREBP1c. Nucleic Acids Res 31:7165–7174
Lee JN, Ye J (2004) Proteolytic activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein induced by cellular stress through depletion of Insig-1. J Biol Chem 279:45257–45265
Lehmann JM, Kliewer SA, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Oliver BB, Su JL, Sundseth SS, Winegar DA, Blanchard DE, Spencer TA, Willson TM (1997) Activation of the nuclear receptor LXR by oxysterols defines a new hormone response pathway. J Biol Chem 272:3137–3140
Lindgren FT, Jensen LC, Wills RD, Stevens GR (1972) Subfractionation of S f 4–10 5, S f 4–20 and high density lipoproteins. Lipids 7:194–201
Luong A (2000) Identification of three novel SREBP-activated target genes: acetyl CoA synthetase, 3-β-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase, and CL-6/INSIG1. PhD dissertation. University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas, Dallas, pp 1–137
Magana MM, Koo SH, Towle HC, Osborne TF (2000) Different sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 isoforms utilize distinct co-regulatory factors to activate the promoter for fatty acid synthase. J Biol Chem 275:4726–4733
Masoro EJ (2005) Overview of caloric restriction and ageing. Mech Ageing Dev 126:913–22
Matsumoto M, Ogawa W, Akimoto K, Inoue H, Miyake K, Furukawa K, Hayashi Y, Iguchi H, Matsuki Y, Hiramatsu R, Shimano H, Yamada N, Ohno S, Kasuga M, Noda T (2003) PKClambda in liver mediates insulin-induced SREBP-1c expression and determines both hepatic lipid content and overall insulin sensitivity. J Clin Invest 112:935–944
Messa C, Notarnicola M, Russo F, Cavallini A, Pallottini V, Trentalance A, Bifulco M, Laezza C, Caruso GM (2005) Estrogenic regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis and cell growth in DLD-1 human colon cancer cells. Scand J Gastroenterol 40:1454–1461
Miserez AR, Cao G, Probst LC, Hobbs HH (1997) Structure of the human gene encoding sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBF2). Genomics 40:31–40
Mohn KL, Laz TM, Hsu J-C, Melby AE, Bravo R, Taub R (1991) The immediate-early growth response in regenerating liver and insulin-stimulated H-35 cells: comparison with serum-stimulated 3T3 cells and identification of 41 novel immediate-early genes. Mol Cell Biol 11:381–390
Moller N, Gormsen L, Fuglsang J, Gjedsted J (2003) Effects of ageing on insulin secretion and action. Horm Res 60:102–104
Moon YA, Lee JJ, Park SW, Ahn YH, Kim KS (2000) The roles of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins in the transactivation of the rat ATP citrate-lyase promoter. J Biol Chem 275:30280–30286
Moon YA, Shah NA, Mohapatra S, Warrington JA, Horton JD (2001) Identification of a mammalian long chain fatty acyl elongase regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 276:45358–45366
Murthy S, Albright E, Mathur SN, Field FJ (1990) Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid on triacylglycerol transport in CaCo-2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1045:147–155
Murthy S, Albright E, Mathur SN, Davidson NO, Field FJ (1992) Apolipoprotein B mRNA abundance is decreased by eicosapentaenoic acid in CaCo-2 cells. Effect on the synthesis and secretion of apolipoprotein B. Arterioscler Thromb 12:691–700
Naar AM, Beaurang PA, Robinson KM, Oliner JD, Avizonis D, Scheek S, Zwicker J, Kadonaga JT, Tjian R (1998) Chromatin, TAFs, and a novel multiprotein coactivator are required for synergistic activation by Sp1 and SREBP-1a in vitro. Genes Dev 12:3020–3031
Naar AM, Beaurang PA, Zhou S, Abraham S, Solomon W, Tjian R (1999) Composite co-activator ARC mediates chromatin-directed transcriptional activation. Nature 398:828–832
Nagoshi E, Yoneda Y (2001) Dimerization of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 via the helix–loop–helix-leucine zipper domain is a prerequisite for its nuclear localization mediated by importin beta. Mol Cell Biol 21:2779–2789
