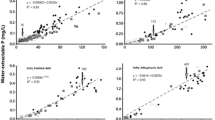
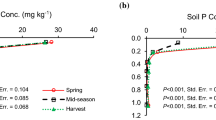
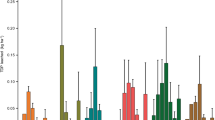
Abstract
Phosphorus (P) losses from agricultural systems are a cause of degraded surface water quality of lakes and streams. In freshwater systems, P is often the most limiting nutrient for algae growth and an increase in P additions to these systems can cause a shift in ecology. These shifts can result in a degradation of the water resource as habitat or for recreation. In an effort to combat the negative effects of agriculture management practices on surface water quality, federal and state regulations require some level of assessment to guide P applications. Areas with large amounts of potato production are of particular concern with respect to P loss since potatoes are a high P demanding crop and are inefficient users of applied P. In many cases, soils in potato production are managed with a higher soil test P concentration compared to other crops and P applications for optimum production exceed P removal. When potato production fields are maintained at high soil test P levels, this may increase the risk of P loss in runoff. However, based on soils and landscape positions where potatoes are grown, there may be little risk of transport. While there appears to be little risk of P loss on low-sloping, sandy soils, output from the Wisconsin Phosphorus Index suggests that more steeply sloping fields can pose some risk, especially when soil test P concentrations exist at above optimum levels. At high soil test P levels, no P may be required for optimum yield in rotated crops, but production practices of these crops may need to be altered to reduce P losses. Furrow-irrigated and tile-drained fields may also pose risks of P loss to the environment. While the P demands of potato are greater than those for most crops, it is likely that most of this P will not be exported via surface runoff. Careful management considerations must be made when producing potatoes on high sloping soils, especially those close to surface water bodies. Future considerations of P management and water quality will focus on assessing leaching risk of P and this contribution to surface waters.
Resumen
Las pérdidas de fósforo (P) de sistemas agrícolas son una causa de degradación en la calidad del agua superficial de lagos y corrientes. En los sistemas de agua dulce, el P es a menudo el nutriente más limitante para el crecimiento de algas y un aumento en la adición de P a estos sistemas puede causar un cambio en la ecología. Estos cambios pueden resultar en degradación del recurso hídrico como hábitat o para recreación. En un esfuerzo para combatir los efectos negativos de prácticas de manejo en agricultura en la calidad del agua superficial, las regulaciones federales y estatales requieren algún nivel de análisis para guiar las aplicaciones de P. Las áreas con grandes cantidades de producción de papa son de preocupación particular con respecto a pérdida de P, ya que las papas son un cultivo de alta demanda de P y usan ineficientemente el P aplicado. En muchos casos, los suelos en la producción de papa se manejan con una concentración más alta de P en suelos probados en comparación con otros cultivos, y las aplicaciones de P para producción óptima exceden a su remoción. Cuando los campos de producción de papa se mantienen a altos niveles de P en el suelo, esto pudiera aumentar el riesgo de pérdida de P por lixiviación. No obstante, con base en los suelos y posiciones en el paisaje donde se cultivan las papas, pudiera haber poco riesgo de transporte. Mientras que aparentemente pudiera haber poco riesgo en pérdida de P en suelos arenosos, de laderas suaves, la información del Índice de Fósforo de Wisconsin sugiere que campos con mayor inclinación pudieran representar algún riesgo, especialmente cuando las concentraciones probadas de P existen por encima de los niveles óptimos. A altos niveles de P, pudiera no requerirse para rendimiento óptimo en cultivos en rotación, pero las prácticas de producción de estos cultivos pudieran necesitar alteración para reducir pérdidas de P. Campos de riego por surcos y con drenaje con losas pudieran también representar riesgos de pérdida de P al ambiente. Mientras que las demandas de P en papa son mayores que las de la mayoría de los cultivos, es probable que la mayor parte de este P no se exportará por vía de lixiviación superficial. Deben de hacerse consideraciones cuidadosas de manejo al producir papas en suelos de grandes inclinaciones, especialmente aquellos cercanos a los cuerpos de agua superficial. Futuras consideraciones en el manejo de P y calidad del agua se enfocarán en el análisis de riesgo de lixiviación de P y su contribución a aguas superficiales.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andraski, T.W., and L.G. Bundy. 2003. Relationships between phosphorus levels in soil and in runoff from corn production systems. Journal of Environmental Quality 32: 310–316.
