Abstract
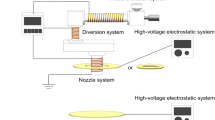
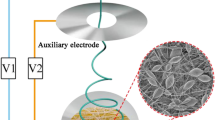
The electric field and temperature are the two important factors that influence the diameter and properties of fiber in the melt electrospinning process. It is commonly known that the polymer jet behavior is governed by the electric field within spinning area. In present work, a comprehensively-designed and properly-conducted analysis was carried out to investigate into the effects of electric field on the jet behaviors, diameters, crystalline structure and mechanical properties of the resultant fibers. An auxiliary electrode was invited to enhance the electric field strength. The high-speed photography was adopted to capture the jet motion, and also, the numerical simulation was used to understand the electric field distribution. By making use of the whipping amplitude and whipping frequency, the characteristics of jet behavior were described. It was found that by applying an auxiliary electrode, the average fiber diameter reduced from 61.01 µm to 9.06 µm, and the crystallinity and strength of the fiber was improved with the help of the higher electric filed intensity. In addition, the more uniform electric field would produce finer and more uniform fiber because of the more stable jet motion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Maghsoodlou, B. Noroozi, and A. K. Haghi, Nano, 12, 1750028 (2017).
S. Kaur, S. Sundarrajan, and D. Rana, J. Membr. Sci., 392, 101 (2012).
Y. S. Zheng, H. H. Gong, and Y. C. Zeng, Rsc Adv., 5, 48533 (2015).
P. P. Tsai, H. Schreuder- Gibson, and P. Gibson, J. Electrostat., 54, 333 (2002).
Z. M. Huang, Y. Z. Zhang, and M. Kotaki, Compos. Sci. Technol., 63, 2223 (2003).
D. Li, J. Mccann, and Y. Xia, Small, 1, 83 (2005).
Z. G. Wang, Y. Wang, and H. Xu, J. Phys. Chem. C., 113, 2955 (2009).
N. Ogata, G. Lu, and T. Iwata, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 104, 1368 (2010).
N. Ogata, S. Yamaguchi, and N. Shimada, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 104, 1640 (2007).
S. Tian, N. Ogata, and N. Shimada, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 113, 1282 (2009).
N. Shimada, N. Ogata, and K. Nakane, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 125, E384 (2012).
N. Shimada, H. Tsutsumi, and K. Nakane, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 116, 2998 (2010).
T. D. Brown, P. D. Dalton, and D. W. Hutmacher, Adv. Mater., 23, 5651 (2011).
A. A. Uglov and A. N. Kokora, Sov. J. Quantum. Electron., 7, 671 (2007).
J. Fang, L. Zhang, and D. Sutton, J. Nanomater., 2012, 16 (2012).
L. Cao, D. Su, and Z. Su, Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 32, 1167 (2014).
L. Cao, M. Dong, and A. Zhang, Polym. Eng. Sci., 53, 2674 (2013).
Y. S. Zheng, C. Zhuang, and R. Gong, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 53, 14876 (2014).
Y. S. Zheng, S. Xie, and Y. Zeng, J. Mater. Sci., 48, 6647 (2013).
L. M. Bellan and H. G. Craighead, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. Microelectron. Nanometer. Struct. Process. Meas. Phe., 24, 3179 (2006).
M. Lauricella, F. Cipolletta, G. Pontrelli, D. Pisignano, and S. Succi, Phys. Fluids., 29, 082003 (2017).
C. Grasl, M. M. Arras, M. Stoiber, H. Bergmeister, and H. Schima, Appl. Phys. Lett., 102, 053111 (2013).
Y. Yang, Z. Jia, and Q. Li, IEEE. T. Dielect. El. In., 16, 409 (2009).
Y. Yang, Z. Jia, and Q. Li, IEEE. T. Dielect. El. In., 17, 1592 (2010).
Acknowledgments
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11702169), and Talents Action Program of Shanghai University of Engineering Science (Grant No. 2017RC522017) to Dr. Y. Zheng. This work was also supported by Talents Action Program of Shanghai University of Engineering Science (Grant No. 2017RC432017) and Shanghai Local Capacity- Building Project (Grant No. 19030501200) to Dr. B. Xin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zheng, Y., Mu, X. et al. The Effects of Electric Field on Jet Behavior and Fiber Properties in Melt Electrospinning. Fibers Polym 21, 984–992 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-9849-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-9849-0