Nagoshi E, Immoto N, Sato R, Yoneda Y (1999) Nuclear import of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2, a basic helix–loop–helix-leucine zipper (bHLH-Zip)-containing transcription factor, occurs through the direct interaction of importin beta with HLH-Zip. Mol Biol Cell 10:2221–2233
Ness GC, Lopez D (1995) Transcriptional regulation of rat hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptor and cholesterol 7 alpha hydroxylase by thyroid hormone. Arch Biochem Biophys 323:404–408
Neufeld EB, Cooney AM, Pitha J, Dawidowicz EA, Dwyer NK, Pentchev PG, Blanchette-Mackie EJ (1996) Intracellular trafficking of cholesterol monitored with a cyclodextrin. J Biol Chem 271:21604–21613
Nguyen TT (1999) The cholesterol-lowering action of plant stanol esters. J Nutr 129:2109–2112
Nielsen LB, Stender S, Kjeldsen K (1993) Effect of lovastatin on cholesterol absorption in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Pharmacol Toxicol 72:148–151
Nohturfft A, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1998a) Sterols regulate processing of carbohydrate chains of wild-type SREBP cleavageactivating protein (SCAP), but not sterol-resistant mutants Y298C or D443N. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12848–12853
Nohturfft A, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1998b) Topology of SREBP cleavage-activating protein, a polytopic membrane protein with a sterol-sensing domain. J Biol Chem 273:17243–17250
Nohturfft A, Yabe D, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Espenshade PJ (2000) Regulated step in cholesterol feedback localized to budding of SCAP from ER membranes. Cell 102:315–323
Ockner RK, Manning JA (1974) Fatty acid-binding protein in small intestine. Identification, isolation, and evidence for its role in cellular fatty acid transport. J Clin Invest 54:326–338
Ockner RK, Hughes FB, Isselbacher KJ (1969) Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: role in triglyceride and cholesterol transport during fat absorption. J Clin Invest 48:2367–2373
Oram JF, Heinecke JW (2005) ATP-binding cassette transporter A1: a cell cholesterol exporter that protects against cardiovascular disease. Physiol Rev 85:1343–1372
Osborne TF (2000) Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): key regulators of nutritional homeostasis and insulin action. J Biol Chem 275:32379–32382
Ostlund RE Jr, Racette SB, Okeke A, Stenson WF (2002) Phytosterols that are naturally present in commercial corn oil significantly reduce cholesterol absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 75:1000–1004
Pallottini V, Martini C, Cavallini G, Donati A, Bergamini E, Notarnicola M, Caruso MG, Trentalance A (2006) Modified HMG-CoA reductase and LDLr regulation is deeply involved in age-related hypercholesterolemia. J Cell Biochem 98:1044–1053
Pasqualini JR (2005) Enzymes involved in the formation and transformation of steroid hormones in the fetal and placental compartments. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 97:401–415
Peng Y, Schwarz EJ, Lazar MA, Genin A, Spinner NB, Taub R (1997) Cloning, human chromosomal assignment, and adipose and hepatic expression of the CL-6/INSIG1 gene. Genomics 43:278–284
Podar K, Anderson KC (2006) Caveolin-1 as a potential new therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Cancer Lett 233:10–15
Ribaux PG, Iynedjian PB (2003) Analysis of the role of protein kinase B (cAKT) in insulin-dependent induction of glucokinase and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) mRNAs in hepatocytes. Biochem J 376:697–705
Rosenblum SB, Huynh T, Afonso A, Davis HR Jr, Yumibe N, Clader JW, Burnett DA (1998) Discovery of 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-(3R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-(3S)-hydroxypropyl]-(4S)-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone (SCH 58235): a designed, potent, orally active inhibitor of cholesterol absorption. J Med Chem 41:973–980