Andraski, B.J., D.H. Mueller, and T.C. Daniel. 1985. Phosphorus losses in runoff as affected by tillage. Soil Science Society of America Journal 49: 1523–1527.
Barber, S.A. 1995. Soil nutrient bioavailability—A mechanistic approach, 2nd ed. New York: Wiley.
Berg, R.D., and D.L. Carter. 1980. Furrow erosion and sediment losses on irrigated cropland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 35: 267–270.
Bishop, R.F., C.R. MacEachern, and D.C. MacKay. 1967. The relation of soil test values to fertilizer response by the potato. IV. Available phosphorus and phosphatic fertilizer requirements. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 47: 175–185.
Bjorneberg, D.L., D.T. Westermann, and J.K. Aase. 2002. Nutrient losses in surface irrigation runoff. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 57: 524–529.
Brown, M.J., C.W. Robbins, and L.L. Freeborn. 1998. Combining cottage cheese whey and straw reduces erosion while increasing infiltration in furrow irrigation. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 53: 152–156.
Brye, K.R., T.W. Andraski, W.M. Jarrell, L.G. Bundy, and J.M. Norman. 2002. Phosphorus leaching under a restored tallgrass prairie and corn agroecosystems. Journal of Environmental Quality 31: 769–781.
Buczko, U., and R.L. Kuchenbuch. 2007. Phosphorus indices as risk-assessment tools in the USA and Europe—A review. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science 170: 445–460.
Buda, A.R., P.J.A. Kleinman, M.S. Srinivasan, R.B. Bryant, and G.W. Feyerecsen. 2009. Effects of hydrology and field management on phosphorus transport in runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality 38: 2273–2284.
Bundy, L.G., and S.J. Sturgul. 2001. A phosphorus budget for Wisconsin cropland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 56: 243–249.
Bundy, L.G., T.W. Andraski, and J.M. Powell. 2001. Management practice effects on phosphorus losses in runoff in corn production systems. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 1822–1828.
Chien, S.H., L.I. Pronchnow, S. Tu, and C.S. Snyder. 2011. Agronomic and environmental aspects of phosphate fertilizer varying in source and solubility: An update review. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 89: 229–255.
Chow, L., Z. Xing, G. Benoy, H.W. Rees, F. Meng, Y. Jiang, and J.L. Raigle. 2011. Hydrology and water quality across gradients of agricultural intensity in the Little River watershed area, New Brunswick, Canada. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 66: 71–84.
Cogger, C., and J.M. Duxbury. 1984. Factors affecting phosphorus losses from cultivated organic soils. Journal of Environmental Quality 13: 111–114.
Correll, D.L. 1998. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 261–266.
Cox, F.R., and S.E. Hendricks. 2000. Soil test phosphorus and clay content effects on runoff water quality. Journal of Environmental Quality 29: 1582–1586.
Cox, J.W., C.A. Kirby, D.J. Chittleborough, L.J. Smythe, and N.K. Fleming. 2000. Mobility of phosphorus through intact soil cores collected from the Adelaide Hills, South Australia. Australian Journal of Soil Research 38: 973–990.
Cross, A.F., and W.H. Schlesinger. 1995. A literature review and evaluation of the Hedley fractionation: Applications to the biogeochemical cycle of soil phosphorus in natural ecosystems. Geoderma 64: 197–214.
Daniel, T.C., D.R. Edwards, and A.N. Sharpley. 1993. Effect of extractable soil surface phosphorus on runoff water quality. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 36: 1079–1085.
Daniel, T.C., A.N. Sharpley, and J.L. Lemunyon. 1998. Agricultural phosphorus and eutrophication: A symposium overview. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 251–257.
Davenport, J.R., P.H. Milburn, C.J. Rosen, and R.E. Thornton. 2005. Environmental impacts of potato nutrient management. American Journal of Potato Research 82: 321–328.
Dils, R.M., and A.L. Heathwaite. 1999. The controversial role of tile drainage in phosphorus export from agricultural land. Water Science and Technology 39: 55–61.
