Abstract
The PLGA ultrafine fibrous scaffold was successfully fabricated by electrospinning. The morphology and properties of the PLGA vascular scaffolds were examined. In particular, the in vitro degradation behavior of the electrospun PLGA vascular scaffolds was investigated by means of morphology, microstructure, mass loss, Mw, and breaking strength characterization. The results showed that electrospun scaffold possessed ultrafine fibrous and porous structure, and had adequate mechanical properties to be developed as a substitute for native blood vessels. In vitro degradation study showed that the PLGA ultrafine fibrous scaffold could biodegrade in the PBS solution, and the mass loss, Mw, and breaking strength studies indicated that degradation rate of the electrospun PLGA nanofibers was greater in the first 2 weeks. After the degradation of 2 weeks, the degradation slowed down. Furthermore, with the extension of the degradation time, the thermal decomposition temperature of the PLGA scaffold decreased gradually. The results indicated that the electrospun PLGA vascular scaffold could be considered as an ideal candidate for tissue-engineered blood vessel.
Similar content being viewed by others
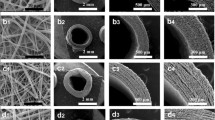
References
S. D. Wang, Y. Z. Zhang, H. W. Wang, and Z. H. Dong, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 48, 345 (2011).
J. A. Matthews, G. E. Wnek, D. G. Simpson, and G. L. Bowlin, Biomacromolecules, 3, 232 (2002).
M. Gu, K. Wang, W. Li, C. Qin, J. Wang, and L. Dai, Fiber. Polym., 12, 65 (2011).
S. D. Wang, Y. Z. Zhang, G. B. Yin, H. W. Wang, and Z. H. Dong, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 113, 2675 (2009).
S. J. Kim, D. H. Jang, W. H. Park, and B. M. Min, Polymer, 51, 1320 (2010).
R. Dorati, C. Colonna, I. Genta, T. Modena, and B. Conti, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 95, 697 (2010).
E. A. Sander, A. M. Alb, and E. A. Nauman, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 70, 506 (2004).
V. Rajesh, S. Kirubanandan, and S. K. Dhirendra, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 95, 1605 (2010).
H. J. Shin, C. H. Lee, I. H. Cho, Y. J. Kim, Y. J. Lee, and I. A. Kim, J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed., 17, 103 (2006).
E. I. Vargha-Butler, E. Kiss, C. N. C. Lam, Z. Keresztes, E. Kalman, and L. Zhang, Colloid. Polym. Sci., 279, 1160 (2001).
T. I. Croll, A. J. O’Connor, G. W. Stevens, and J. J. Cooper-White, Biomacromolecules, 5, 463 (2004).
C. E. Holy, S. M. Dang, J. E. Davies, and M. S. Shoichet, Biomaterials, 20, 1177 (1999).
T. Yoshioka, N. Kawazoe, and T. Tateishi, Biomaterials, 29, 2438 (2008).
L. Lu, S. J. Peter, M. D. Lyman, H. L. Lai, S. M. Leite, J. A. Tamada, S. Uyama, J. P. Vacanti, R. Langer, and A. G. Mikos, Biomaterials, 21, 1837 (2000).
C. M. Vaz, S. V. Tuij, and C. V. C. Bouten, Acta Biomaterial, 1, 575 (2005).
S. Y. Li, S. D. Wang, Y. Z. Zhang, H. W. Wang, and P. Qiu, Synthetic Fiber China, 11, 22 (2009).
S. Wang, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, G. Yin, and Z. Dong, Biomacromolecules, 10, 2240 (2009).
S. J. Lee, J. Liu, S. H. Oh, S. Soker, A. Atala, and J. J. Yoo, Biomaterials, 29, 2891 (2008).
P. J. Schaner, N. D. Martin, and T. N. Tulenko, J. Vasc. Surg., 40, 146 (2004).
R. P. F. Lanao, S. C. G. Leeuwenburgh, J. G. C. Wolke, and J. A. Jansen, Acta Biomaterialia, 7, 3459 (2011).
H. M. Kim, T. Kokubo, and S. Fujibayashi, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 52, 553 (2000).
J. Stitzel, J. Liu, S. J. Lee, M. Komura, J. Berry, and S. Soker, Biomaterials, 27, 1088 (2006).
K. Billiar, J. Murray, and D. Laude, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 56, 101 (2001).
S. D. Wang, Y. Z. Zhang, G. B. Yin, H. W. Wang, and Z. H. Dong, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 30, 670 (2010).
Elisabeth, R. Caroline, M. Liz, B. Jonathan, C. Mike, F. M. Aline, and S. Alberto, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 93, 1869 (2008).
A. M. Reed and D. K. Gilding, Polymer, 22, 494 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Zhang, Y. Preparation, structure, and in vitro degradation behavior of the electrospun poly(lactide-co-glycolide) ultrafine fibrous vascular scaffold. Fibers Polym 13, 754–761 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0754-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-012-0754-z



