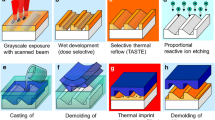
Abstract
Nanoimprint lithography (NIL) is one of the most promising technologies for nanofabrication because it can create nano- and microscale structures and devices in a cost-effective manner. In the NIL process, a mold with patterns on its surface comes in contact with a polymer film on a substrate. The patterns are transferred to the polymer film and then the mold is separated from the film. Mechanical contact between the mold and the polymer film, and between the film and the substrate, is inevitable. In some cases, during the separation process, adhesion and friction forces at the interfaces can deform and fracture the transferred patterns and detach the polymer film from the substrate. Thus, controlling the adhesion and friction between the materials in contact is very important in achieving a successful pattern transfer and making the NIL process a robust nanofabrication technique. Many theoretical and experimental research efforts have been made to clarify the tribological phenomena in NIL and to reduce defects due to adhesion and friction. This article describes the tribological problems encountered and reviews the related research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. D. Gates, Q. Xu, J. C. Love, D. B. Wolfe and G. M. Whitesides, Unconventional nanofabrication, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 34 (2004) 339–372.
B. D. Gates, Q. Xu, M. Stewart, D. Ryan, C. G. Willson and G. M. Whitesides, New approaches to nanofabrication: molding, printing, and other techniques, Chem. Rev. 105 (2005) 1171–1196.
L. J. Guo, Recent progress in nanoimprint technology and its applications, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37 (2004) 123–141.
H. Schift, Nanoimprint lithography: An old story in modern times? A review, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 26(2) (2008) 458–480.
S. Y. Chou, P. R. Krauss and P. J. Renstrom, Imprint of sub-25 nm vias and trenches in polymers, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67(20) (1995) 3114–3116.
J. Haisma, M. Verheijein, K. van den Heuvel and J. van den Berg, Mold-assisted nanolithography: A process for reliable pattern replication, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 14(6) (1996) 4124–4128.
T. Bailey, B. J. Choi, M. Colburn, M. Meissl, S. Shaya, J. G. Ekerdt, S. V. Sreenivasan and C. G. Willson, Step and flash imprint lithography: Template surface treatment and defect analysis, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 18(6) (2000) 3572–3577.
M. D. Austin, H. Ge, W. Wu, M. Li, Z. Yu, D. Wasserman, S. A. Lyon and S. Y. Chou, Fabrication of 5 nm linewidth and 14 nm pitch features by nanoimprint lithography, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(26) 2004 5299–5301.
D. S. Macintyre, Y. Chen, D. Gourlay, E. Boyd, D. Moran, X. Cao, K. Elgaid, C. R. Stanley, I. Thayne and S. Thoms, Nanoimprint lithography process optimization for the fabrication of high electron mobility transistors, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 21(6) (2004) 2783–2787.
C. Chao and L. J. Guo, Polymer microring resonators fabricated by nanoimprint technique, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 20(6) (2002) 2862–2866.
E. M. Arakcheeva, E. M. Tanklevskaya, S. I. Nesterov, M. V. Maksimov, S. A. Gurevich, J. Seekamp and C. M. S. Torres, Fabrication of semiconductor- and polymer-based photonic crystals using nanoimprint lithography, Tech. Phys. 50(8) (2005) 1043–1047.
P. C. Kao, S. Y. Chu, T. Y. Chen, C. Y. Zhan, F. C. Hong, C. Y. Chang, L. C. Hsu, W. C. Liao and M. H. Hon, Fabrication of large-scaled organic light emitting devices on the flexible substrates using low-pressure imprinting lithography, Elec. Dev. IEEE Transactions 52(8) (2005) 1722–1726.
S. W. Ahn, K. D. Lee, J. S. Kim, S. H. Kim, J. D. Park, S. H. Lee and P. W. Yoon, Fabrication of a 50 nm half-pitch wire grid polarizer using nanoimprint lithography, Nanotechnology 16(9) (2005) 1874–1877.
Y. Hirai, S. Yoshida and N Takagi, Defect analysis in thermal nanoimprint lithography, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 20(6) (2003) 2765–2770.
Y. Hirai, S. Yoshida, N. Takagi, Y. Tanaka, H. Yabe, K. Sasaki, H. Sumitani and K. Yamamoto, High aspect pattern fabrication by nanoimprint lithography using fine diamond mold, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 (2003) 3863–3866.
R. W. Jaszewski, H. Schift, P. Groning and G. Margaritondo, Properties of thin anti-adhesive films used for the replication of microstructures in polymers, Microelectronic Eng. 45(1–4) (1997) 381–384.
M. Beck, M. Graczyk, I. Maximov, E.-L. Sarwe, T. G. I. Ling, M. Keil and L. Montelius, Improving stamps for 10 nm level wafer scale nanoimprint lithography, Microelectronic Eng. 61–62 (2002) 441–448.
A. Ulman, Formation and structure of self-assembled monolayers, Chem. Rev. 96 (1996) 1533–1554.
J. K. Chen, F. H. Ko, K. F. Hsieh, C. T. Chou and F. C. Chang, Effect of fluoroalkyls substituents on the reactions of alkylchlorosilanes with mold surfaces for nanoimprint lithography, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 22(6) (2004) 3233–3241.
G. Y. Jung, Z. Li, W. Wu, Y. Chen, D. L. Olynick, S. Y. Wang, W. M. Tong and R. S. Williams, Vapor-phase selfassembled monolayer for improved mold release in nanoimprint lithography, Langmuir 21 (2005) 1158–1161.
H. Schift, S. Saxer, S. G. Park, C. Padeste, U. Pieles and J. Gobrecht, Controlled co-evaporation of silanes for nanoimprint stamps, Nanotechnology 16 (2005) S171–S175.
