Abstract
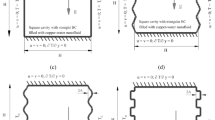
In this work, natural convection and entropy generation in a square cavity with an obstacle filled with Cu-water nanofluid is numerically studied. Horizontal walls of the cavity are adiabatic and vertical walls are maintained at a different constant temperature. The study has been done for the Rayleigh numbers between 103 and 106, the obstacle dimensions (W/L) of 0.1–0.5 and for base fluid as well as nanofluid. It is found that, using the nanofluid overall leads to increase the flow strength, Nusselt number and entropy generation and decrease the Bejan number especially at high Rayleigh numbers. It is observed that by increasing the obstacle dimensions, the entropy generation increases and the Bejan number decreases, but the effect of the obstacle dimensions on Nusselt number depends on Rayleigh number. For the present thermal system, the increasing Nusselt number compared to increasing entropy generation due to increase obstacle dimensions is significant at low Rayleigh numbers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. J. Ho, M. W. Chen and Z. W. Li, Numerical simulation of natural convection of nanofluid in a square enclosure: effect due to uncertainties of viscosity and thermal conductivity, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 51 (2008) 4506–4516.
S. M. Aminossadati and B. Ghasemi, Natural convection cooling of a localised heat source at the bottom of a nanofluid-filled enclosure, Eur. J. Mech. B-Fluid 28(5) (2009) 630–640.
E. Abu-Nada and A. J. Chamkha, Effect of nanofluid variable properties on natural convection in enclosures filled with a CuO-EG-Water nanofluid, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49 (2010) 2339–2352.
K. C. Lin and A. Violi, Natural convection heat transfer of nanofluids in a vertical cavity: Effects of non-uniform particle diameter and temperature on thermal conductivity, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 31 (2010) 236–245.
M. Jahanshahi, S. F. Hosseinizadeh, M. Alipanah, A. Dehghani and G. R. Vakilinejad, Numerical simulation of free convection based on experimental measured conductivity in a square cavity using Water/SiO2 nanofluid, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37 (2010) 687–694.
R. L. Hamilton and O. K. Crosser, Thermal conductivity of heterogeneous two component systems, I&EC Fundamentals 1(3) (1962) 187–191.
H. E. Patel, T. Pradeep, T. Sundararajan, A. Dasgupta, N. Dasgupta and S. K. Das, A microconvection model for thermal conductivity of nanofluid, Pramana-J. Phys. 65 (2005) 863–869.
K. D. Hemanth, H. E. Patel, V. R. R. Kumar, T. Sundararajan, T. Pradeep and S. K. Das, Model for heat conduction in nanofluids, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 (2004) 144301–1-4.
H. C. Brinkman, The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions, J. Chem. Phys. 20 (1952) 571–581.
H. Chang, C. S. Jwo, C. H. Lo, T. T. Tsung, M. J. Kao and H. M. Lin, Rheology of CuO nanoparticle suspension prepared by ASNSS, Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 10 (2005) 128–132.
A. S. Teja, M. P. Beck, Y. Yuan and P. Warrier, The limiting behavior of the thermal conductivity of nanoparticles and nanofluids, J. Applied Physics, 107 (2010) 114319.
N. Shalkevich, W. Escher, T. Burgi, B. Michel, L. Si-Ahmed and D. Poulikakos, On the thermal conductivity of gold nanoparticle colloids, Langmuir, 26(2) (2010) 663–670.
A. Bejan, Entropy generation through heat and fluid flow, Wiley, New York, 1982.
K. Hooman, Entropy-energy analysis of forced convection in a porous-saturated circular tube considering temperature-dependent viscosity effects, Int. J. Exergy. 3 (2006) 436–451.
G. Ibanez, S. Cuevas and M. L. de Haro, Minimization of entropy generation by asymmetric convective cooling, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 46 (2003) 1321–1328.
R. D. C. Oliveski, M. H. Macagnan and J. B. Copetti, Entropy generation and natural convection in rectangular cavities, Appl. Therm. Eng. 29 (2009) 1417–1425.
P. K. Singh, K. B. Anoop, T. Sundararajan and S. K. Das, Entropy generation due to flow and heat transfer in nanofluids, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 53 (2010) 4757–4767.
J. R. Lee and M. Y. Ha, A numerical study of natural convection in a horizontal enclosure with a conducting body, Int. J. of Heat Mass Transf. 48 (2005) 3308–3318.
G. A. Sheikhzadeh, A. Arefmanesh, M. H. Kheirkhah and R. Abdollahi, Natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a cavity with partially active side walls, Eur. J. Mech. B-Fluid 30(2) (2011) 166–176.
K. Khanafer and K. Vafai, A critical synthesis of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 54 (2011) 4410–4428.
K. Khanafer, K. Vafai and M. Lightstone, Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 46 (2003) 3639–3653.
E. Abu-nada, A. J. Chamkha, Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven inclined square enclosure filled with a nanofluid, Eur. J. Mech. B-Fluid 29(6) (2010) 472–482.
F. Talebi, A. H. Mahmoudi and M. Shahi, Numerical study of mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity utilizing nanofluid, Int. Comm. Heat Mass Tran. 37 (2010) 79–90.
M. Magherbi, H. Abbassi and A. B. Brahim, Entropy generation at the onset of natural convection, Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 46(18) (2003) 3441–3450.
S. V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Hemisphere Pub, New York, 1980.
G. De Vahl Davis, Natural convection of air in a square cavity a bench mark numerical solution, Int. J. Numer. Method H. 3 (1983) 249–264.
S. Kondaraju and J. Sang Lee, Two-phase numerical model for thermal conductivity and convective heat transfer in nanofluids, Nanoscale Res Lett. 6(1) (2011) 239.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Jun Sang Park
Ghanbar Ali Sheikhzadeh is an Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Department at University of Kashan; Kashan, Iran. He received his Ph.D in Mechanical Engineering from Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman. His research work concerns numerical analysis and application of heat transfer in nano-systems and other areas of thermal and fluid sciences. Dr. Sheikhzadeh has published many journal and conference papers on these topics.
Majid Nikfar is a researcher of Energy Research Institute at University of Kashan; Kashan, Iran. He received his Master’s degree from University of Kashan; Kashan, Iran. His research interest is fluid dynamics, heat transfer and combustion.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhzadeh, G.A., Nikfar, M. & Fattahi, A. Numerical study of natural convection and entropy generation of Cu-water nanofluid around an obstacle in a cavity. J Mech Sci Technol 26, 3347–3356 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0805-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-012-0805-9