Djodjic, F., L. Berstrom, B. Ulen, and A. Shirmohammadi. 1999. Mode of transport of surface-applied phosphorus-33 through a clay and sandy soil. Journal of Environmental Quality 28: 1273–1282.
Dorich, R.A., D.W. Nelson, and L.E. Sommers. 1980. Algal availability of sediment phosphorus in drainage water of the Black Creek Watershed agricultural runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality 9: 557–562.
Dunn, A.M., G. Julien, W.R. Ernst, A. Cook, K.G. Doe, and P.M. Jackman. 2011. Evaluation of buffer zone effectiveness in mitigating the risks associated with agricultural runoff in Prince Edward Island. Science of the Total Environment 409: 868–882.
Ebeling, A., K. Kelling, and L. Bundy. 2002. Phosphorus management on high phosphorus soils. New Horizons in Soil Science 2002–12. Department of Soil Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Edwards, W.M., and L.B. Owens. 1991. Large storm effects on total soil erosion. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 46: 75–77.
Eghball, B., and J.E. Gilley. 1999. Phosphorus and nitrogen in runoff following beef cattle manure or compost application. Journal of Environmental Quality 28: 1201–1210.
Eghball, B., G.D. Binford, and D.D. Baltensperger. 1996. Phosphorus movement and adsorption in a soil receiving long-term manure and fertilizer application. Journal of Environmental Quality 25: 1339–1343.
Eghball, B., J.E. Gilley, L.A. Kramer, and T.B. Moorman. 2000. Narrow grass hedge effects on phosphorus and nitrogen in runoff following manure and fertilizer application. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 55: 172–176.
Gburek, W.J., and A.N. Sharpley. 1998. Hydrologic controls on phosphorus loss from agricultural watersheds. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 267–277.
Gburek, W.J., A.N. Sharpley, L. Heathwaite, and G.J. Folmar. 2000. Phosphorus management at the watershed scale: a modification of the phosphorus index. Journal of Environmental Quality 29: 130–144.
Ginting, D., J.F. Moncrief, S.E. Gupta, and S.D. Evans. 1998. Corn yield, runoff, and sediment losses from manure and tillage systems. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 1396–1402.
Good, L.W., J. Panuska, and P. Vadas. 2010. Current calculations in the Wisconsin P index. Available at: http://wpindex.cals.wisc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/PIndexCalc_11_18_20101.pdf.
Good, L.W., P. Vadas, J. Panuska, C.A. Bonilla, and W.E. Jokela. 2012. Testing the Wisconsin phosphorus index with year-round, field-scale runoff monitoring. Journal of Environmental Quality 41: 1730–1740.
Hansen, H.C.B., P.E. Hansen, and J. Magid. 1999. Empirical modeling of the kinetics of phosphate sorption to macropore materials in aggregated subsoils. European Journal of Soil Science 50: 317–327.
Hart, M.R., B.F. Quin, and M.L. Nguyen. 2004. Phosphorus runoff from agricultural land and direct fertilizer effects: A review. Journal of Environmental Quality 33: 1954–1972.
Heathwaite, A.L., and R.M. Dils. 2000. Characterizing phosphorus loss in surface and subsurface hydrological pathways. Science of the Total Environment 251: 523–538.
Heckrath, G., P.C. Brookes, P.R. Poulton, and K.W.T. Goulding. 1995. Phosphorus leaching from soils containing different phosphorus concentrations in the Broadbalk experiment. Journal of Environmental Quality 24: 904–910.
Hesketh, N., and P.C. Brookes. 2000. Development of an indicator for risk of phosphorus leaching. Journal of Environmental Quality 29: 105–110.
Hopkins, G.B., D.A. Horneck, M.J. Pavek, B.D. Geary, N.L. Olsen, J.W. Ellsworth, G.D. Newberry, J.S. Miller, R.E. Thornton, and G.W. Harding. 2007. Evaluation of potato production best management practices. American Journal of Potato Research 84: 19–27.
Hopkins, B.G., D.A. Horneck, and A.E. MacGuidwin. 2013. Phosphorus use efficiency in potato: Rhizosphere modification and extension. American Journal of Potato Research (this issue).
Hudson, N. 1995. Soil conservation, 3rd ed. London: B.T. Batsford Limited.
Humphreys, F.R., and W.L. Pritchett. 1971. Phosphorus adsorption and movement in some sandy forest soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 35: 495–500.
