Abstract
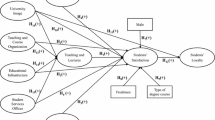
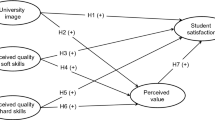
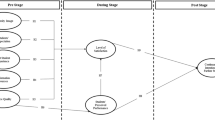
The aim of the present work is to validate a model of antecedents and consequences of university perceived value among graduates, and to analyse the moderating role of their level of involvement with Higher Education. Perceived value is proposed as the principal antecedent of perceived value, comprising four dimensions: teaching staff, infrastructures, administration staff, and support services. Overall satisfaction with the university and the overall image of the institution are taken as consequences, for the purpose of this study. The final sample – comprising 352 university graduates from all areas of knowledge – was obtained via computer-assisted telephone interviewing (CATI). The theoretical model was estimated using Consistent Partial Least Squares (PLSc) and Multi-group Analysis (PLS–MGA). The results of the analysis confirm that perceived quality is a multidimensional construct formed by four distinct dimensions. It is found to determine perceived value, which, in turn, has a major influence on overall satisfaction and overall image of the institution, although the latter depends directly on satisfaction but not on perceived value in the case of graduates with a high level of involvement. These findings contribute to a better understanding of how university management can improve graduate satisfaction, via perceived quality and perceived value, and how graduate satisfaction is a major antecedent of overall image-formation. Further, the present results confirm that the extent of graduates’ involvement in Higher Education appears to moderate the effect of value on image, this moderation being greater among those graduates presenting a lower level of involvement. The conclusions from the research provide valuable information that can help guide university management in decision-making and strategy development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, K., Alam, K. F., & Alam, M. (1997). An empirical study of factors affecting accounting students' career choice in New Zealand. Accounting Education, 6(4), 325–335.
Aitken, N. D. (1982). College student performance, satisfaction and retention: Specification and estimation of a structural model. The Journal of Higher Education, 53(1), 32–50.
Aldridge, S., & Rowley, J. (1998). Measuring customer satisfaction in higher education. Quality Assurance in Education, 6(4), 197–204.
Ali, F., Zhou, Y., Hussain, K., Nair, P. K., & Ragavan, N. A. (2016). Does higher education service quality effect student satisfaction, image and loyalty? A study of international students in Malaysian public universities. Quality Assurance in Education, 24(1), 70–94.
Alves, H. (2011). The measurement of perceived value in Higher Education: A unidimensional approach. The Service Industries Journal, 31(12), 1943–1960.
Alves, H., & Raposo, M. (2007). Conceptual model of student satisfaction in Higher Education. Total Quality Management, 18(5), 571–588.
Alves, H., & Raposo, M. (2010). The influence of university image on student behaviour. The International Journal of Educational Management, 24(1), 73–85.
AMA: American Marketing Association (2013) Dictionary. http://www.marketingpower.com/_layouts/Dictionary.aspx?source=footer.
Andreassen, T. W., & Lindestad, B. (1998). Customer loyalty and complex services: The impact of corporate image on quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty for customers with varying degrees of service expertise. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 9(1), 7–23.
Appleton-Knapp, S. L., & Krentler, K. A. (2006). Measuring student expectations and their effects on satisfaction: The importance of managing student expectations. Journal of Marketing Education, 28, 254–264.
Association of Universities and Colleges of Canada. (2011). Trends in Higher Education. Ottawa: The Association of Universities and Colleges of Canada.
Astin, A. W. (1999). Student involvement: A developmental theory for higher education. Journal of College Student Development, 40(5), 518–529.
Athanassopoulos, A. (2000). Customer satisfaction cues to support market segmentation and explain switching behavior. Journal of Business Research, 47(3), 191–207.
Athiyaman, A. (1997). Linking student satisfaction and service quality perceptions: The case of university education. European Journal of Marketing, 31(7), 528–540.
Bailey, R. (2013). Exploring the engagement of lecturers with learning and teaching agendas through a focus on their beliefs about, and experience with, student support. Studies in Higher Education, 38(1), 43–155.
Baumann, C., & Winzar, H. (2016). The role of secondary education in explaining competitiveness. Asia Pacific Journal of Education, 36(1), 1–18.
