Abstract
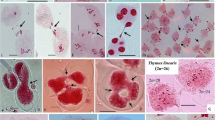
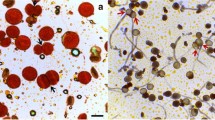
Dianthus angulatus (Caryophyllaceae) is cytologically examined here for the first time for the area of India. The diploid chromosome count of 2n = 30, ascertained here, represents a new cytotype, supplementing the earlier report of a hexaploid cytotype with 2n = 90 from outside of India. We report here the occurrence of two plants showing impaired meiosis due to irregular synapsis and cytomixis collected from Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh (India). The other plants of this species collected in Lahaul-Spiti region showed normal male meiosis (n = 15) with a high (95%−100%) pollen fertility and normal seed set, and they reproduce sexually. Irregular synapsis in two plants from the Kinnaur region is characterized by the complete absence of chromosome pairing and the presence of 30 univalents at diakinesis and meta-anaphase. In addition, other meiotic irregularities were found, such as unoriented chromosomes, laggards, precocious movements of univalents at anaphase-I and micronuclei at telophase. Microsporogenesis was also abnormal, resulting in the formation of monads, dyads, triads, polyads, and tetrads with micronuclei. The occurrence of intra- and intermicrosporal chromatin material transfer during microsporogenesis was observed, which is a rather rarely observed phenomenon. The synaptic irregularities coupled with chromatin transfer in these plants seem to be responsible for the high pollen sterility (38%−42%) and heterogeneously sized pollen grains. In these plants no seeds were set, and plants reproduced vegetatively through root suckers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahloowalia BS (1969) Effect of temperature and barbiturates on a desynaptic mutant of rye grass. Mutat Res 7:205–213
Baker BS, Carpenter ATC, Esposito MS, Esposito RE, Sandler L (1976) The genetic control of meiosis. Ann Rev Genet 10:53–134
Balao F, Casimiro-Soriguer R, Talavera M, Herrera J, Talavera S (2009) Distribution and diversity of cytotypes in Dianthus broteri as evidenced by genome size variations. Ann Bot (Oxford) 104:965–973
Cai X, Makaroff C (2001) The dsy10 mutation of Arabidopsis results desynapsis and a general breakdown in meiosis. Sex Pl Reprod 14:63–67
Carolin RC (1957) Cytological and hybridization studies in the genus Dianthus. New Phytol 56:81–97
De M, Sharma AK (1983) Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of an apomictic ornamental Ervatamia divaricata (Linn.) Alston. Cytologia 48:201–207
Doroszewska T, Berbeć A (1996) Chromosome pairing and microsporogenesis in interspecific F1 hybrids of N. africana with different cultivars of N. tabacum. J Genet Breed 50:75–82
Doroszewska T, Berbeć A (2000) Cytological investigations of polyploid interspecific hybrids of N. africana with different cultivars of N. tabacum. J Genet Breed 54:77–82
Erickson AN, Markhart AH (2002) Flower developmental stage and organ sensitivity of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) to elevated temperature. Pl Cell Environm 25:123–130
Falistocco E, Tosti T, Falcinelli M (1995) Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of diploid Dactylis, one of the origins of 2n gametes. J Heredity 86:448–453
Fuzinatto VA, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB (2008) Evaluation of microsporogenesis in an interspecific Brachiaria hybrid (Poaceae) collected in distinct years. Genet Molec Res 7:424–432
Gatt MK, Hammett KRW, Markham KR, Murray BG (1998) Yellow pinks: interspecific hybridization between Dianthus plumarius and related species with yellow flowers. Sci Hort 77:207–218
Gentscheff G (1937) Experimental and caryological investigation of the relationship among the species of the genus Dianthus L. PhD. Thesis, University of Sofia, Sofia
Ghaffari SM (2006) Occurrence of diploid and polyploid microspores in Sorghum bicolor (Poaceae) is the result of cytomixis. African J Biotechnol 5:1450–1453
Holmgren PK, Holmgren NH, Barnett LC (1990) Index Herbariorum. Part I: The Herbaria of the World, ed. 8. Regnum Veg 120:1−693. Updates available on-line: http://sciweb.nybg.org/science2/IndexHerbariorum.asp
Kaul ML, Murthy TG (1985) Mutant genes affecting higher plant meiosis. Theor Appl Genet 70:449–466
Kim JS, Oginuma K, Tobe H (2009) Syncyte formation in the microsporangium of Chrysanthemum (Asteraceae): a pathway to intraspecific polyploidy. J Pl Res 122:439–444
Koduru PRK, Rao KM (1981) Cytogenetics of synaptic mutants in higher plants. Theor Appl Genet 59:197–214
Krusteva D (1995) Results from the hybridization between N. rustica L. var. brasilica and N. tabacum L. J Genet Breed 5:226–233
Kumar P, Singhal VK (2008) Cytology of Caltha palustris L. (Ranunculaceae) from cold regions of Western Himalayas. Cytologia 73:137–143
Kumar P, Singhal VK, Kaur D, Kaur S (2010) Cytomixis and associated meiotic abnormalities affecting pollen fertility in Clematis orientalis. Biol Pl 54:181–184
Li HW, Pao WK, Li CH (1945) Desynapsis in common wheat. Amer J Bot 32:92–101
