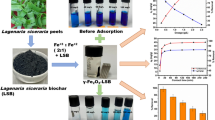
Abstract
The ability of Fe3O4 Fenton-like reaction to produce glucose from lignocellulosic biomass was investigated. Fe3O4 magnetite nanoparticles were chemically synthesized from iron salts (a mixture of 1 M FeCl2 and 2M FeCl3) using an ammonia solution (30% NH4OH). The synthesized Fe3O4 nanoparticles were further characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. Reed stems and rice straw biomasses pretreated with optimized Fenton-like reagents (Fe3O4 and H2O2) increased glucose production by 177 and 87%, respectively, compared to the control without the catalysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salunke, B. K., E. Sathiyamoorthi, T. K. Tran, and B. S. Kim (2017) Phyto-synthesized silver nanoparticles for biological applications. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 34: 943–951.
Salunke, B. K., S. S. Sawant, S. I. Lee, and B. S. Kim (2016) Microorganisms as efficient biosystem for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles: Current scenario and future possibilities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 1–16.
Lee, S. H., B. K. Salunke, and B. S. Kim (2014) Sucrose density gradient centrifugation separation of gold and silver nanoparticles synthesized using Magnolia kobus plant leaf extracts. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 19: 169–174.
Borase, H. P., B. K. Salunke, R. B. Salunkhe, C. D. Patil, J. E. Hallsworth, B. S. Kim, and S. V. Patil (2014) Plant extract: A promising biomatrix for ecofriendly, controlled synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 173: 1–29.
Dauthal, P. and M. Mukhopadhyay (2015) Agro-industrial wastemediated synthesis and characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles and their catalytic activity for 4-nitroaniline hydrogenation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32: 837–844.
Gu, X., Y. Zhang, H. Sun, X. Song, C. Fu, and P. Dong (2015) Mussel-inspired polydopamine coated iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application. J. Nanomater. 2015: 154592.
Fatima, H. and K.-S. Kim (2017) Magnetic nanoparticles for bioseparation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 34: 589–599.
Wu, W., Z. Wu, T. Yu, C. Jiang, and W. S. Kim (2015) Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 16: 023501.
Zhang, Y., L. Zhang, X. Song, X. Gu, H. Sun, C. Fu, and F. Meng (2015) Synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with MPEG-PEI via photochemistry as new MRI contrast agent. J. Nanomater. 2015: 417389.
Zeng, T., W. W. Chen, C. M. Cirtiu, A. Moores, G. Song, and C. J. Li (2010) Fe3O4 nanoparticles: a robust and magnetically recoverable catalyst for three-component coupling of aldehyde, alkyne and amine. Green Chem. 12: 570–573.
Gawande, M. B., P. S. Branco, and R. S. Varma (2013) Nanomagnetite (Fe3O4) as a support for recyclable catalysts in the development of sustainable methodologies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42: 3371–3393.
Varma, R. S. (2014) Nano-catalysts with magnetic core: Sustainable options for greener synthesis. Sustain. Chem. Proc. 2: 11.
Gao, L., J. Zhuang, L. Nie, J. Zhang, Y. Zhang, N. Gu, T. Wang, J. Feng, D. Yang, S. Perrett, and X. Yan (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2: 577–583.
Jung, H., H. Park, J. Kim, J. H. Lee, H. G. Hur, N. V. Myung, and H. Choi (2007) Preparation of biotic and abiotic iron oxide nanoparticles (IOnPs) and their properties and applications in heterogeneous catalytic oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41: 4741–4747.
Mei, N., B. Liu, J. Zheng, K. Lv, D. Tang, and Z. Zhang (2015) A novel magnetic palladium catalyst for the mild aerobic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid in water. Catal. Sci. Technol. 5: 3194–3202.
Wang, S., Z. Zhang, B. Liu, and J. Li (2013) Silica coated magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles supported phosphotungstic acid: a novel environmentally friendly catalyst for the synthesis of 5-ethoxymethylfurfural from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and fructose. Catal. Sci. Technol. 3: 2104–2112.
Lai, D. M., L. Deng, Q. X. Guo, and Y. Fu (2011) Hydrolysis of biomass by magnetic solid acid. Energy Environ. Sci. 4: 3552–3557.
Xiong, Y., Z. Zhang, X. Wang, B. Liu, and J. Lin (2014) Hydrolysis of cellulose in ionic liquids catalyzed by a magneticallyrecoverable solid acid catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 235: 349–355.
Wang, S., Z. Zhang, and B. Liu (2015) Catalytic conversion of fructose and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid over a recyclable Fe3O4–CoOx magnetite nanocatalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3: 406–412.
Bhalkikar, A., Z. C. Gernhart, and C. L. Cheung (2015) Recyclable magnetite nanoparticle catalyst for one-pot conversion of cellobiose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in water. J. Nanomater. 2015: 264037.