Baumann, C., Hamin, H., & Yang, S. J. (2016). Work ethic formed by pedagogical approach: Evolution of institutional approach to education and competitiveness. Asia Pacific Business Review, 22(3), 1–21.
Beerli Palacio, A., Díaz Meneses, G., & Pérez Pérez, P. J. (2002). The configuration of the university image and its relationship with the satisfaction of students. Journal of Educational Administration, 40(5), 485–505.
Beerli Palacio, A., & Martin, J. D. (2004). Factors influencing destination image. Annals of Tourism Research, 31(3), 657–681.
Bess, J. L., & Shearer, R. E. (1994). College image and finances: are they related to how much students learn. New York: New York University.
Bigné, E., Moliner, M., & Sánchez, J. (2003). Perceived quality and satisfaction in multiservice organizations: The case of Spanish public services. Journal of Services Marketing, 17(4), 420–442.
Bitner, M. J., Booms, B., & Tetreault, M. (1990). The service encounter: diagnosing favourable and unfavourable incidents. Journal of Marketing, 54(1), 71–84.
Blázquez Resino, J. J., Chamizo González, J., Cano Montero, E. I., & Gutiérrez Broncano, S. (2013). Calidad de vida universitaria: Identificación de los principales indicadores de satisfacción estudiantil. Revista de Educación, 362(3), 458–484.
Bloemer, J., & Ruyter, K. (1998). On the relationship between store image, store satisfaction and store loyalty. European Journal of Marketing, 32(5/6), 499–513.
Borden, V. M. H. (1995). Segmenting student markets with a student satisfaction and priorities survey. Research in Higher Education, 36(1), 73–88.
Brown, R. M., & Mazzarol, T. W. (2009). The importance of institutional image to student satisfaction and loyalty within higher education. Higher Education, 58(1), 81–95.
Brunner, T. A., Stöcklin, M., & Opwis, K. (2008). Satisfaction, image and loyalty: New versus experienced customers. European Journal of Marketing, 42(9/10), 1095–1105.
Bryce, H. (2007). The public’s trust in nonprofit organizations: The role of relationship marketing and management. California Management Review, 49(4), 112–132.
Chen, C. F., & Chen, F. S. (2010). Experience quality, perceived value, satisfaction and behavioral intentions for heritage tourists. Tourism Management, 31(1), 29–35.
Chen, C. F., & Tsai, D. (2007). How destination image and evaluative factors affect behavioral intentions? Tourism Management, 28(4), 1115–1122.
Chen, C. F., & Tsai, M. H. (2008). Perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty of TV travel product shopping: Involvement as a moderator. Tourism Management, 29(6), 1166–1171.
Cheng, T. M., & Lu, C. C. (2013). Destination image, novelty, hedonics, perceived value, and revisiting behavioral intention for island tourism. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 18(7), 766–783.
Chin, W. W. (1998a). The partial least squares approach to structural equation modelling. In G. A. Marcoulides (Ed.), Modern methods for business research (pp. 295–336). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Chin, W. W. (1998b). Issues and opinion on structural equation modelling. MIS Quarterly, 22(1), 8–15.
Chin, W.W., Marcolin, B. L., & Newsted, P. R. (1996). A partial least squares latent variable modeling approach for measuring interaction effects: Results from a Monte Carlo Simulation Study and Voice Mail Emotion/Adoption Study. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Information Systems, Cleveland, Ohio.
Chiu, C. M., Wang, E. T., Fang, Y. H., & Huang, H. Y. (2014). Understanding customers' repeat purchase intentions in B2C e-commerce: The roles of utilitarian value, hedonic value and perceived risk. Information Systems Journal, 24(1), 85–114.
Choi, K.-S., Cho, W.-H., Lee, S., Lee, H., & Kim, C. (2004). The relationships among quality, value, satisfaction and behavioural intention in health care provider choice: A South Korean study. Journal of Business Research, 57, 913–921.
Chung, E., & McLarney, C. (2000). The classroom as a service encounter: Suggestions for value creation. Journal of Management Education, 24(4), 484–500.
Clemes, M. D., Cohen, D. A., & Wang, Y. (2013). Understanding Chinese university students' experiences: An empirical analysis. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 25(3), 391–427.
Cronin Jr., J. J., Brady, M. K., & Hult, G. T. M. (2000). Assessing the effects of quality, value and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioural intentions in service environments. Journal of Retailing, 76(2), 193–218.
