Abstract
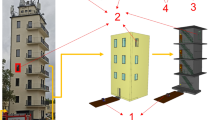
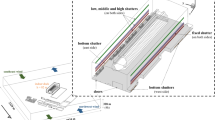
Large eddy simulation (LES) method is applied to systematically investigate the cooling fluid flow and the temperature distribution under the operating of air conditioning in the deeply underground subway station. The Shin-Gum-Ho subway station in Seoul which is the 8th floor and 43.6 m deep is selected for this analysis. The entire station is covered for simulation. The ventilation mode for air conditioning is kept as ordinary state. Different operating conditions for Platform screen door (PSD) are applied. First one is PSD is completely close and second one is PSD is regularly open & close which imitate the actual circumstances in the platform. The ventilation diffusers are modeled as 95 square shapes in the lobby and 222 squares in the platform. The temperature variations and flow behaviors are numerically simulated after operating of air conditioning for the whole station and the calculated results are compared with experimental data [11]. LES method solves the momentum and thermal equations. Werner-Wengle wall law is applied to viscous sublayers for near wall resolution. The total grid numbers are 7.5 million and the whole domain is divided to 22 blocks. Multi blocks are computed in parallel using MPI. The results show the temperature difference in the platform between PSD-close and PSD-regularly open & close cases is 3-4°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. J. Jang, The study of renewable energy for application to the railway system, KRRI-STUDY 2009-G-04–01, Korea Railroad Research Institute (2002).
I. Kim, H. N. Kim and J. S. Park, Analysis of factors to affect the amount of power consumption on Seoul subway Line 9, 2013 Spring Conference & Annual Meeting of the Korean Society for Railway (2013).
S. J. Bae, S. H. Hwang and C. H. Shin, A Study of air quality and cooling efficiency improvement by PSD installation, 2009 Autumn Conference & Annual Meeting of the Korean Society for Railway (2009).
B. W. Han, Y. M. Kim and J. H. Hong, Effect of Traininduced Wind on Tunnel Ventilation in a Subway Tunnel, Proceeding of the 50 th Meeting of KOSAE Korean Society for Atmospheric Environment (2010).
J.-Y. Kim, Development of Optimum Design Technology of Platform Screen Door Systems for the Environment Improvement and Disaster Prevention of Urban Railway, Proceedings of 2008 Winter Conference & Annual Meeting of the Society of Air-conditioning and Refrigerating Engineers of Korea (2008) 84–87.
M. Juraeva, J. R. Kyung and S.-H. Jeong, Influence of mechanical ventilation-shaft connecting location on subway tunnel ventilation performance, Journal of Wind Engineering Industrial Aerodynamics, 119 (1994) 114–120.
H. J. Gerhardt and O. Kruger, Wind and train driven air movements in train stations, Journal of Wind Engineering Industrial Aerodynamics, 74–76 (1998) 589–597.
J.-Y. Kim and K.-Y Kim, Effects of vent shaft location on the ventilation performance in a subway tunnel, Journal of Wind Engineering Industrial Aerodynamics, 97 (2009) 174–179.
J. Ji, J. Y. Han, C. G. Fan, Z. H. Gao and J. H. Sun, Influence of cross-sectional area and aspect ratio of shaft on natural ventilation in urban road tunnel, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 67 (2013) 420–431.
C. G. Fan, J. Ji, W. Wang and J. H. Sun, Effects of vertical shaft arrangement on natural ventilation performance during tunnel fires, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 73 (2014) 158–169.
Y.-J. Jang, H.-S. Lee and D.-S. Park, Experimental Study for the Capacity of Ordinary and Emergency Ventilation System in Deeply Underground Subway Station, Journal of The Korean Society for Railway, 15 (6) (2012) 579–587.
Y.-J. Jang, An investigation of higher-order closures in the computation of the flow around a generic car, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 22 (2008) 1019–1029.
Y.-J. Jang, M. A. Leschziner, K. Abe and L. Temmerman, Investigation of anisotropy-resolving turbulence models by reference to highly-resolved LES data for separated flows, Flow, Turbulence and Combustion, 69 (2002) 161–203.
J. Smagorinsky, General circulation experiments with the primitive equation, I, the basic experiment, Monthly Weather Review, 91 (3) (1963) 99–164.
K. J. McGrattan, R. McDermontt, S. Hostikka and J. Floyd, Fire Dynamics Simulator (ver. 5) User’s Guide, NIST (2010).
H. Werner and H. Wengle, Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow over and around a cube in a plate channel, 8 th Symposium on Turbulent Shear Flows (1991) 155–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Donghyun You
Yong-Jun Jang received his Ph.D. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Texas A&M University, USA in 2000. He worked as Research Associate in the Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London, UK from 2000 to 2004. Dr. Jang is currently a Principal Researcher in Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI). His research interests include Railroad Safety and Energy Efficiency.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, YJ., Kim, JH., Park, SH. et al. Large eddy simulation of cooling flows in underground subway station according to different psd operating conditions. J Mech Sci Technol 29, 5257–5265 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-1127-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-1127-5