Robinet P, Fradagrada A, Monier MN, Marchetti M, Cogny A, Moatti N, Paul JL, Vedie B, Lamaze C (2006) Dynamin is involved in endolysosomal cholesterol delivery to the endoplasmic reticulum: role in cholesterol homeostasis. Traffic 7:811–823
Roth G, Kotzka J, Kremer L, Lehr S, Lohaus C, Meyer HE, Krone W, Muller-Wieland D (2000) MAP kinases Erk1/2 phosphorylate sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP)-1a at serine 117 in vitro. J Biol Chem 275:33302–33307
Sakai J, Rawson RB, Espenshade PJ, Cheng D, Seegmiller AC, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1998) Molecular identification of the sterol-regulated luminal protease that cleaves SREBPs and controls lipid composition of animal cells. Mol Cell 2:505–514
Sato R, Inoue J, Kawabe Y, Kodama T, Takano T, Maeda M (1996) Sterol-dependent transcriptional regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2. J Biol Chem 271:26461–26464
Sheng Z, Otani H, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1995) Independent regulation of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins 1 and 2 in hamster liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:935–938
Shimano H, Horton JD, Hammer RE, Shimomura I, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1996) Overproduction of cholesterol and fatty acids causes massive liver enlargement in transgenic mice expressing truncated SREBP-1a. J Biol Chem 98:1575–1584
Shimano H, Horton JD, Shimomura I, Hammer RE, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1997) Isoform 1c of sterol regulatory element binding protein is less active than isoform 1a in livers of transgenic mice and in cultured cells. J Clin Invest 99:846–854
Shimomura I, Shimano H, Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1997) Differential expression of exons 1a and 1c in mRNAs for sterol regulatory element binding protein-1 in human and mouse organs and cultured cells. J Clin Invest 99:838–845
Siperstein MD, Chaikoff IL, Reinhardt WO (1952) C14-Cholesterol. V. obligatory function of bile in intestinal absorption of cholesterol. J Biol Chem 198:111–114
Steffensen KR, Gustafsson JA (2004) Putative metabolic effects of the liver X receptor (LXR). Diabetes 53(Suppl. 1):S36–S42
Sudhop T, Lutjohann D, Kodal A, Igel M, Tribble DL, Shah S, Perevozskaya I, von Bergmann K (2002) Inhibition of intestinal cholesterol absorption by ezetimibe in humans. Circulation 106:1943–1948
Sugii S, Reid PC, Ohgami N, Du H, Chang TY (2003) Distinct endosomal compartments in early trafficking of low density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol. J Biol Chem 278:27180–27189
Sun LP, Li L, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2005) Insig required for sterol-mediated inhibition of Scap/SREBP binding to COPII proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem 280:26483–26490
Sundqvist A, Ericsson J (2003) Transcription-dependent degradation controls the stability of the SREBP family of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13833–13838
Tontonoz P, Mangelsdorf DJ (2003) Liver X receptor signaling pathways in cardiovascular disease. Mol Endocrinol 17:985–993
Traber MG, Kayden HJ, Rindler MJ (1987) Polarized secretion of newly synthesized lipoproteins by the Caco-2 human intestinal cell line. J Lipid Res 28:1350–1363
Tso P, Drake DS, Black DD, Sabesin SM (1984) Evidence for separate pathways of chylomicron and very low-density lipoprotein assembly and transport by rat small intestine. Am J Physiol 247:G599–G610
Turley SD, Dietschy JM (2003) Sterol absorption by the small intestine. Curr Opin Lipidol 14:233–240
Turley SD, Schwarz M, Spady DK, Dietschy JM (1998) Gender-related differences in bile acid and sterol metabolism in outbred CD-1 mice fed low- and high-cholesterol diets. Hepatology 28:1088–1094
