Abstract
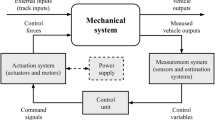
In this study, a vehicle velocity estimation algorithm for an in-wheel electric vehicle is proposed. This algorithm estimates the vehicle velocity using the concept of effective inertia, which is based on the motor torque, the angular velocity of each wheel and vehicle acceleration. Effective inertia is a virtual mass that changes according to the state of a vehicle, such as acceleration, deceleration, turning or driving on a low friction road. The performance of the proposed vehicle velocity estimation algorithm was verified in various conditions that included straight driving, circle driving and low friction road driving using the in-wheel electric vehicle that was equipped with an in-wheel system in each of its rear wheels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao, X., Yu, Z. and Xu, T. (2008). Longitudinal velocity estimation for an electric vehicle with four in-wheel motors. SAE Paper No. 2008-01-0605.
Hori, Y. (2004). Future vehicle driven by electricity and control-research on four-wheel-motored “UOT electric march II”. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 51, 5, 954–962.
Hwang, J. K. and Song, C. K. (2005). Fuzzy estimation of vehicle speed an accelerometer and wheel sensors. Int. J. Automotive Technology 6, 4, 359–365.
Hwang, J. K., Uchanski, M. and Song, C. K. (2005). Vehicle speed estimation based on Kalman filtering of accelerometer and wheel speed measurements. Int. J. Automotive Technology 6, 5, 475–481.
Imsland, L., Johansen, T. A. and Fossen, T. I. (2006a). Nonlinear observer for vehicle velocity estimation. SAE Paper No. 2006-01-1285.
Imsland, L., Johansen, T. A., Fossen, T. I., Grip, H. F. and Kalkkuhl, J. C. (2006b). Vehicle velocity estimation using nonlinear observers. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics, Automatica, 42, 2091–2103.
Kim, J., Park, C., Hwang, S., Hori, Y. and Kim, H. (2010). Control algorithm for an independent motor-drive vehicle. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology 59, 7, 3213–3222.
Li, L., Song, J., Kong, L. and Huang, Q. (2009). Vehicle velocity estimation for real-time dynamic stability control. Int. J. Automotive Technology 10, 6, 675–685.
Mei, T. X. and Li, H. (2010). Measurement of absolute vehicle speed with a simplified inverse model. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology 59, 3, 1164–1171.
Mutoh, N., Nishida, O. and Takayanagi, T. (2010). Driving torque distribution method for front- and rear-wheel independent-drive-type electric vehicles (FRID EVs) at the time of cornering. EVS-25.
Song, C. K., Uchanski, M. and Hedrick, J. K. (2002). Vehicle speed estimation using accelerometer and wheel speed measurements. SAE Paper No. 2002-01-2229.
Wu, L. J. (2011). Experimental study on vehicle speed estimation using accelerometer and wheel speed measurements. Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering (MACE), 294–297.
Zhao, L. H., Liu, Z. Y. and Chen, H. (2011). Design of a nonlinear observer for vehicle velocity estimation and experiments. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology 19, 3, 664–672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, S.Y., Ko, J.W., Lee, S.M. et al. Vehicle velocity estimation using effective inertia for an in-wheel electric vehicle. Int.J Automot. Technol. 15, 815–821 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-014-0085-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-014-0085-8