Cronin, J. J., & Taylor, S. A. (1992). Measuring service quality: A reexamination and extension. Journal of Marketing, 56(3), 55–68.
Cuthbert, P. F. (1996). Managing Service Quality in HE: Is SERVQUAL the answer? Part 1. Managing Service Quality, 6(2), 11–16.
da Costa, F. R., & Pelissari, A. S. (2016). Factors affecting corporate image from the perspective of distance learning students in public higher education institutions. Tertiary Education and Management, 22(4), 287–299.
Dana, S. W., Brown, F. W., & Dodd, N. G. (2001). Student perception of teaching effectiveness: A preliminary study of the effects of professors’ transformational and contingent reward leadership behaviours. Journal of Business Education, 2, 53–70.
Del Barrio-García, S., & Luque-Martínez, T. (2012). Análisis de ecuaciones estructurales. In T. Luque-Martínez (ed.), Técnicas de análisis de datos en investigación de mercados. Madrid. Ed. Pirámide.
Delaney, A. M. (2001). Assessing undergraduate education from graduating seniors' perspective: Peer institutions provide the context. Tertiary Education and Management, 7(3), 255–276.
DeShields Jr., O. W., Kara, A., & Kaynak, E. (2005). Determinants of business student satisfaction and retention in higher education: Applying Herzberg’s two factor theory. International Journal of Educational Management, 19(2), 128–139.
Dholakia, U. M. (2001). A motivational process model of product involvement and consumer risk perception. European Journal of Marketing, 35(11/12), 1340–1362.
Dib, H., & Alnazer, M. (2013). The impact of service quality on student satisfaction and behavioral consequences in Higher Education services. International Journal of Economy, Management and Social Sciences, 2(6), 285–290.
Dijkstra, T. K., & Henseler, J. (2012). Consistent and asymptotically Normal PLS estimators for linear structural equations. http://www.rug.nl/staff/t.k.dijkstra/Dijkstra-Henseler-PLSc-linear.pdf.
Dijkstra, T.K., & Schermelleh-Engel, K. (2013). Consistent partial least squares for nonlinear structural equation models. Psychometrika, in press (available online). http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11336-013-9370-0
Dlačić, J., Arslanagić, M., Kadić-Maglajlić, S., Marković, S., & Raspor, S. (2014). Exploring perceived service quality, perceived value, and repurchase intention in higher education using structural equation modelling. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 25(1-2), 141–157.
Dodds, W. B. (1991). In search of value: How price and store name information influence buyers’ product perceptions. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 8(2), 15–24.
Douglas, J. A., Douglas, A., McClelland, R. J., & Davies, J. (2015). Understanding student satisfaction and dissatisfaction: An interpretive study in the UK higher education context. Studies in Higher Education, 40(2), 329–349.
Douglas, J., McClelland, R., & Davies, J. (2008). The development of a conceptual model of student satisfaction with their experience in higher education. Quality Assurance in Education, 16(1), 19–35.
Dowling, G. R. (1986). Managing your corporate image. Industrial Marketing Management, 15(2), 109–115.
Duarte, P. O., Raposo, M. B., & Alves, H. B. (2012). Using a satisfaction index to compare students’ satisfaction during and after higher education service consumption. Tertiary Education and Management, 18(1), 17–40.
Duque, L. C., & Weeks, J. R. (2010). Towards a model and methodology for assessing student learning outcomes and satisfaction. Quality Assurance in Education, 18(2), 84–105.
Eisingerich, A. B., Auh, S., & Merlo, O. (2014). Acta non verba? The role of customer participation and word of mouth in the relationship between service firms’ customer satisfaction and sales performance. Journal of Service Research, 17(1), 40–53.
Elliott, K. M., & Healy, M. A. (2001). Key factors influencing student satisfaction related to recruitment and retention. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 10(4), 1–11.
Elliott, K. M., & Shin, D. (2002). Student Satisfaction: An alternative approach to assessing this important concept. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 24(2), 197–209.
Fakeye, P., & Crompton, J. (1991). Image difference between prospective, first-time and repeat visitors to the Lower Rio Grande Valley. Journal of Travel Research, 30(2), 10–16.
Fares, D., Achour, M., & Kachkar, O. (2013). The impact of service quality, student satisfaction, and university reputation on student loyalty: A case study of International students in IIUM, Malaysia. Information Management and Business Review, 5(12), 584–591.
