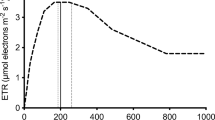
Abstract
Light quality is a significant environmental factor that influences photosynthetic pigments in cyanobacteria. In the present study, we illuminated the marine cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. with white (350 ∼ 700 nm), red (630 nm), green (530 nm), and blue (450 nm) light emitting diodes (LEDs) and measured pigment levels (chlorophyll, carotenoid, and phycobiliprotein) and expression of photosynthesis-related genes (pebA, psbB, and psaE). The amount of photosynthetic pigments (total pigments, chlorophyll, and phycobiliproteins) was higher in the green and blue LED groups than in the white and red LED groups after 8 days of culture. The cells were prepared in a 1.5 mL solution for the analysis of the total pigments, chlorophyll, and carotenoid, and in a 2 mL for analysis of phycobiliproteins. The mRNA expression levels of pebA and psbB significantly increased after 8 days of cultivation under green and blue light, while the mRNA expression levels of psaE decreased. These results indicate that green and blue light increase the accumulation of photosynthetic pigments. In contrast red light induced mRNA expression of psaE and stimulated cell growth in Synechococcus sp.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dring, M. J. (1988) Photocontrol of development in algae. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 39: 157–174.
Richardson, K., J. Beardall, and J. A. Raven (1983) Adaptations of unicellular algae to irradiance: An analysis of strategies. New Phytol. 93: 157–191.
Sánchez-Saavedra, M. P. and D. Voltolina (1994) The chemical composition of Chaetoceros sp. (Bacillariophyceae) under different light conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B107: 39–44.
Stomp, M., J. Huisman, L. Vörös, E. R. Pick, M. Laamanen, T. Haverkamp, and L. J. Stal (2007) Colourful coexistence of red and green picocyanobacteria in lakes and seas. Ecol. Lett. 10: 290–298.
Li, W. K. W. (1994) Primary production of prochlorophytes, cyanobacteria, and eukaryotic ultraphytoplankton: Measurements from flow cytometric sorting. Limnol. Oceanogr. 39: 169–175.
Liu, H. B., H. A. Nolla, and L. Campbell (1997) Prochlorococcus growth rate and contribution to primary production inthe equatorial and subtropical north pacific ocean. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 12: 39–47.
Vijaya, V. and N. Anand (2009) Blue light enhance the pigment synthesis in cyanobacterium Anabaena ambigua rao (nostacales). ARPN J. Agricul. Biol. Sci. 4: 1–8.
Bennet, A. and L. Bogorad (1973) Complementary chromatic adaptation in filamentous blue green algae. J. Cell Biol. 58: 419–433.
Tandeau, D. and N. T. Marsac (2003) Phycobiliproteins and phycobilisomes: The early observations. Photosynth. Res. 76: 197–205.
Morena, J., H. Rodriguey, V. A. Vargas, J. Rivas, and M. G. Guerrero (1995) Nitrogen fixing Cyanobacteria a source of phycobilin proteins pigments-composition and growth performance of then filamentous strains. J. Appl. Phycol. 7: 17–23.
Chaneva, G., S. Furnadzhieva, K. Minkova, and J. Lukavsky (2007) Effect of light and temperature on the cyanobacterium Arthronema africanum-a prospective hycobiliprotein-producing strain. J. Appl. Phycol. 19: 537–544.
Korbee, N., F. L. Figueroa, and J. Aguilera (2005) Effect of light quality on the accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, proteins and mycosporine-like amino acids in the red alga Porphyra leucosticta (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 80: 71–78.
Lönneporge, A., L. K. Lind, S. R. Kalla, P. Gustafsson, and G. Öquist (1985) Acclimation process in the light-harvesting system of cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans following a light shift from white to red light. Plant Physiol. 78: 110–114.
Millard, A., M. R. J. Clokie, D. A. Shub, and N. H. Mann (2004) Genetic organization of the psbAD region in phages infecting marine Synechococcus strains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101: 11007–11012.
Lindell, D., J. D. Jaffe, Z. I. Johnson, G. M. Church, and S. W. Chisholm (2005) Photosynthesis genes in marine viruses yield proteins during host infection. Nature 438: 86–89.
Alfonso, M., I. Perewoska, and D. Kirilovsky (2000) Redox controlof psbA gene expression in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803: Involvement of the cytochrome b6f complex. Plant Physiol. 122: 505–516.
