Abstract
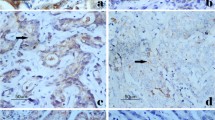
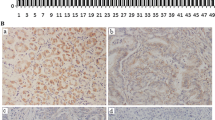
YAP1 is overexpressed in numerous cancers, but its molecular mechanism in the carcinogenesis and clinic significance in tumor diagnosis and prognosis remains to be determined. We attempted to analyze the clinicopathologic significance of YAP1 expression and the correlation of the YAP1 levels with the progression, metastasis and prognosis of patients with gastric carcinoma. By immunohistochemistry, we determined YAP1 expression in 214 of primary gastric carcinoma (GC), 167 of matched normal gastric mucosa, 40 of chronic atrophic gastritis, 11 of dysplasia and 73 of intestinal metaplasia. The positive rate of YAP1 in gastric carcinoma was significantly higher than that in normal gastric mucosa, chronic atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia. In the gastric cancers with lymph node metastasis, the positive rate of YAP1 was much higher than that in the group without lymph node metastasis. Moreover, gastric cancer patients with YAP1 overexpression demonstrated poorer prognosis than those with YAP1 negative staining. Finally, multivariate analysis of 191 patients with gastric carcinoma indicated that YAP1 overexpression, the invasion depth and lymph node metastasis were high hazard factors for gastric carcinoma. Our results demonstrated that YAP1 overexpression is correlated to the progression, lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of gastric carcinoma, suggesting that overexpression of YAP1 might be an adjuvant factor for predicting lymph node metastasis, and a useful biomarker for the diagnosis and prediction of prognosis in patients with gastric cancers.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAG:
-
Chronic atrophic gastritis
- Dys:
-
Dysplasia
- ESCC:
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GC:
-
Gastric carcinoma
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- IM:
-
Intestinal metaplasia
- SRC:
-
Signet ring cell carcinoma
- YAP1:
-
Yes-associated protein 1
References
Jackson C, Cunningham D, Oliveira J (2009) Gastric cancer: ESMO clinical recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 20:34–36
Thun MJ, DeLancey JO, Center MM, Jemal A, Ward EM (2010) The global burden of cancer: priorities for prevention. Carcinogenesis 31:100–110
Zhao B, Wei X, Li W, Udan RS, Yang Q, Kim J, Xie J, Ikenoue T, Yu J, Li L, Zheng P, Ye K, Chinnaiyan A, Halder G, Lai ZC, Guan KL (2007) Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev 21:2747–2761
Dong J, Feldmann G, Huang J, Wu S, Zhang N, Comerford SA, Gayyed MF, Anders RA, Maitra A, Pan D (2007) Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in drosophila and mammals. Cell 130:1120–1133
Zender L, Spector MS, Xue W, Flemming P, Cordon-Cardo C, Silke J, Fan ST, Luk JM, Wigler M, Hannon GJ, Mu D, Lucito R, Powers S, Lowe SW (2006) Identification and validation of oncogenesin liver cancer using an integrative oncogenomic approach. Cell 125:1253–1267
Zhang X, George J, Deb S, Degoutin JL, Takano EA, Fox SB, AOCS Study group, Bowtell DD, Harvey KF (2011) The Hippo pathway transcriptional co-activator, YAP, is an ovarian cancer oncogene. Oncogene 30:2810–2822
Goulev Y, Fauny JD, Gonzalez-Marti B, Flagiello D, Silber J, Zider A (2008) SCALLOPED interacts with YORKIE, the nuclear effector of the Hippo tumor-suppressor pathway in Drosophila. Curr Biol 18:435–441
Zhang L, Ren F, Zhang Q, Chen Y, Wang B, Jiang J (2008) The TEAD/TEF family of transcription factor Scal-loped mediates Hippo signaling in organ size control. Dev Cell 14:377–387
Wu S, Liu Y, Zheng Y, Dong J, Pan D (2008) TheTEAD/TEF family protein Scalloped mediates transcrip-tional output of the Hippo growth-regulatory pathway. Dev Cell 14:388–398
Huang J, Wu S, Barrera J, Matthews K, Pan D (2005) The Hipposignaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Dro sophila homolog of YAP. Cell 122:421–434
Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR (2007) YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr Biol 17:2054–2060
Overholtzer M, Zhang J, Smolen GA, Muir B, Li W, Sgroi DC, Deng CX, Brugge JS, Haber DA (2006) Transforming properties of YAP, a candidate oncogene on the chromosome 11q22 amplicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12405–12410
Tufail R, Jorda M, Zhao W, Reis I, Nawaz Z (2011) Loss of Yes-associated protein (YAP) expression is associated with estrogen and progesterone receptors negativity in invasive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131:743–750
Steinhardt AA, Gayyed MF, Klein AP, Dong J, Maitra A, Pan D, Montgomery EA, Anders RA (2008) Expression of Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum Pathol 39:1582–1589
Zhang J, Ji JY, Yu M, Overholtzer M, Smolen GA, Wang R, Brugge JS, Dyson NJ, Haber DA (2009) YAP-dependent induction of amphiregulin identifies a non-cell-autonomous component of the Hippo pathway. Nat Cell Biol 11:1444–1450
Xu MZ, Yao TJ, Lee NP, Ng IO, Chan YT, Zender L, Lowe SW, Poon RT, Luk JM (2009) Yes-associated protein is an independent prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 115:4576–4585
Lam-Himlin DM, Daniels JA, Gayyed MF, Dong J, Maitra A, Pan D, Montgomery EA, Anders RA (2006) The hippo pathway in human upper gastrointestinal dysplasia and carcinoma: a novel oncogenic pathway. Int J Gastrointest Cancer 37:103–109
Kang W, Tong JH, Chan AW, Lee TL, Lung RW, Leung PP, So KK, Wu K, Fan D, Yu J, Sung JJ, To KF (2011) Yes-associated protein 1 exhibits oncogenic property in gastric cancer and its nuclear accumulation associates with poor prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 17:2130–2139
Da CL, Xin Y, Zhao J, Luo XD (2009) Significance and relationship between Yes-associated protein and survivin expression in gastric carcinoma and precancerous lesions. World J Gastroenterol 15:4055–4061
Song M, Cheong JH, Kim H, Noh SH, Kim H (2012) Nuclear expression of Yes-associated protein 1 correlates with poor prognosis in intestinal type gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 32:3827–3834
Zhang J, Xu ZP, Yang YC, Zhu JS, Zhou Z, Chen WX (2012) Expression of Yes-associated protein in gastric adenocarcinoma and inhibitory effects of its knockdown on gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 25:583–590
Zhang J, Yang YC, Zhu JS, Zhou Z, Chen WX (2012) Clinicopathologic characteristics of YES-associated protein 1 overexpression and its relationship to tumor biomarkers in gastric cancer. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 25:977–987
Zhou GX, Li XY, Zhang Q, Zhao K, Zhang CP, Xue CH, Yang K, Tian ZB (2013) Effects of the hippo signaling pathway in human gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:5199–5205
Authors’ Contributions
XY and HXB conceived the study and drafted the manuscript. HXB, XYP and ZJ collected and analyzed the data. XY secured funding. XY, HXB and XYP contributed to the quality control of study inclusion and discussion. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Grant Support
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.81071650; 30973503); Special foundation for Science and Technology Program in Liaoning Province, China (2013225303-103); the Supporting Project for Climbing Scholars in Liaoning Provincial Universities, China (2009-2012).
Conflict of Interest
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Xin, Y., Xiao, Y. et al. Overexpression of YAP1 is Correlated with Progression, Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Gastric Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 805–811 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9757-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9757-y