Flores, W., Chen, J. C. V., & Ross, W. H. (2014). The effect of variations in banner ad, type of product, website context, and language of advertising on Internet users’ attitudes. Computers in Human Behavior, 31, 37–47.
Fornell, C., Johnson, D., Anderson, E., Cha, J., & Bryant, B. E. (1996). The American customer satisfaction index: Nature, purpose, and findings. Journal of Marketing, 60(4), 7–18.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50.
Fram, E. H. (1982). Maintaining and Enhancing a College or University Image. Rochester: Institute of Technology.
Freeland, R. E., Spenner, K. I., & McCalmon, G. (2015). I gave at the campus exploring student giving and its link to young alumni donations after graduation. Nonprofit and Voluntary Sector Quarterly, 44(4), 755–774.
Gefen, D. (2002). Customer loyalty in E-Commerce. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 3(1), 27–51.
Gielnik, M. M., Frese, M., Kahara-Kawuki, A., Katono, I. W., Kyejjusa, S., Ngoma, M., & Oyugi, J. (2015). Action and action-regulation in entrepreneurship: Evaluating a student training for promoting entrepreneurship. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 14(1), 69–94.
Greenwald, A., & Leavitt, C. (1984). Audience involvement in advertising: Four levels. Journal of Consumer Research, 11(1), 187–202.
Greenwald, A., & Leavitt, C. (1985). Cognitive theory and audience involvement. In Alwitt & Mitchell (Eds.), Psychological Processes and Advertising Effects. NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Grönross, C. (1984). A service quality model and its marketing implications. European Journal of Marketing, 18(4), 36–44.
Grönroos, C. (1989). Defining marketing: a market-oriented approach. European Journal of Marketing, 23(1), 52–60.
Grummon, P. (2012). Trends in Higher Education. USA: Society for College and University Planning.
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1995). Multivariate data analysis with readings. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Hair, J. F., Hult, G., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2014). A primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Hannaford, W., Erffmeyer, R., & Tomkovick, C. (2005). Assessing the value of an undergraduate marketing technology course: What do educators think? Marketing Education Review, 15(1), 67–76.
Hartman, D. E., & Schmidt, S. L. (1995). Understanding student/alumni satisfaction from a consumer’s perspective: The effects of institutional performance and program outcomes. Research in Higher Education, 36(2), 197–217.
Harvey, L. (1995). Keeping the customer satisfied: The Student Satisfaction approach. Resource Document. Quality in Higher Education. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=478016
He, H., & Li, Y. (2011). Key service drivers for high-tech service brand equity: The mediating role of overall service quality and perceived value. Journal of Marketing Management, 27, 77–99.
Helgesen, Ø., & Nesset, E. (2007). Images, satisfaction and antecedents: Drivers of student loyalty? A case study of a Norwegian University College. Corporate Reputation Review, 10(1), 38–59.
Hemsley-Brown, J., & Oplatka, I. (2006). Universities in a competitive global marketplace: A systematic review of the literature on higher education marketing. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 19(4), 316–338.
Hemsley-Brown, J., Melewar, T. C., Nguyen, B., & Wilson, E. J. (2016). Exploring brand identity, meaning, image, and reputation (BIMIR) in higher education: A special section. Journal of Business Research, 69(8), 3019–3022.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Langer, M. F., & Hansen, U. (2001). Modeling and managing student loyalty: An approach based on the concept of relationship quality. Journal of Service Research, 4(2), 331–344.
Henseler, J., Hubona, G., & Ray, P. A. (2016). Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: Updated guidelines. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 116(1), 2–20.
Hill, C. J., & Motes, W. H. (1995). Professional versus generic retail services: New insights. Journal of Services Marketing, 9(2), 23–35.
Hodge, P., Wright, S., Barraket, J., Scott, M., Merville, R., & Richardson, S. (2011). Revisiting ‘how we learn’ in academia: Practice-based learning exchanges in three Australian universities. Studies in Higher Education, 36(2), 167–183.
Hu, H.-H., Kandampully, J., & Juwaheer, T. D. (2009). Relationship and impacts of service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction, and image: An empirical study. The Service Industries Journal, 29(2), 111–125.
Ivy, J. (2001). Higher education institution image: A correspondence analysis approach. International Journal of Educational Management, 15(6/7), 276–282.