Uchida K, Nomura Y, Kadowaki M, Takase H, Takano K, Takeuchi N (1978) Age-related changes in cholesterol and bile acid metabolism in rats. J Lipid Res 19:544–552
Vahouny GV, Connor WE, Roy T, Lin DS, Gallo LL (1981) Lymphatic absorption of shellfish sterols and their effects on cholesterol absorption. Am J Clin Nutr 34:507–513
Vahouny GV, Roy T, Gallo LL, Story JA, Kritchevsky D, Cassidy M, Grund BM, Treadwell CR (1978) Dietary fiber and lymphatic absorption of cholesterol in the rat. Am J Clin Nutr 31(10 Suppl):S208–S210
Valdivieso V, Palma R, Wunkhaus R, Antezana C, Severin C, Contreras A (1978) Effect of aging on biliary lipid composition and bile acid metabolism in normal Chilean women. Gastroenterology 74(5 Pt 1):871–874
Vanhanen H, Kesaniemi YA, Miettinen TA (1992) Pravastatin lowers serum cholesterol, cholesterol-precursor sterols, fecal steroids, and cholesterol absorption in man. Metabolism 41:588–595
Wang DQ, Carey MC (1996) Complete mapping of crystallization pathways during cholesterol precipitation from model bile: influence of physical-chemical variables of pathophysiologic relevance and identification of a stable liquid crystalline state in cold, dilute and hydrophilic bile salt-containing systems. J Lipid Res 37:606–630
Wang D, Sul HS (1998) Insulin stimulation of the fatty acid synthase promoter is mediated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Involvement of protein kinase B/Akt. J Biol Chem 273:25420–25426
Wang DQ (2002) Aging per se is an independent risk factor for cholesterol gallstone formation in gallstone susceptible mice. J Lipid Res 43:1950–1959
Wang DQ (2003) New concepts of mechanisms of intestinal cholesterol absorption. Ann Hepatol 2:113–121
Wang DQ, Lammert F, Cohen DE, Paigen B, Carey MC (1999) Cholic acid aids absorption, biliary secretion, and phase transitions of cholesterol in murine cholelithogenesis. Am J Physiol 276(3 Pt 1):G751–G760
Wang DQ, Tazuma S, Cohen DE, Carey MC (2003) Feeding natural hydrophilic bile acids inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption: studies in the gallstone-susceptible mouse. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G494–G502
Wang HH, Afdhal NH, Wang DQ (2004) Estrogen receptor alpha, but not beta, plays a major role in 17-beta-estradiol-induced murine cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology 127:239–249
Wang X, Sato R, Brown MS, Hua X, Goldstein JL (1994) SREBP-1, a membrane-bound transcription factor released by sterol-regulated proteolysis. Cell 77:53–62
Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A (2004) Maintaining cholesterol homeostasis: sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. World J Gastroenterol 10:3081–3087
Yabe D, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2002) Insig-2, a second endoplasmic reticulum protein that binds SCAP and blocks export of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12753–12758
Yuan G, Wang J Hegele RA (2006) Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: an underrecognized cause of early cardiovascular disease. Can Med Assoc J 174:1124–1129
Zannis VI, Chroni A, Kypreos KE, Kan HY, Cesar TB, Zanni EE, Kardassis D (2004) Probing the pathways of chylomicron and HDL metabolism using adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Curr Opin Lipidol 15:151–166
Zelcer N, Tontonoz P (2006) Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling. J Clin Invest 116:607–614
Zilversmit DB (1965) The composition and structure of lymph chylomicrons in dog, rat, and man. J Clin Invest 44:1610–1622
Acknowledgments
The authors are gratefully indebted to Prof. Anna Trentalance (Full Professor of Physiology, University of “ROMA TRE”) for the helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martini, C., Pallottini, V. Cholesterol: from feeding to gene regulation. Genes Nutr 2, 181–193 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-007-0049-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-007-0049-y