Abstract
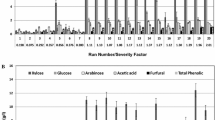
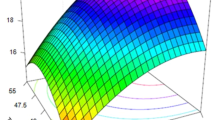
Hydrolytic conditions of rice hulls by acid and alkaline treatments before enzymatic saccharification were optimized in this study. Based on the results of single-factor experiments and an orthogonal array experiment, reaction time was found to be the most important factor for the acidic hydrolysis of rice hulls. Maximum yield of sugars from 1 g of rice hulls by acidic treatment under optimized conditions was 213.6 mg. The yield of lignin removal from acidic pretreated rice hulls by alkaline treatment increased with increase in reaction temperature and time. The amount of sugars obtained from 1 g of pretreated rice hulls by enzymatic saccharification was 307.7 mg, and the conversion rate of sugars from crude fibers in pretreated rice hulls was about 72%. Instrumental analyses with FTIR and SEM indicated that lignin in rice hulls was partially removed by alkaline treatment, and the structure of rice hulls became deformed and more fibers were exposed to cellulases after acidic treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray, K. A., L. Zhao, and M. Emptage (2006) Bioethanol. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 10: 141–146.
Jefferson, M. (2006) Sustainable energy development: performance and prospects. Renew. Energ. 31: 571–582.
Muratov, G. and C. Kim (2002) Enzymatic hydrolysis of cotton fibers in supercritical CO2. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 7: 85–88.
Mansfield, S. D., C. Mooney, and J. N. Saddler (1999) Substrate and enzyme characteristics that limit cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Prog. 15: 804–816.
Sun, Y. and J. Cheng (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 83: 1–11.
Mosier, N., C. Wyman, B. Dale, R. Elander, Y. Y. Lee, M. Holtzapple, and M. Ladisch (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 96: 673–686.
Lee, J. (1997) Biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol. J. Biotechnol. 56: 1–24.
Wyman, C. E., B. E. Dale, R. T. Elander, M. Holtzapple, M. R. Ladisch, and Y. Y. Lee (2005) Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies. Bioresour. Technol. 96: 1959–1966.
Jo, K. I., Y. J. Lee, B. K. Kim, B. H. Lee, C. H. Chung, S. W. Nam, S. K. Kim, and J. W. Lee (2008) Pilot-scale production of carboxymethylcellulase from rice hull by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DL-3. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 13:182–188.
Mansilla, H. D., J. Baeza, S. Urzua, G. Maturana, J. Villasenor, and N. Duran (1998) Acid-catalysed hydrolysis of rice hull: evaluation of furfural production. Bioresour. Technol. 66: 189–193.
Guo, Y. and D. A. Rockstraw (2006) Activated carbons prepared from rice hull by one-step phosphoric acid activation. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 100: 12–19.
Sharma, A., S. K. Khare, and M. N. Gupta (2001) Hydrolysis of rice hull by crosslinked Aspergillus niger cellulase. Bioresour. Technol. 78: 281–284.
Moniruzzaman, M. and L. O. Ingram (1998) Ethanol production from dilute acid hydrolysate of rice hulls using genetically engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Lett. 20: 943–947.
Saha, B. C. and M. A. Cotta (2008) Lime pretreatment, enzymatic saccharification, and fermentation of rice hulls to ethanol. Biomass Bioenerg. 32: 971–977.
Saha, B. C. and M. A. Cotta (2007) Enzymatic saccharification and fermentation of alkaline peroxide pretreated rice hulls to ethanol. Enz. Microb. Tech. 41: 528–532.
Matin, C., G. J. De M. Rocah, M. Perez, Y. Lopez, E. Hernadez, and Y. Plasencia (2007) Acid prehydroysis, alkaline delignification and enzymatic hydrolysis of rice hulls. Cellulose Chemi. Technol. 41: 129–135.
Miller, G. L. (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428.
Montgomery, D. C. (1991) Design and analysis of experiments. 3rd ed., pp. 417–423. John Wiley, NY, USA.
Palmqvist, E. and B. Hahn-Hägerdal (2000) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II: inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresour. Technol. 74: 25–33.
Ooshima, H., M. Kurakake, J. Kato, and Y. Harano (1991) Enzymatic activity of cellulase adsorbed on cellulose and its change during hydrolysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 31: 253–266.
Pandey, K. K. (1999) A study of chemical structure of softwood and hardwood. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 71: 1969–1975.
Chen, H. Z. (2005) Biotechnology of cellulose. pp. 23–36. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, China.
Gomare, S. S., J. P. Jadhav, and S. P. Govindwar (2008) Degradation of sulfonated azo dyes by the purified lignin peroxidase from Brevibacillus laterosporus MTCC 2298. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 13: 136–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, GY., Gao, W., Jin, IH. et al. Pretreatment and saccharification of rice hulls for the production of fermentable sugars. Biotechnol Bioproc E 14, 828–834 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0029-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-0029-8