Abstract
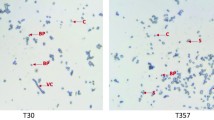
Four local Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) isolates that had been serologically identified as Bt var. kurstaki (Btk2, Btk3, and Btk66) and Bt var. mexicanensis (Btm27), in addition to two reference strains (4D20 and 4AC1), were laboratory assayed as microbial control agents against the Egyptian cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification analysis revealed that each of the six experimental strains carries, at least, a cry1 type gene which expresses a protein toxin active against lepidopterous insects. Additionally, PCR amplification results demonstrated that 4D20 and Btk66 contain the Lepidoptera- and Diptera-active cry2 type gene and that Btk66 contains Coleoptera-active cry7 and cry8 genes. Among the six strains, Btk66 and Btm27 were the most promising microbial control agents against S. littoralis. The present findings were the first to report that Btm27 (classified as B. thuringiensis var. mexicanensis) is a very potent microbial control agent against S. littoralis-tested larvae. For more characterization of these two isolates, the sspO gene was investigated as a molecular chronometer. The DNA sequencing results proved that Btk66 and Btm27 carry sspO open reading frames with identical nucleotide sequences, suggesting a strong phylogenetic relationship between the two strains.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El Mageed AEM, Shalaby SM (2011) Toxicity and biochemical impacts of some new insecticide mixtures on cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Plant Prot Sci 47:166–175
Alfazairy A, El-Minshawy AM, Hendi R, Karam H (2003) Production of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner by inexpensive and low technology for microbial control of the red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). In: Proceedings of the first international Egyptian-Romanian conference on towards new trends for plant protection and environment conservation, Egypt, 6−8 Dec 2003, pp 123–141
Ash C, Farrow JAE, Dorsch M, Stackebrandt E, Collins MD (1991) Comparative analysis of Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and related species on the basis of reverse transcriptase sequencing of 16S rRNA. Int J Syst Bacteriol 41:343–346
Ben-Dov E, Zaritsky A, Dahan B, Barak Z, Sinai R, Manasherob R, Khamraev A, Troitskaya E, Dubitsky A, Berezina N, Margalith Y (1997) Extend screening by PCR for seven cry-group genes from field-collected strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4883–4890
Burges HD, Thompson EM (1971) Standardization and assay of microbial insecticides. In: Burges HD, Hussey NW (eds) Microbial control of insects and mites. Academic, New York, p 709
Busch U, Nitschko H (1999) Review in methods for the differentiation of microorganisms. J Chromatogr 722:263–278
Cabrera-Hernandez A, Setlow P (2000) Analysis of the regulation and function of five genes encoding small, acid-soluble spore proteins of Bacillus subtilis. Gene 248:169–181
Crickmore N (2006) Beyond the spore—past and future developments of Bacillus thuringiensis as a biopesticide. J Appl Microbiol 101:616–619
Dutton A, Klein H, Romeis J, Bigler F (2003) Prey mediated effects of Bacillus thuringiensis spray on the predator Chrysoperla carnea in maize. Biol Control 26:209–215
El-Helow ER (2001) Identification and molecular characterization of a novel Bacillus strain capable of degrading Tween-80. FEMS Microbiol Lett 196:119–122
Fang J, Xiaoli X, Ping W, Zhou ZJ, Anthony SM, Jiaan C, Ming FG, Zhicheng S (2007) Characterization of chimeric Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3 toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:956–961
Federici BA (1999) Bacillus thuringiensis in biological control. In: Bellows TS, Fisher TW, Caltagirone LE (eds) Handbook of biological control: principles and applications of biological control. Academic, New York, pp 575–593
Ferrandis MD, Juarez-Pérez VM, Frutos R, Bel Y, Ferré J (1999) Distribution of cryI, cryII and cryV genes within Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from Spain. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:179–185
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis. Cambridge University Press, London, p 337