International Plant Nutrition Institute (IPNI). 2010. Soil test levels in North America. IPNI Publication 30–3110. Norcross: International Plant Nutrition Institute.
Kelling, K.A., R.P. Wolkowski, J.G. Iyer, R.B. Corey, and W.R. Stevenson. 1992. Potato responses to phosphorus application and using petiole analysis in determine P status. Proceedings of the Wisconsin Annual Potato Meetings 5: 39–50.
Kimmel, R.J., G.M. Pierzynski, K.A. Janssen, and P.L. Barnes. 2001. Effects of tillage and phosphorus placement on phosphorus runoff losses in a grain sorghum-soybean rotation. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 1324–1330.
Kleinman, P.J.A., B.A. Needelman, A.N. Sharpley, and R.W. McDowell. 2003. Using soil phosphorus profile data to assess phosphorus leaching potential in manured soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 67: 215–224.
Kotak, B.G., S.L. Kenefick, D.L. Fritz, C.G. Rousseaux, E.E. Prepas, and S.E. Hrudey. 1993. Occurrence and toxicological evaluation of cyanobacterial toxins in Alberta lakes and farm dugouts. Water Resources 27: 495–506.
Kung, K.J.S., T.S. Steenhuis, E.J. Kladivko, T.J. Gish, G. Bubenzer, and C.S. Helling. 2000. Impact of preferential flow on the transport of adsorbing and non-adsorbing tracers. Soil Science Society of America Journal 64: 1290–1296.
Laboski, C.A.M., and J.B. Peters. 2012. Nutrient application guidelines for field, vegetable and fruit crops in Wisconsin. Madison, Wisconsin: University of Wisconsin-Extension, Publication A2809.
Lang, N.S., R.G. Stevens, R.E. Thornton, W.L. Pan, and S. Victory. 1999. Potato nutrient management for central Washington. Pullman, Washington: Cooperative Extension, Washington State University EB1871.
Lawton, L.A., and G.A. Codd. 1991. Cyanobacterial (blue-green algae) toxins and their significance in UK and European waters. Journal of the Institution of Water and Environmental Management 5: 460–465.
Lemunyon, J.L., and R.G. Gilbert. 1993. The concept and need for a phosphorus assessment tool. Journal of Production Agriculture 6: 483–496.
Lentz, R.D., R.E. Sojka, and C.W. Robbins. 1998. Reducing phosphorus losses from surface-irrigated fields: Emerging polyacrylamide technology. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 305–312.
Maguire, R.O., and J.T. Sims. 2002. Soil testing to predict phosphorus leaching. Journal of Environmental Quality 31: 1601–1609.
McDowell, R., A. Sharpley, and G. Folmar. 2001. Phosphorus export from an agricultural watershed: Linking source and transport mechanisms. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 1587–1595.
Miller, M.H. 1979. Contribution of nitrogen and phosphorus to subsurface drainage water from intensively cropped mineral and organic soils in Ontario. Journal of Environmental Quality 8: 42–48.
Moncrief, J.M, P.L. Bloom, N. Hansen, D. Mulla, P. Bierman, A. Birr, and M. Mozaffarri. 2006. Minnesota phosphorus site risk index technical guide. Department of Soil, Water, and Climate, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota.
Mozaffari, M., and J.T. Sims. 1994. Phosphorus availability and sorption in an Atlantic coastal plain watershed dominated by animal-based agriculture. Soil Science 157: 97–107.
Mueller, D.H., R.C. Wendt, and T.C. Daniel. 1984. Phosphorus losses as affected by tillage and manure application. Soil Science Society of America Journal 54: 1702–1711.
Nair, V.D., K.M. Portier, D.A. Graetz, and M.L. Walker. 2004. An environmental threshold for degree of phosphorus saturation in sandy soils. Journal of Environmental Quality 33: 277–293.
Ozanne, P.G. 1980. Phosphate nutrition of plants—A general treatise. In The role of phosphorus in agriculture, ed. F.E. Khasawneh, E.C. Sample, and E.I. Kamprath, 559–589. Madison: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America.
Parry, R. 1998. Agricultural phosphorus and water quality: A U.S. Environmental Protection Agency perspective. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 258–261.