Jin, N. P., Lee, S., & Lee, H. (2015). The effect of experience quality on perceived value, satisfaction, image and behavioral intention of water park patrons: New versus repeat visitors. International Journal of Tourism Research, 17(1), 82–95.
Johnson, M. D., Gustafsson, A., Andreassen, T. W., Lervik, L., & Cha, J. (2001). The evolution and future of national customer satisfaction index models. Journal of Economic Psychology, 22(2), 217–245.
Johnston, R. (1995). The determinants of service quality: Satisfiers and dissatisfiers. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 6(5), 53–71.
Joseph, M., Yakhou, M., & Stone, G. (2005). An educational institution’s quest for service quality: Customers’ perspective. Quality Assurance in Education, 13(1), 66–82.
Kheiry, B., Rad, B. M., & Asgari, O. (2012). University intellectual image impact on satisfaction and loyalty of students (Tehran selected universities). African Journal of Business Management, 6(37), 10205–10211.
Kim, H., Woo, E., & Uysal, M. (2015). Tourism experience and quality of life among elderly tourists. Tourism Management, 46, 465–476.
Krugman, H. E. (1965). The impact of television advertising: Learning without involvement. Public Opinion Quarterly, 29(3), 349–356.
Kumar, N., Hubbard, J. D., & Stern, L. W. (1994). The nature and consequences of marketing channel intermediary commitment. Cambridge: Marketing Science Institute.
Kuo, Y. F., Wu, C. M., & Deng, W. J. (2009). The relationships among service quality, perceived value, customer satisfaction, and post-purchase intention in mobile value-added services. Computers in Human Behavior, 25(4), 887–896.
Lai, L. S. L., To, W. M., Lung, J. W. Y., & Lai, T. M. (2012). The perceived value of higher education: The voice of Chinese students. Higher Education, 63(3), 271–287.
Landrum, R., Turrisi, R., & Harless, C. (1998). University image: The benefits of assessment and modeling. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 9(1), 53–68.
Landrum, R. E., Turrisi, R., & Harless, C. (1999). University image: the benefits of assessment and modeling. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 9(1), 53–68.
Laroche, M., Bergeron, J., & Goutaland, C. (2003). How intangibility affects perceived risk: the moderating role of knowledge and involvement. Journal of Services Marketing, 17(2), 122–140.
Laurent, G., & Kapferer, J. N. (1985). Measuring consumer involvement profiles. Journal of Marketing Research, 22(1), 41–53.
LeBlanc, G., & Nguyen, N. (1997). Searching for excellence in business education: An exploratory study of customer impressions of service quality. International Journal of Educational Management, 11(2), 72–79.
LeBlanc, G., & Nguyen, N. (1999). Listening to the customer's voice: Examining perceived service value among business college students. The International Journal of Educational Management, 13(4), 187–198.
Ledden, L., & Kalafatis, S. P. (2010). The impact of time on perceptions of educational value. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 23(2), 141–157.
Ledden, L., Kalafatis, S. P., & Mathioudakis, A. (2011). The idiosyncratic behaviour of service quality, value, satisfaction and intention to recommend in higher education: An empirical examination. Journal of Marketing Management, 27(11-12), 1232–1260.
Ledden, L., Kalafatis, S. P., & Samouel, P. (2007). The relationship between personal values and perceived value of education. Journal of Business Research, 60(9), 965–974.
Lervik, L., & Johnson, M. D. (2003). Service equity, satisfaction and royalty: From transaction-specific to cumulative evaluations. Journal of Service Research, 5(3), 184–195.
Lin, C., Sher, P. J., & Shih, H. (2005). Past progress and future directions in conceptualizing customer perceived value. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 16(4), 318–336.
Lohmöller, J. B. (1989). Latent variable path modeling with partial least squares. Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag.
Lovelock, C. H. (1983). Classifying services to gain strategic marketing insights. Journal of Marketing, 47(3), 9–20.
Luque-Martínez, T. (2012). Técnicas de análisis de datos en investigación de mercados. Pirámide: Madrid. Ed.
Luque-Martínez, T., & Del Barrio-García, S. (2009). Modelling university image: The teaching staff viewpoint. Public Relations Review, 35(3), 325–327.