Namuco OS, O’Toole JC (1986) Reproductive stage water stress and sterility. I. Effect of stress during meiosis. Crop Sci 26:317–321
Pagliarini MS (2000) Meiotic behavior of economically important plant species: the relationship between fertility and male sterility. Genet Molec Biol 23:997–1002
Palakarcheva M, Dorossiev L (1992) Results of hybridization between the species N. gossei D. and N. tabacum L. In Anonymous (ed) Coresta Congress. Jerez de la Frontera, p 163
Person C (1955) An analytical study of chromosome behaviour in haploid wheat. Canad J Bot 33:11–30
Porch TG, Jahn M (2001) Effects of high-temperature stress on microsporogenesis in heat-sensitive and heat tolerant genotypes of Phaseolus vulgaris. Pl Cell Environm 24:723–731
Prakken R (1943) Studies of asynapsis in rye. Hereditas 29:475–495
Randolph LF (1928) Chromosome numbers in Zea mays L. Cornell Univ Agric Exp Sta Mem 117:1–44
Rieger R, Michaelis A, Green MM (1976) Glossary of Genetics and Cytogenetics. Ed. 4. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Riley R, Law CN (1965) Genetic variation in chromosome pairing. Advances Genet 13:57–107
Romanova LI, Tret’yakova IN (2005) Specific features of microsporogenesis in the Siberian larch growing under the conditions of technogenic load. Russ J Developmental Biol 36:99–104
Saini HS (1997) Effects of water stress on male gametophyte development in plants. Sex Pl Reprod 10:67–73
Sharma SK, Bisht MS, Pandit MK (2010) Synaptic mutation-driven male sterility in Panax sikkimensis Ban. (Araliaceae) from Eastern Himalaya, India. Pl Syst Evol 287:29–36
Sheidai M, Jafari S, Taleban P, Keshavarzi M (2009). Cytomixis and unreduced pollen grain formation in Alopecurus L. and Catbrosa Beauv. (Poaceae). Cytologia 74:31–41
Singh RJ (2002) Plant cytogenetics. Ed. 2, CRC Press, Boca Raton
Singhal VK, Gill BS (1985) Cytomixis in some woody species. Biologica 1:168–175
Singhal VK, Kumar P (2008a) Impact of cytomixis on the meiosis, pollen viability and pollen size in wild populations of Himalayan poppy (Meconopsis aculeata Royle). J Biosci 33:371–380
Singhal VK, Kumar P (2008b) Cytomixis during microsporogenesis in the diploid and tetraploid cytotypes of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal, 1852 (Solanaceae). Comp Cytogenet 2:85–92
Singhal VK, Kumar P (2010) Variable sized pollen grains due to impaired male meiosis in the cold desert plants of Western Himalayas (India). In Kaiser BJ (ed) Pollen: Structure, types and effects. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NY, pp 101–126
Singhal VK, Kaur D, Kumar P (2008) Effect of cytomixis on the pollen size in ‘Seabuckthorn’ (Hippophae rhamnoides L., Elaeagnaceae). Cytologia 73:167–172
Singhal VK, Kumar P, Kaur D, Rana PK (2009) Chromatin transfer during male meiosis resulted into heterogeneous sized pollen grains in Anemone rivularis Buch.-Ham. ex DC. from Indian cold deserts. Cytologia 74:229–234
Singhal VK, Kaur S, Kumar P (2010) Aberrant male meiosis, pollen sterility and variable sized pollen grains in Clematis montana Buch.-Ham. ex DC. from Dalhousie hills, Himachal Pradesh. Cytologia 75:31–36
Stanley RG, Linskens HF (1974). Pollen biology. Biochemistry, management. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Stoyanova M (1970) Prouchvania na hibridi mezhdu vidovete N. tabacum i N. glauca Grah. Otdalechena hibridizatsia na rasteniyata. In Anonymous (ed) Nauchna Sesiya na Instituta Genetika u Selektsiya na Rasteniyata. Sofia, pp 127–136 (In Bulgarian, with English summary)
Trojak-Goluch A, Berbeć A (2003) Cytological investigations of the interspecific hybrids of Nicotiana tabacum L. × N. glauca Grah. J Appl Genet 44:45–54
Villeneuve AM, Hillers KJ (2001) Whence meiosis? Cell 106:647–650
Weiss H, Dobeš C, Schneeweiss GM, Greimler J (2002) Occurrence of tetraploid and hexaploid cytotypes between and within populations in Dianthus sect. Plumaria (Caryophyllaceae). New Phytol 156:85–94
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the University Grants Commission, New Delhi for providing financial assistance under the DRS SAP I&II and ASIST program and CSIR for providing senior research fellowship to senior author. Further support was provided by the UGC under the Dr. D.S. Kothari Post- Doctoral Fellowship Scheme {Award Letter No. F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/13-427/2011(BSR)} to Dr. Puneet Kumar. Thanks are also due to the Head, Department of Botany for necessary laboratory and library facilities. The authors are very grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their assistance and valuable suggestions, which were helpful in improving the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Singhal, V.K. & Kaur, D. Impaired Male Meiosis due to Irregular Synapsis Coupled with Cytomixis in a New Diploid Cytotype of Dianthus angulatus (Caryophyllaceae) from Indian Cold Deserts. Folia Geobot 47, 59–68 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12224-011-9107-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12224-011-9107-8