Pote, D.H., T.C. Daniel, A.N. Sharpley, P.A. Moore Jr., D.R. Edwards, and D.J. Nichols. 1996. Relating extractable soil phosphorus to phosphorus losses in runoff. Soil Science Society of America Journal 60: 855–859.
Pote, D.H., T.C. Daniel, D.J. Nichols, A.N. Sharpley, P.A. Moore Jr., D.M. Miller, and D.R. Edwards. 1999. Relationship between phosphorus levels in three Ultisols and phosphorus concentration in runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality 28: 170–175.
Quinton, J.N., J.A. Catt, and T.M. Hess. 2001. The selective removal of phosphorus from soil: Is event size important? Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 538–545.
Repking, M.J. 2008. Investigation of phosphorus requirement of potato in Wisconsin and phosphorus leaching potential in the central sands. M.S. Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Romkens, M.J.M., D.W. Nelson, and J.V. Mannering. 1973. Nitrogen and phosphorus composition of surface runoff as affected by tillage method. Journal of Environmental Quality 2: 292–295.
Rosen, C.J., K.A. Kelling, J.C. Stark, and G.A. Porter. 2013. Optimizing phosphorus fertilizer management in potato production. American Journal of Potato Research (this issue).
Ryden, J.C., J.K. Syers, and R.F. Harris. 1973. Phosphorus in runoff and streams. Advances in Agronomy 25: 1–45.
Sanderson, J.B., J.A. MacLeod, B. Douglas, R. Coffin, and T. Bruulsema. 2003. Phosphorus research in potato in PEI. Acta Horticulturae 619: 409–417.
Sawyer, C.N. 1947. Fertilization of lakes by agricultural and urban drainage. Journal of New England Water Works Association 61: 109–127.
Schinder, D.W. 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Sharkoff, J.L., J.G. Davis, and T.A.B.auder. 2012. Colorado phosphorus index risk assessment, Version 5. Agronomy Technical Note No. 95 (revised). USDA-NRCS State of Colorado. Available at: http://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/CO/COATN_95.pdf.
Sharpley, A.N. 1995. Dependence of runoff phosphorus on extractable soil phosphorus. Journal of Environmental Quality 24: 920–926.
Sharpley, A.N., and P.J.A. Withers. 1994. The environmentally-sound management of agricultural phosphorus. Fertilizer Research 39: 133–146.
Sharpley, A.N., S.J. Smith, O.R. Jones, W.A. Berg, and G.A. Coleman. 1992. The transport of bioavailable phosphorus in agricultural runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality 21: 30–35.
Sharpley, A.N., T.C. Daniel, and D.R. Edwards. 1993. Phosphorus movement in the landscape. Journal of Production Agriculture 6: 492–500.
Sharpley, A.N., S.C. Chapra, R. Wedepohl, J.T. Sims, T.C. Daniel, and K.R. Reddy. 1994. Managing agricultural phosphorus for protection of surface waters: Issues and options. Journal of Environmental Quality 23: 437–451.
Sharpley, A.N., T.C. Daniel, J.T. Sims, J.L. Lemunyon, R.G. Stevens, and R. Parry. 1999. Agricultural phosphorus and eutrophication. Washington DC: Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, ARS-149. 42 pp.
Sharpley, A.N., R.W. McDowell, and P.J. Kleinman. 2001. Phosphorus loss from land to water: Integrating agricultural and environmental management. Plant and Soil 237: 287–307.
Sharpley, A.N., J.L. Weld, D.B. Beegle, P.J.A. Kleinman, W.J. Gburek, F.A. Moore Jr., and G. Mullins. 2003. Development of phosphorus indices for nutrient management planning strategies in the United States. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 58: 137–152.
Sharpley, A.N., P.J.A. Kleinman, P. Jordan, L. Bergstrom, and A.L. Allen. 2009. Evaluating the success of phosphorus management from field to watershed. Journal of Environmental Quality 38: 1981–1988.
Sharpley, A.N., D. Beegle, C. Bolster, L. Good, B. Joern, Q. Ketterings, J. Lory, R. Mikkelsen, D. Osmond, and P. Vadas. 2012. Phosphorus indices: Why we need to take stock of how we are doing. Journal of Environmental Quality 41: 1711–1719.
