Abstract
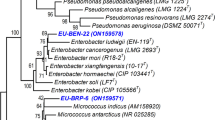
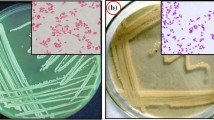
This study intended to determine the ability of endophytic bacteria recovered from root nodules of Cicer arietinum L. and Vigna unguiculata L. (Walp.) plants to synthesize exopolysaccharide (EPS) and to enhance the production by changing nutritional factors. Twenty endophytic bacteria isolated from root nodules of Cicer arietinum and Vigna unguiculata were tested for their production of EPS. High EPS-producing isolates were identified on phenotypic and genotypic characteristics. Among 20 isolates, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (C6) and Brevibacillus parabrevis (V4) isolated from root nodules of Cicer arietinum and Vigna unguiculata produced a high EPS yield in comparison with other isolates. Using 1% of sucrose as sole carbon source increases the concentration of EPS produced by S. maltophilia and B. parabrevis (65 and 107%, respectively). EPS produced by S. maltophilia and B. parabrevis was increased by the addition of fructose and lactose (0.1%). Addition of 1.68 g/L KNO3 or 2.49 g/L glycine to modified yeast extract mannitol medium (YEMB) significantly increased EPS production by S. maltophilia and B. parabrevis. Furthermore, the presence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles (25–50 µg/mL) in the modified YEMB medium increased EPS yield by B. parabrevis. Chemical characterization of EPS by GC–MS and FTIR indicate that the EPS biochemical composition is dependent on the bioavailability of carbon substrates and is controlled by limiting nutrients. The combination of the best two carbon sources sucrose (0.9%) and fructose or lactose (0.1%) in the presence of KNO3 or glycine as the best nitrogen sources significantly increased EPS yield of S. maltophilia and B. parabrevis, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla MH, El-enany AE, Bagy MK, Bashandy SR (2014) Alleviating the inhibitory effect of salinity stress on nod gene expression in R. tibeticum fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) symbiosis by isoflavonoids treatment. Plant Interact 9:275–284
Arena A, Maugeri TL, Pavone B, Iannello D, Gugliandolo C, Bisignano G (2006) Antiviral and immunoregulatory effect of a novel exopolysaccharide from a marine thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis. Int Immunopharmacol 6(1):8–13
Castellane TCL, Lemos MVF, deMacedo Lemos EG (2014) Evaluation of the biotechnological potential of Rhizobium tropici strains for exopolysaccharide production. Carbohydr Polym 111:191–197
Castellane TCL, Otoboni AMM, de Macedo Lemos EG (2015) Characterization of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Rhizobia Species. Rev Bras Ci Solo 39:1566–1575
Chen C, Bauske EM, Mussan G, Rodriguez-Kabana R, Kloepper JW (1995) Biological control of Fusarium wilt on cotton by use of endophytic bacteria. Biol Control 5:83–91
De PS, Basu PS (1996) Production of extracellular polysaccharides by a Rhizobium species from the root nodules of Tephrosia purpurea Pers. Acta Biotechnol 16:155–162
Deng ZS, Zhao LF, Kong ZY, Yang WQ, Lindström K, Wang ET, Wei GH (2011) Diversity of endophytic bacteria within nodules of the Sphaerophysa salsula in different regions of Loess Plateau in China. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76(3):463–475
Denkhaus E, Meisen S, Telgheder U, Wingender J (2007) Chemical and physical methods for characterisation of biofilms. Microchim Acta 158:1–27
Donot F, Fontana A, Baccou JC, Schorr-Galindo S (2012) Microbial exopolysaccharides: main examples of synthesis, excretion genetics and extraction. Carbohydr Polym 87:951–962
Farahmandjou M, Soflaee F (2015) Synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles by simple co-precipitation method. Phys Chem Res 3:191–196
Ibáñez F, Angelini J, Taurian T, Tonelli ML, Fabra A (2009) Endophytic occupation of peanut root nodules by opportunistic Gammaproteobacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 32(1):49–55
Inturri R, Stivala A, Sinatra F, Morrone R, Blandino G (2014) Scanning electron microscopy observation of adhesion properties of Bifidobacterium longum W11 and chromatographic analysis of its exopolysaccaride. JFNS 5:1787–1792
Janczarek M, Skorupska A (2009) Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii rosR gene expression is regulated by catabolic repression. FEMS Microbiol Lett 291:112–119
Jiao Y, George D, Cody GD, Harding AK, Wilmes P, Schrenk M, Wheeler KE, Banfield JF, Thelen MP (2010) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances from acidophilic microbial biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(9):2916–2922
Kan FL, Chen ZY, Wang ET, Tian CF, Sui XH, Chen WX (2007) Characterization of symbiotic and endophytic bacteria isolated from root nodules of herbaceous legumes grown in Qinghai-Tibet plateau and in other zones of China. Arch Microbiol 188(2):103–115
Karbowiak T, Ferret E, Debeaufort F, Voilley A, Cayot A (2007) Investigation of water transfer across thin layer biopolymer films by infrared spectroscopy. Membr Sci 370:82–90
Kishk YF, Al-Sayed HM (2007) Free-radical scavenging and antioxidative activities of some polysaccharides in emulsions. LWT Food Sci Technol 40(2):270–277
Kodali VP, Das S, Sen R (2009) An exopolysaccharide from a probiotic: biosynthesis dynamics, composition and emulsifying activity. Food Res Int 42(5):695–699
Kuykendall LD (2005) Family I. Rhizobiaceae Conn 1938, 321AL. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Stanley JT (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology.vol 2, part C. Springer, New York, pp 324–361
Lee C, Kim JY, Lee W, Nelson KL, Yoon J, Sedlak DL (2008) Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ Sci Technol 42(13):4927–4933
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Kumar Yadhu, Buchner A, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