Sullivan, M. B., M. L. Coleman, P. Weigele, F. Rohwer, and S. W. Chisholm (2005) Three Prochlorococcus cyanophage genomes: Signature features and ecological interpretations. PLoS Biol. 3: e144.
Barta, D. J., T. W. Tibitts, R. J. Bula, and R. C. Morrow (1992) Evaluation of light emitting diode characteristics for a space based plant irradiation source. Adv. Space. Res. 12: 141–149.
Matthijs, H. C. P., H. Balke, B. M. A. Van Hes Kroon, L. R. Mur, and R. A. Binot (1996) Application of light-emitting diodes in bioreactors: Flashing light effects and energy economy in algal culture (Chlorella pyrenoidosa). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 50: 98–107.
Schubert, E. F. (2003) Light-Emitting Diodes. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Shin, H. S., J. Lee, and C. Y. Choi (2011) Effects of LED light spectra on oxidative stress and the protective role of melatonin in relation to the daily rhythm of the yellowtail clownfish, Amphiprion clarkia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 160: 221–228.
Prézelin, B. B., H. F. Glover, B. Ver Hoven, D. Steingerg, H. A. Matlick, O. Schofield, N. Nelson, and M. Wyman (1989) Bluegreen light effects on light-limited rates of photosynthesis: Relationship to pigmentation and productivity estimates for Synechococcus population from the Sargasso Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 54: 121–136.
Walne, P. R. (1966) Experiments in the large-scale culture of the larvae of Ostrea edulis. L, Fishery Investigations (London) 25: 1–53.
Wellburn, A. R. (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 144: 307–313.
Blumwald, E. and E. Tel-Or (1982) Osmo regulation and cell composition in salt-adaptation of Nostoc muscorum. Arch. Microbiol. 132: 168–172.
Figueroa, F. L., J. Aguilera, and F. X. Niell (1995) Red and blue light regulation of growth and photosynthetic metabolism in Porphyra umbilicalis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 30: 11–18.
Wood, N. B. and R. Haselkorn (1980) Control of phycobiliprotein proteolysis and heterocyst differentiation in Anabaena. J. Bacteriol. 141: 1375–1385.
Elmorjani, K. and M. Herdman (1987) Metabolic control of phycocyanin degradation in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803: A glucose effect. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133: 1685–1694.
Botella-Pavía, P. and M. Rodríguez-Concepción (2006) Carotenoid biotechnology in plants fornutritionally improved foods. Physiol. Plant. 126: 369–381.
Stahl, W. and H. Sies (2003) Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Mol. Aspects Med. 24: 345–351.
Dall’Osto, L., C. Lico, J. Alric, G. Giuliano, M. Havaux, and R. Bassi (2006) Lutein is needed for efficient chlorophyll triplet quenching in the major LHCII antenna complex of higher plants and effective protoprotection in vivo under strong light. BMC Plant Biol. 6: 32–32.
Chen, M., Y. Li, D. Birch, and R. D. Willows (2012) A cyanobacterium that contains chlorophyll f-a red-absorbing photopigment. FEBS Lett. 586: 3249–3254.
Glover, H. E., M. D. Keller, and R. W. Spinrad (1987) The effects of light quality and intensity on photosynthesis and growth of marine eukaryotic and prokaryotic phytoplankton clones. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 105: 137–159.
Ashraf, M. and P. J. C. Harris (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: An overview. Photosynth. 21: 163–190.
Hauschild, C. A., M. C. Heather, H. J. G. Murter, and F. R. Pick (1991) Effect of spectral quality on growth and pigmentation of picocyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 27: 698–702.
Sauer, J., U. Schreiber, R. Schmid, U. Völker, and K. Forchhammer (2001) Nitrogen starvation-induced chlorosis in Synechococcus PCC 7942. Low-level photosynthesis as a mechanism of long-term survival. Plant Physiol. 126: 233–243.
Aidar, E., S. M. F. Gianesella-Galvão, T. C. S. Sigaud, C. S. Asano, T. H. Liang, K.R. V. Rezende, M. K. Oishi, F. J. Aranha, G. M Milani, and M. A. L. Sandes (1994) Effects of light quality on growth biochemical composition and photosynthetic production in Cyclotella caspia Grunov and Tetraselmisgracilis Kylin Butcher. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 180: 175–187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, N.N., Shin, H.S., Park, H.G. et al. Profiles of photosynthetic pigment accumulation and expression of photosynthesis-related genes in the marine cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp.: Effects of LED wavelengths. Biotechnol Bioproc E 19, 250–256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0700-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0700-y