Shepard, R. 2000. Nitrogen and phosphorus management on Wisconsin farms: Lessons learned for agricultural water quality programs. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 55: 63–68.
Shi, X.N., L.S. Wu, W.P. Chien, and Q.J. Wang. 2011. Solute transfer from the soil surface to overland flow: A review. Soil Science Society of America Journal 75: 1214–1225.
Simard, R.R., S. Beauchemin, and P.M. Haygarth. 2000. Potential for preferential pathways of phosphorus transport. Journal of Environmental Quality 29: 97–105.
Sims, J.T. 1998. Phosphorus soil testing: Innovation for water quality protection. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 29: 1471–1489.
Sims, J.T., R.R. Simard, and B.C. Joern. 1998. Phosphorus loss in agricultural drainage: Historical perspective and current research. Journal of Environmental Quality 27: 277–293.
Sims, J.T., A.C. Edwards, O.F. Schoumans, and R.R. Simard. 2000. Integrating soil phosphorus testing into environmentally based agricultural management practices. Journal of Environmental Quality 29: 60–71.
Sinaj, S., C. Stamm, G.S. Toor, L.M. Condron, T. Hendry, H.J. Di, K.C. Cameron, and E. Frossard. 2002. Phosphorus extractability and leaching losses from two grassland soils. Journal of Environmental Quality 31: 319–330.
Spencer, W.F. 1957. Distribution and availability of phosphates added to a Lakeland fine sand. Soil Science Society of America Journal 21: 141–144.
Stark, J., D. Westermann, and B. Hopkins. 2004. Nutrient management guidelines for Russet Burbank potatoes. Moscow, Idaho, University of Idaho Extension Bulletin 840.
Sullivan, D.M., and R.G. Stevens. 2003. Agricultural phosphorus management using the Oregon/Washington phosphorus indexes. Oregon State University Extension Service EM 8848-E. Available at: http://extension.oregonstate.edu/catalog/pdf/em/em8848-e.pdf.
Trout, T.J. 1996. Furrow irrigation erosion and sedimentation: On-field distribution. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineering 39: 1717–1723.
U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). 1998. Farm and ranch irrigation survey. In 1997 Census of agriculture, Vol. 3 – Special studies. Washington DC: USDA, National Agricultural Statistics Service. 148 pp.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). 1996. Clean water action plan: Restoring and protecting America’s waters. Washington DC: Environmental Protection Agency.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). 2009. National water quality inventory: Report to Congress. Report EPA 841-R-08–001. Washington DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 37 pp.
USDA-Natural Resource Conservation Service. 2013b. Phosphorus loss potential and manure application rates. Available at: http://www.mn.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/ecs/nutrient/planning/planning.htm.
USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2006. Idaho nutrient transport risk assessment (INTRA). TN-Water Quality No. 6. Boise, Idaho. Available at: ftp://ftp-fc.sc.egov.usda.gov/ID/technical/technotes/water_quality/waterquality_tn6.pdf.
USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2013a. Maine phosphorus index ver. 3. Maine Field Office Technical Guide. Available at: http://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/treemenuFS.aspx.
USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service-North Dakota. 2007. North Dakota nutrient management workbook. Available at: http://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/toc.aspx?CatID=9040.
Vadas, P.A., L.B. Owens, and A.N. Sharpley. 2008. An empirical model for dissolved phosphorus in runoff from surface-applied fertilizers. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 127: 59–65.
Wendt, R.C., and R.B. Corey. 1980. Phosphorus variation in surface runoff from agricultural lands as a function of land use. Journal of Environmental Quality 9: 130–136.
Westermann, D.T., D.L. Bjorneberg, J.K. Aase, and C.W. Robbins. 2001. Phosphorus losses in furrow irrigation runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 1009–1015.
Withers, P.J.A., and H.P. Jarvie. 2008. Delivery and cycling of phosphorus in rivers: A review. Science of the Total Environment 400: 379–395.
Zvomuya, F., S.C. Gupta, and C.J. Rosen. 2005. Phosphorus leaching in sandy outwash soils following potato-processing wastewater application. Journal of Environmental Quality 34: 1277–1285.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruark, M.D., Kelling, K.A. & Good, L.W. Environmental Concerns of Phosphorus Management in Potato Production. Am. J. Potato Res. 91, 132–144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-014-9372-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-014-9372-1