Hu, L., X. Tang, Z. Wu, L. Lin, J. Xu, N. Xu, and B. Dai (2015) Magnetic lignin-derived carbonaceous catalyst for the dehydration of fructose into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in dimethylsulfoxide. Chem. Eng. J. 263: 299–308.
Yin, S., J. Sun, B. Liu, and Z. Zhang (2015) Magnetic material grafted cross-linked imidazolium based polyionic liquids: An efficient acid catalyst for the synthesis of promising liquid fuel 5-ethoxymethylfurfural from carbohydrates. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3: 4992–4999.
Sawant, S. S., B. K. Salunke, T. K. Tran, and B. S. Kim (2016) Lignocellulosic and marine biomass as resource for production of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 33: 1505–1513.
Binod, P., R. Sindhu, R. R. Singhania, S. Vikram, L. Devi, S. Nagalakshmi, N. Kurien, R. K. Sukumaran, and A. Pandey (2010) Bioethanol production from rice straw: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 4767–4774.
Sawant, S. S., T. K. Tran, and B. S. Kim (2017) Potential of Saccharophagus degradans for production of polyhydroxyalkanoates using cellulose. Proc. Biochem. 57: 50–56.
Jung, Y. H., H. K. Kim, H. M. Park, Y.-C. Park, K. Park, J.-H. Seo, and K. H. Kim (2015) Mimicking the Fenton reactioninduced wood decay by fungi for pretreatment of lignocellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 179: 467–472.
Sluiter, A., B. Hames, R. Ruiz, C. Scarlata, J. Sluiter, and D. Templeton (2006) Determination of sugars, byproducts, and degradation products in liquid fraction process samples. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Technical Report NREL/TP-510-42623, http://www.nrel.gov/docs/gen/fy08/42623.pdf.
Graat, P. C. and M. A. Somers (1996) Simultaneous determination of composition and thickness of thin iron-oxide films from XPS Fe 2p spectra. Appl. Surf. Sci. 100: 36–40.
Xiong, Z., S. Li, and Y. Xia (2016) Highly stable water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles synthesized through combined coprecipitation, surface-modification, and decomposition of a hybrid hydrogel. New J. Chem. 40: 9951–9957.
Zhang, H., J. Li, W. Sun, Y. Hu, G. Zhang, M. Shen, and X. Shi (2014) Hyaluronic acid-modified magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MR imaging of surgically induced endometriosis model in rats. PLoS One 9: e94718.
Cai, C. M., N. Nagane, R. Kumar, and C. E. Wyman (2014) Coupling metal halides with a co-solvent to produce furfural and 5-HMF at high yields directly from lignocellulosic biomass as an integrated biofuels strategy. Green Chem. 16: 3819–3829.
Liu, L., J. Sun, C. Cai, S. Wang, H. Pei, and J. Zhang (2009) Corn stover pretreatment by inorganic salts and its effects on hemicellulose and cellulose degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 5865–5871.
Marcotullio, G., E. Krisanti, J. Giuntoli, and W. De Jong (2011) Selective production of hemicellulose-derived carbohydrates from wheat straw using dilute HCl or FeCl3 solutions under mild conditions. X-ray and thermo-gravimetric analysis of the solid residues. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 5917–5923.
Bobleter, O. (1994) Hydrothermal degradation of polymers derived from plants. Prog. Polym. Sci. 19: 797–841.
Sasaki, M., B. Kabyemela, R. Malaluan, S. Hirose, N. Takeda, T. Adschiri, and K. Arai (1998) Cellulose hydrolysis in subcritical and supercritical water. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 13: 261–268.
Mukherjee, A., M. J. Dumont, V. Raghavan (2015) Review: Sustainable production of hydroxymethylfurfural and levulinic acid: Challenges and opportunities. Biomass Bioenerg. 72: 143–183.
Moon, S. A., B. K. Salunke, B. Alkotaini, E. Sathiyamoorthi, and B. S. Kim (2015) Biological synthesis of manganese dioxide nanoparticles by Kalopanax pictus plant extract. IET Nanobiotechnol. 9: 220–225.
Salunke, B. K., S. S. Sawant, T. K. Kang, D. Y. Seo, Y. Cha, S. A. Moon, B. Alkotaini, E. Sathiyamoorthi, and B. S. Kim (2015) Potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as nanocatalyst for enhanced degradation of cellulose by cellulose. J. Nanomater. 2015: 289410.
Nadaf, N. Y. and S. S. Kanase (2016) Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by Bacillus marisflavi and its potential in catalytic dye degradation. Arab. J. Chem. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.09.020.
Li, L., C. Zeng, L. Ai, and J. Jiang (2015) Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-iron nanoparticles with superior enzyme mimetic activity for biosensing application. J. Alloy. Compd. 639: 470–477.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koo, H., Salunke, B.K., Iskandarani, B. et al. Improved degradation of lignocellulosic biomass pretreated by Fenton-like reaction using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioproc E 22, 597–603 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-017-0225-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-017-0225-x