Luque-Martínez, T., Del Barrio-García, S., Ibáñez-Zapata, J. A., & Rodríguez-Molina, M. A. (2007). Modeling a city's image: The case of Granada. Cities, 24(5), 335–352.
Luque-Martínez, T., et al. (2015). The University of Granada in light of its V Centenary. In Reflections on the future of the University. Granada: Editorial Universidad de Granada.
MacKenzie, S. B., Lutz, R. J., & Belch, G. E. (1986). The role of attitude toward the ad as a mediator of advertising effectiveness: A test of competing explanations. Journal of Marketing Research, 23(2), 130–143.
Mai, L. W. (2005). A comparative study between UK and US: The student satisfaction in Higher Education and its influential factors. Journal of Marketing Management, 21(7/8), 859–878.
Martensen, A., Grønholdt, L., Eskildsen, J. K., & Kristensen, K. (2000). Measuring student oriented quality in higher education: Application of the ECSI methodology. Sinergie rapporti di ricerca, 9, 371–383.
Marzo-Navarro, M., Pedraja-Iglesias, M., & Rivera-Torres, P. (2005). Measuring customer satisfaction in summer courses. Quality Assurance in Education, 13(1), 53–65.
Matherly, L. L. (2012). A causal model predicting student intention to enrol moderated by university image: Using strategic management to create competitive advantage in higher education. International Journal of Management in Education, 6(1), 38–55.
McDougall, G. H. G., & Levesque, T. (2000). Customer satisfaction with services: Putting perceived value into the equation. Journal of Services Marketing, 14(5), 382–410.
Mehta, A., & Purvis, S. C. (1997). Evaluating advertising effectiveness through advertising response modeling. In W. D. Wells (Ed.), Measuring advertising effectiveness (pp. 325–334). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Miron, M., & Segal, E. (1978). “The good university teacher” as perceived by the students. Higher Education, 7(1), 27–49.
Moosmayer, D. C., & Siems, F. U. (2012). Values education and student satisfaction: German business students' perceptions of universities' value influences. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 22(2), 257–272.
Moreno, F. C., Prado-Gascó, V., Hervás, J. C., Núñez-Pomar, J., & Sanz, V. A. (2015). Spectator emotions: Effects on quality, satisfaction, value, and future intentions. Journal of Business Research, 68(7), 1445–1449.
Munteanu, C., Ceobanu, C., Bobâlca, C., & Oana, A. (2010). An analysis of customer satisfaction in a higher education context. International Journal of Public Sector Management, 23(2), 124–140.
Neave, G., & Veiga, A. (2013). The Bologna Process: Inception, ‘take up’ and familiarity. Higher Education, 66(3), 59–77.
Nguyen, N., & LeBlanc, G. (1998). The mediating role of corporate image on customers’ retention decisions: An investigation in financial services. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 16(2), 52–65.
OCDE. (2016). Education at a Glance 2016: OECD Indicators. OECD.
Oh, H. (2000). Diners’ perceptions of quality, value and satisfaction. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly, 41(3), 58–66.
Oldfield, B., & Baron, S. (2000). Students’ perceptions of service quality in a UK university business and management faculty. Quality Assurance in Education, 8(2), 85–95.
Oliver, R. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. Journal of Marketing Research, 17(4), 460–469.
Oliver, R. L. (1996). Varieties of value in the consumption satisfaction response. Advances in Consumer Research, 23(1), 143–147.
Parameswararan, R., & Glowacka, A. E. (1995). University image: An information processing perspective. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 6(2), 41–56.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1985). A conceptual model of service quality and its implication for future research. Journal of Marketing, 49(4), 41–50.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1994). Reassessment of expectations as a comparison standard in measuring service quality: Implications for further research. Journal of Marketing, 58(2), 111–124.
Patterson, P. G., & Spreng, R. A. (1997). Modelling the relationship between perceived value, satisfaction and repurchase intentions in a business-to-business, services context: An empirical examination. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 8(5), 414–434.
Peng, P. J., & Samah, A. J. A. (2006). Measuring students’ satisfaction for quality education in an e-learning university. Unitar E-Journal, 2(1), 11–21.
Petruzzellis, L., & Romanazzi, S. (2010). Educational value: How students choose university: Evidence from an Italian University. International Journal of Educational Management, 24(2), 139–158.
Petty, R. E., & Cacioppo, J. T. (1986). The elaboration likelihood model of persuasion. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 19, 123–205.