MacLeod FA, Guiot SR, Costerton JW (1995) Electron microscopic examination of the extracellular polymeric substances in anaerobic granular biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 11:481–485
Navard P (2005) The new European polysaccharide network of excellence. Cellulose 12:337–338
Nouha K, Yan S, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2015) EPS producing microorganisms from municipal wastewater activated sludge. Pet Environ Biotechnol 7:1
Poli A, Anzelmo G, Fiorentino G, Nicolaus B, Tommonaro G, Donato P (2011) Polysaccharides from wastes of vegetable industrial processing: new opportunities for their eco-friendly re-use. In: Elnashar M (ed) Biotechnol biopolym. InTech, New York, pp 33–56
Prabhavathi E, Mallaiah KV (2009) Extracellular polysaccharide production by Rhizobium sp. nodulating Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verde. Asian Bio Sci 4(1):20–23
Prabhu YT, Rao KV, Kumari BS, Pavani T (2015) Decoration of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on O-MWCNTs and its antibacterial studies. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 26:263–270
Radchenkova N, Tomova A, Kambourova M (2011) Biosynthesis of an exopolysaccharide produced by Brevibacillus thermoruber 438. Biotechnol Equip 25:77–79
Rajendar V, Rajitha B, Dayakar T, Chakra CHS, Rao KV (2016) Systematic approach on the fabrication of Mn doped ZnO semiconducting nanoparticles by mixture of fuel approach for antibacterial applications. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 27:521–531
Rao M, Blane U, Zonnenberg M (1985) PC-State Version I A. Pilot edition, Uni Georgia
Ruas-Madiedo P, Zoon P (2003) Effect of exopolysaccharide-producing Lactococcus lactis strains and temperature on the permeability of skim milk gels. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 213(2):245–253
Ruas-Madiedo P, Hugenholtz J, Zoon P (2002) An overview of the functionality of exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. Int Dairy J 12(2):163–171
Ryan RP, Germaine K, Franks A, Ryan DJ, Dowling DN (2007) Bacterial endophytes: recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiol Lett 278:1–9
Sardari RRR, Kulcinskaja E, Ron EYC, Björnsdóttir S, Friðjónsson ÓH, Hreggviðsson GO, Karlsson EN (2017) Evaluation of the production of exopolysaccharides by two strains of the thermophilic bacterium Rhodothermus marinus. Carbohydr Polym 156:1–8
Sheng G, Yu H, Yue Z (2005) Production of extracellular polymeric substances from Rhodopseudomonas acidophila in the presence of toxic substances. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:216–222
Sturz AV, Christie BR, Matheson BG, Nowak J (1997) Biodiversity of endophytic bacteria which colonize red clover nodules, roots, stems and foliage and their influence on host growth. Biol Fertil Soils 25:13–19
Tallon R, Bressollier P, Urdaci MC (2003) Isolation and characterization of two exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus plantarum EP56. Res Microbiol 154:705–712
Tran N, Mir A, Mallik D, Sinha A, Nayar S, Webster TJ (2010) Bactericidal effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Nanomedicine 5:277–283
Trevelyan WE, Harrison JS (1952) Studies on yeast metabolism. Biochem J 50:298
Vincent JM (1970) A manual for the practical study of root nodules bacteria. Blackwell, Oxford
Welman AD, Maddox IS (2003) Exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: perspectives and challenges. Trends Biotechnol 21(6):269–274
Wingender J, Neu TR, Flemming HC (1999) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: characterization, structures and function. Springer, Berlin
Wu X, Tang J, Zhang Y, Wang H (2009) Low temperature synthesis of Fe3O4 nanocrystals by hydrothermal decomposition of a metallorganic molecular precursor. Mater Sci Eng 157:81–86
Yasar Yildiz S, Anzelmo G, Ozer T, Radchenkova N, Genc S, Di Donato P, Nicolaus B, Oner ET, Kambourova M (2014) Brevibacillus themoruber: a promising microbial cell factory for exopolysaccharide production. J Appl Microbiol 116(2):314–324
You G, Hou J, Xu Y, Wang C, Wang P, Miao L, Ao Y, Li Y, Lv B (2015) Effects of CeO2 nanoparticles on production and physicochemical characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms in sequencing batch biofilm reactor. Bioresour Technol 194:91–98
Zakhia F, De Lajudie P (2001) Taxonomy of rhizobia. Agronomie 21(6–7):569–576
Zakhia F, Jeder H, Willems A, Gillis M, Dreyfus B, De Lajudie P (2006) Diverse bacteria associated with root nodules of spontaneous legumes in Tunisia and first report for nifH-like gene within the genera Microbacterium and Starkeya. Microb Ecol 51(3):375–393
Zgadzaj R, Garrido-Oter R, Jensen DB, Koprivova A, Schulze-Lefert P, Radutoiu S (2016) Root nodule symbiosis in Lotus japonicus drives the establishment of distinctive rhizosphere, root, and nodule bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(49):7996–8005
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Dr. George Bennett (Rice University, USA) for critical reading, helpful comments, constructive suggestions, and careful corrections for further improvement of this manuscript. The authors are very grateful for the insightful and helpful comments, constructive suggestions, and careful corrections made by the editor and the anonymous referees for further improvements of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd-Alla, M.H., Bashandy, S.R., Nafady, N.A. et al. Enhancement of exopolysaccharide production by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Brevibacillus parabrevis isolated from root nodules of Cicer arietinum L. and Vigna unguiculata L. (Walp.) plants. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 29, 117–129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-018-0671-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-018-0671-1