Janse I, Hamidjaja RA, Bok JM, Van Rottrdam BJ (2010) Reliable detection of Bacillus anthracis, Francisella tularensis and Yersinia pestis by using multiplex PCR including internal controls for nucleic acid extraction and amplification. BMC Microbiol 10:314
Loseva O, Ibrahim M, Candas M, Koller CN, Bauer LS, Bulla LA Jr (2002) Changes in protease activity and Cry3Aa toxin binding in Colorado potato beetle: implications for insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:567–577
Martin H (1959) The scientific principles of crop protection. Arnold, 4th edn. London, pp 359
McKinney N, Goldman S, Hunter-Cevera J, Leighton T, Long G, Nelson B (1998) Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the B. anthracis clade: spore structural proteins as evolutionary chronometers. In: 3rd international anthrax conference, Society of Applied Microbiology & University of Plymouth, Plymouth, 7–10 Sept 1998
Mohamed SA, Badr NA, El-Hafez AA (2000) Efficacy of two formulations of pathogenic bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis against the first instar larvae of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) and Agrotis ipsilon (Hfn.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Egy J Agric Res 78:1025–1040
Nazarian A, Jahangiri R, Jouzani GS, Seifinejad A, Soheilivand S, Bagheri O, Keshavarzi M, Alamisaeid K (2009) Coleopteran-specific and putative novel cry genes in Iranian native Bacillus thuringiensis collection. J Invertebr Pathol 102:101–109
Pineda S, Schneider MI, Smagghe G, Martinez AM, Del Estal P, Vinuela E, Valle J, Budia F (2007) Lethal and sublethal effects of methoxyfenozide and spinosad on Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 100:773–780
Porcar M, Caballero P (2000) Molecular and insecticidal characterization of a Bacillus thuringiensis strain isolated during a natural epizootic. J Appl Microbiol 89:309–316
Rajamohan F, Lee MK, Dean DH (1998) Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal proteins: molecular mode of action. In: Moldave K (ed) Progress in nucleic acid research and molecular biology, vol 60. Academic, New York, pp 1–27
Romeilah M, Abdel-Megeed MA (2000) The role of certain bacterial preparations (Bacillus thuringiensis) in controlling the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Egy J Agric Res 78:1877–1887
Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J 9:283–300
Seifinejad A, Salehi Jouzani GR, Hosseinzadeh A, Abdmishani C (2008) Characterization of Lepidoptera-active cry and vip genes in Iranian Bacillus thuringiensis strain collection. Biol Control 44:216–226
Vyras J, Cox J, Setlow B, Clman WH, Setlow P (2011) Extremely variable conservation of γ-type small, acid-soluble proteins from spores of some species in the bacterial order Bacillales. J Bacteriol 193:1884–1892
Walker L, Levine H, Jucker M (2006) Koch’s postulates and infectious proteins. Acta Neuropathol 112:1–4
Wang J, Boets A, Van Rie J, Ren G (2003) Characterization of cry1, cry2 and cry9 genes in Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from China. J Invertebr Pathol 82:63–71
Yamamoto S, Bouvet PJ, Harayam S (1999) Phylogenetic structures of the genus Acinetobacter based on gyrB sequences: comparison with the grouping by DNA-DNA hybridization. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:87–95
Zeigler DR (1999) Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus. In: Bacillus Genetic Stock Center catalog of strains, 7th edn, vol 2. Ohio State University, Ohio, p 7
Zhong C, Ellar DJ, Bishop A, Johnson C, Lin S, Hart ER (2000) Characterization of a Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin which is toxic to insects in three orders. J Invertebr Pathol 76:131–139
Zhu J, Tan F, Tang J, Li Y, Zheng A, Li P (2009) Characterization of insecticidal crystal protein cry gene of Bacillus thuringiensis from soil of Sichuan Basin, China and cloning of novel haplotypes cry gene. Ann Microbiol 59:1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfazairy, A.A., El-Ahwany, A.M.D., Mohamed, E.A. et al. Microbial control of the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) by Egyptian Bacillus thuringiensis isolates. Folia Microbiol 58, 155–162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-012-0193-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-012-0193-7