Pihlström, M., & Brush, G. J. (2008). Comparing the perceived value of information and entertainment mobile services. Psychology & Marketing, 25(8), 732–755.
Pizam, A., Pizam, A., Shapoval, V., Shapoval, V., Ellis, T., & Ellis, T. (2016). Customer satisfaction and its measurement in hospitality enterprises: A revisit and update. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 28(1), 2–35.
Prayag, G., Hosany, S., Muskat, B., & Del Chiappa, G. (2017). Understanding the relationships between tourists’ emotional experiences, perceived overall image, satisfaction, and intention to recommend. Journal of Travel Research, 56(1), 41–54.
Prayag, G., & Ryan, C. (2012). Antecedents of tourists’ loyalty to Mauritius: The role and influence of destination image, place attachment, personal involvement, and satisfaction. Journal of Travel Research, 51(3), 342–356.
Reychav, I., & Wu, D. (2015). Are your users actively involved? A cognitive absorption perspective in mobile training. Computers in Human Behavior, 44, 335–346.
Ringle, C.M., Wende, S., & Becker, J-M. (2014). SmartPLS 3. Hamburg: SmartPLS. Retrieved from http://www.smartpls.com
Roberts, J., & Styron, R. (2010). Student satisfaction and persistence: Factors vital to student retention. Research in Higher Education, 6, 1–15.
Rothschild, M. L., & Houston, M. J. (1980). Individual differences in voting behavior: Further investigations of involvement, in NA - advances in consumer research volume 07. In J. C. Olson & A. Abor (Eds), Association for Consumer Research pp. 655–658.
Rowley, J. (1997). Beyond service quality dimensions in higher education and towards a service contract. Quality Assurance in Education, 5(1), 7–14.
Russell, M. (2005). Marketing education: A review of service quality perceptions among international students. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 17(1), 65–77.
Rust, R. T., & Oliver, R. L. (1994). Service Quality; New Directions in Theory and Practice. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publication.
Sakthivel, P. B., & Raju, R. (2006). An instrument for measuring engineering education quality from students’ perspective. The Quality Management Journal, 13(3), 23–34.
Sánchez-Fernández, R., & Iniesta-Bonillo, M. Á. (2007). The concept of perceived value: a systematic review of the research. Marketing Theory, 7(4), 427–451.
Sánchez-Fernández, R., & Iniesta-Bonillo, M. Á. (2009). Efficiency and quality as economic dimensions of perceived value: Conceptualization, measurement, and effect on satisfaction. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 16(6), 425–433.
Sánchez, J., Callarisa, L., Rodríguez, R., & Moliner, M. A. (2006). Perceived value of the purchase of a tourism product. Tourism Management, 27, 394–409.
Santini, F. D. O., Ladeira, W. J., Sampaio, C. H., & Costa, G. D. S. (2017). Student satisfaction in higher education: A meta-analytic study. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 1-18.
Schlesinger, W., Cervera, A., & Pérez-Cabañero, C. (2016). Sticking with your university: The importance of satisfaction, trust, image, and shared values. Studies in Higher Education, 1–17. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2015.1136613
Shukla, P. (2010). Effects of perceived sacrifice, quality, value, and satisfaction on behavioural intentions in the service environment. Services Marketing Quarterly, 31, 464–484.
Sinha, I., & DeSarbo, W. S. (1998). An integrated approach toward the spatial modeling of perceived customer value. Journal of Marketing Research, 35(2), 236–249.
Sohail, M. S., & Shaikh, N. M. (2004). Quest for excellence in business education: A study of student impressions of service quality. International Journal of Educational Management, 18(1), 58–65.
Stafford, T. S. (1994). Consumption values and the choice of marketing electives: Treating students like customers. Journal of Marketing Education, 16(2), 26–33.
Stephenson, J., & Yorke, M. (2013). Capability and quality in higher education. New York: Routledge.
Sursock, A., & Smidt, H. (2015). Trends 2015: Learning and Teaching in European Universities. Brussels: European University Association.
Suwanabroma, J., & Gamage, D. (2008). Improving the image of Thai Private Universities with quality services. Education & Society, 26(3), 45–61.
Tam, J. (2004). Customer satisfaction, service quality and perceived value: An integrative model. Journal of Marketing Management, 20(7/8), 897–917.
