Abstract
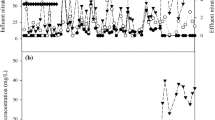
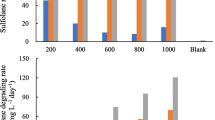
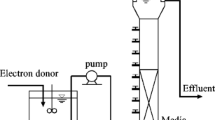
Spent sulfidic caustic was applied to sulfur utilizing autotrophic denitrification as the simultaneous source of electron donor and alkalinity. The two experiment set-up of upflow anoxic hybrid growth reactor (UAHGR) and upflow anoxic suspended growth reactor (UASGR) was adopted and nitrate removals were similar in both reactors. Approximately 90% of the initial nitrate was denitrified at nitrate loading rate of 0.15∼0.40 kgNO3 −/m3·d. The experimental stoichiometric ratio of sulfate production to nitrate removal was ranged from 1.5 to 2.1 mgSO4 2−/mgNO3 −. During the operation period, denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-amplified 16S rDNA fragments for the sludge sample of both reactors showed the change of microbial communities. Thiobacillus denitrificans-like microorganism occupied 28.5% (18 clones) of the 63 clones by cloning the PCR products from the sludge sample of UAHGR. Acidovorax avenae, which can reduce nitrate to nitrogen gas while oxidizing phenol (heterotrophic denitrifier), was also found in 7 clones (11.1%). Although an organic carbon source was not added to the medium, a microorganism (Kaistella koreensis) capable of oxidizing organic compounds was found in 7 clones (11.1%). Therefore, the microbial community of spent sulfidic caustic applied autotrophic denitrification process well corresponds to the substrate components of spent sulfidic caustic. Through the batch cultivation of microorganisms in UAHGR, the microbial kinetic coefficients of spent sulfidic caustic applied autotrophic denitrification were estimated to be µ max = 0.097 h−1, k d = 0.0021 h−1, K s = 200 mgNO3 −/L, and Y = 0.31 mgMLVSS/mgNO3 −.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whitmire, S. L. and S. K. Hamilton (2005) Rapid removal of nitrate and sulfate in freshwater wetland sediments. J. Environ. Qual. 34: 2062–2071.
van der Hoek, J. P., W. A. M. Hijnen, C. A. van Bennekom, and B. J. Mijnarends (1992) Optimization of the sulphur-limestone filtration process for nitrate removal from groundwater. J. Water SRT-Aqua 41: 209–218.
van der Hoek, J. P., J. W. N. M. Kappelhof, and W. A. M. Hijen (1992) Biological nitrate removal from ground water by sulphur/limestone denitrification. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 54: 197–200.
van der Hoek, J. P., J. W. N. M. Kappelhof, and J. C. Schippers (1994) The use of vacuum deaeration in bio logical nitrate removal processes. J. Water SRT-Aqua 43: 84–94.
Flere, J. M. and T. C. Zhang (1999) Nitrate removal with sulfur-limestone autotrophic denitrification processes. J. Environ. Eng. 125: 721–729.
Zhang, T. C. and D. G. Lampe (1999) Sulfur:limestone autotrophic denitrification processes for treatment of nitrate-contaminated water: batch experiments. Water Res. 33: 599–608.
Oh, S. E., Y. B. Yoo, J. C. Young, and I. S. Kim (2001) Effect of organics on sulfur-utilizing autotrophic denitrification under mixotrophic conditions. J. Biotechnol. 92: 1–8.
Koenig, A. and L. H. Liu (2002) Use of limestone for pH control in autotrophic denitrification: continuous flow experiments in pilot-scale packed bed reactors. J. Biotechnol. 99: 161–171.
Wang, H. and J. Qu (2003) Combined bioelectrochemi-cal and sulfur autotrophic denitrification for drinking water treatment. Water Res. 37: 3767–3775.
Sheu, S. H. and H. S. Weng (2001) Treatment of olefin plant spent caustic by combination of neutralization and fenton reaction. Water Res. 35: 2017–2021.
Sipma, J., A. Svitelskaya, B. van der Mark, L. W. Hulshoff Pol, G. Lettinga, C. J. N. Buisman, and A. J. H. Janssen (2004) Potentials of biologi-cal oxidation processes for the treatment of spent sulfidic caustics containing thiols. Water Res. 38: 4331–4340.
Byun, I. G. (2005) Application of Spent Sulfidic Caustic to Sulfur Utilizing Autotrophic Denitrification and Characterization of Microbial Community. Ph.D. Thesis. Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
MaCarty, P. L. (1972) Stoichiometry of biological reactions. International Conference toward a Unified Concept of Biological Waste Treatment Design.
Batchelor, B. and A. W. Lawrence (1978) A kinetic model for autotrophic denitrification using elemental sulfur. Water Res. 12: 1075–1084.
Koenig, A., T. Zhang, L. H. Liu, and H. H. P. Fang (2005) Microbial community and biochemistry process in autotrophic denitrifying biofilm. Chemosphere 58: 1041–1047.
Zhang, T. and H. H. P. Fang (2001) Phylogenetic diversity of a SRB-rich marine biofilm. Appl. Microbiol. Bio technol. 57: 437–440.
Fang, H. H. P., Y. Liu, S. Z. Ke, and T. Zhang (2004) Anaerobic degradation of phenol in wastewater at ambient temperature. Water Sci. Technol. 49: 95–102.
Lim, S. J., Y. H. Ahn, E. Y. Kim, and H. N. Chang (2006) Nitrate removal in a packed bed reactor using volatile fatty acids from anaerobic acidogenesis of food wastes. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11: 538–543.
Tran, H.-T., Y.-J. Park, M.-K. Cho, D.-J. Kim, and D.-H. Ahn (2006) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation process in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor with granular sludge selected from an anaerobic digestor. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11: 199–204.
APHA, AWWA, WEF (1992) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 18th ed., American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation, Washington, DC, USA.
Olaniran, A. O., S. Naidoo, M. G. Masango, and B. Pillay (2007) Aerobic biodegradation of 1,2-dichloroethane and 1,3-dichloropropene by bacteria isolated from a pulp mill wastewater effluent in South Africa. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 12: 276–281.
Holt, J. G., N. R. Krieg, P. H. A. Sneath, J. T. Staley, and S. T. Williams (1994) Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. 9th ed. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD, USA.
Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410.
Kelly, D. P. and A. P. Wood (2000) Confirmation of Thiobacillus denitrificans as a species of the genus Thiobacillus, in the β-subclass of the Proteobacteria, with strain NCIMB 9548 as the type strain. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 547–550.
Kim, M. K., W. T. Im, Y. K. Shin, J. H. Lim, S. H. Kim, B. C. Lee, M. Y. Park, K. Y. Lee, and S. T. Lee (2004) Kaistella koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the Chryseobacterium-Bergeyella-Riemerella branch. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54: 2319–2324.
Chouari, R., D. Le Paslier, P. Daegelen, P. Ginestet, J. Weissenbach, and A. Sghir (2005) Novel predominant archaeal and bacterial groups revealed by molecular analysis of an anaerobic sludge digester. Environ. Microbiol. 7: 1104–1115.
Baek, S. H., K. H. Kim, C. R. Yin, C. O. Jeon, W. T. Im, K. K. Kim, and S. T. Lee (2003) Isolation and characterization of bacteria capable of degrading phenol and reducing nitrate under low-oxygen conditions. Curr. Microbiol. 47: 462–466.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Byun, I., Park, J., Park, S. et al. Characterization of microbial community and kinetics for spent sulfidic caustic applied autotrophic denitrification. Biotechnol Bioproc E 13, 96–101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-007-0181-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-007-0181-y