Teelken, C. (2012). Compliance or pragmatism: How do academics deal with managerialism in higher education? A comparative study in three countries. Studies in Higher Education, 37(3), 271–290.
Teeroovengadum, V., Kamalanabhan, T. J., & Seebaluck, A. K. (2016). Measuring service quality in higher education: Development of a hierarchical model (HESQUAL). Quality Assurance in Education, 24(2), 244–258.
Thomas, E. H., & Galambos, N. (2004). What satisfies students? Mining student-opinion data with regression and decision-tree analysis. Research in Higher Education, 45(3), 251–269.
Turel, O., Serenko, A., & Bontis, N. (2007). User acceptance of wireless short messaging services: Deconstructing perceived value. Information Management, 44(1), 63–73.
Unni, R. M. (2005). Value perceptions and retention of textbooks among marketing and other business majors. Marketing Education Review, 15(2), 71–79.
Upadyaya, K., & Salmela-Aro, K. (2017). Developmental dynamics between young adults’ life satisfaction and engagement with studies and work. Longitudinal and Life Course Studies, 8(1), 20–34.
Van Klaveren, C. (2010). Lecturing style teaching and student performance. Economics of Education Review, 30(4), 729–739.
Vila, L. E., Garcia-Aracil, A., & Gines-Mora, J. (2007). The distribution of job satisfaction among young european graduates: Does the choice of study field matter? The Journal of Higher Education, 78(1), 97–118.
Voss, G. B., & Voss, Z. G. (2000). Strategic orientation and firm performance in an artistic environment. Journal of Marketing, 64(1), 67–83.
Wang, C. (2010). Service quality, perceived value, corporate image, and customer loyalty in the context of varying levels of switching costs. Psychology & Marketing, 27(3), 252–262.
Webb, D., & Jagun, A. (1997). Customer care, customer satisfaction, value, loyalty and complaining behavior: validation in a UK university setting. Journal of Consumer Satisfaction, Dissatisfaction and Complaining Behavior, 10, 139–151.
Wilkins, S., Butt, M. M., Kratochvil, D., & Balakrishnan, M. S. (2015). The effects of social identification and organizational identification on student commitment, achievement and satisfaction in Higher Education. Studies in Higher Education, 1–21. doi: 10.1080/03075079.2015.1034258.
Wold, H. (1982). System under indirect observation using PLS. In C. Fornell (Ed.), A second generation of multivariate analysis (pp. 325–347). New York: Praeger Publishers.
Wong, A., Woo, A., & Tong, C. (2016). Student satisfaction and school reputation: The moderating role of student loyalty and school image. Journal of Marketing and HR, 2(1), 113–125.
Woodruff, R. B. (1997). Customer value: The next source for competitive advantage. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 25(2), 139–153.
Yang, Z., & Peterson, R. (2004). Customer perceived value, satisfaction, and loyalty: The role of switching costs. Psychology & Marketing, 21(10), 799–822.
Zaichkowsky, J. L. (1986). Conceptualizing involvement. Journal of Advertising, 15(2), 4–14.
Zaichowsky, J. L. (1985). Measuring the involvement construct. Journal of Consumer Research, 12(4), 341–352.
Zeegers, P. (2004). Student learning in higher education: A path analysis of academic achievement in science. Higher Education Research & Development, 23(1), 35–56.
Zeithaml, V. A. (1988). Consumer perceptions of price, quality, and value: A means-end model and synthesis of evidence. Journal of Marketing, 52(3), 2–22.
Zeithaml, V. A., Berry, L., & Parasuraman, A. (1996). The behavioral consequences of service quality. Journal of Marketing, 60(2), 31–46.
Zeithaml, V. A., Berry, L. L., & Parasuraman, A. (1988). Communication and control processes in the delivery of service quality. Journal of Marketing, 52(2), 35–48.
Zeithaml, V., & Bitner, M. (2003). Service Marketing: Integrating Customer Focus across the Firm. New York: McGraw Hill.
Zhou, J., & Cole, D. (2016). Comparing international and American students: Involvement in college life and overall satisfaction. Higher Education, 71(1), 1–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doña-Toledo, L., Luque-Martínez, T. & Del Barrio-García, S. Antecedents and consequences of university perceived value, according to graduates: The moderating role of Higher Education involvement. Int Rev Public Nonprofit Mark 14, 535–565 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-017-0186-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-017-0186-y