P. Gallo, B. Viallet, E. Daran and C. Fontaine, Efficient aminosilane adhesion promoter for soft nanoimprint on GaAs, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 (2005) 183111.
D. G. Choi, D. I. Lee, K. D. Kim, J. H. Jeong, J. H. Choi and E. S. Lee, Measurement of surface adhesion force of adhesion promoter and release layer for UV-nanoimprint lithography, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9 (2009) 769–773.
F. A. Houle, E. Guyer, D. C. Miller and R. Dauskardt, Adhesion between template materials and UV-cured nanoimprint resists, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 25(4) (2007) 1179–1185.
D. Truffier-Boutry, M. Zelsmann, J. De Girolamo, J. Boussey, C. Lombard and B. Pépin-Donat, Chemical degradation of fluorinated antisticking treatments in UV nanoimprint lithography, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 (2009) 044110.
A. Erdemir, Genesis of superlow friction and wear in diamondlike carbon films, Tribol. Int. 37 (2004) 1005–1012.
S. Ramachandran, L. Tao, T. H. Lee, S. Sant, L. J. Overzet, M. G. Goeckner, M. J. Kim, G. S. Lee and W. Hu, Deposition and patterning of diamondlike carbon as antiwear nanoimprint templates, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 24(6) (2006) 2993–2997.
A. O. Altun, J. H. Jeong, J. J. Rha, D. G. Choi, K. D. Kim and E. S. Lee, Fabrication of fluorine-doped diamond-like carbon stamps for UV nanoimprint lithography, Nanotechnology 17 (2006) 4659–4663.
K. Nakamatsu, N. Yamada, K. Kanda, Y. Haruyama and S. Matsui, Fluorinated diamond-like carbon coating as antisticking layer on nanoimprint mold, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 45(35) (2006) L954–L956.
K. D. Kim, J. H. Jeong, A. Ali, D. I. Lee, D. G. Choi and E. S. Lee, Replication of an UV-NIL stamp using DLC coating, Microelectronic Eng. 84 (2007) 899–903.
M. Schvartzman, A. Mathur, Y. Kang, C. Jahnes, J. Hone and S. J. Wind, Fluorinated diamondlike carbon templates for high resolution nanoimprint lithography, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 26 (6) (2008) 2394–2398.
D. Y. Khang, and H. H. Lee, Sub-100 nm patterning with an amorphous fluoropolymer mold, Langmuir 20 (2004) 2445–2448.
D. G. Choi, J. H. Jeong, Y. S. Sim, E. S. Lee, W. S. Kim, and B. S. Bae, Fluorinated organic-inorganic hybrid mold as a new stamp for nanoimprint and soft lithography, Langmuir 21 (2005) 9390–9392.
T. T. Truong, R. Lin, S. Jeon, H. H. Lee, J. Maria, A. Gaur, F. Hua, I. Meinel and J. A. Rogers, Soft lithography using acryloxy perfluoropolyether composite stamps, Langmuir 23 (2007) 2898–2905.
J. Y. Kim, D. G. Choi, J. H. Jeong and E. S. Lee, UVcurable nanoimprint resin with enhanced anti-sticking property, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254 (2008) 4793–4796.
T. H. Kim, A. Carlson, J. H. Ahn, S. M. Won, S. Wang, Y. Huang and J. A. Rogers, Kinetically controlled, adhesiveless transfer printing using microstructured stamps, App. Phys. Lett. 94 (2009) 113502.
H. Zeng, N. Maeda, N. Chen, M. Tirrell and J. Israelachvili, Adhesion and friction of polystyrene surfaces around Tg, Macromolecules 39 (2006) 2350–2363.
R. M. Christensen, Theory of Viscoelasticity, An Introduction, 2 nd Edition, Academic Press, New York, USA, (1982).
M. W. Lin, D. J. Hellebusch, K. Wu, E. K. Kim, K. H. Lu, K. M. Liechti, J. G. Ekerdt, P. S. Ho and C. G. Willson, Role of surfactants in adhesion reduction for step and flash imprint lithography, J. Micro/Nanolith. MEMS MOEMS 7(3) (2008) 033005.
J. W. Hutchinson and Z. Suo, Mixed mode cracking in layered materials, Adv. Appl. Mech. 29 (1992) 63–191.
J. H. Kang, K. S. Kim and K. W. Kim, Molecular dynamics study of pattern transfer in nanoimprint lithography, Tribol. Lett. 25 (2007) 93–102.
R. B. Dupaix and W. Cash, Finite element modeling of polymer hot embossing using a glass-rubber finite strain constitutive model, Polym. Eng. Sci. 49(3) (2009) 531–543.
K. L. Mittal, Adhesion measurement of films and coatings, VSP, Netherlands, (1995).
J. Taniguchi, T. Kawasaki, Y. Tokano, Y. Kogo, I. Miyamoto, M. Komuro, H. Hiroshima, N. Sakai and K. Tada, Measurement of adhesive force between mold and photocurable resin in imprint technology, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 41 (2002) 4194–4197.
E. J. Jang, Y. B. Park, H. J. Lee, D. G. Choi, J. H. Jeong, E. S. Lee and S. Hyun, Effect of surface treatments on interfacial adhesion energy between UV-curable resist and glass wafer, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 29(6) (2009) 662–669.
J. Tallal, M. Gordon, K. Berton, A. L. Charley and D. Peyrade, AFM characterization of anti-sticking layers used in nanoimprint, Microelec. Eng. 83 (2006) 851–854.
H. J. Lee, S. Hyun, J. H. Kim, H. J. Lee, D. G. Choi, D. I. Lee, J. H. Jeong and E. S. Lee, Measurement of adhesion force by a symmetric AFM probe for nano-imprint lithography application, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 22 (2008) 1379–1386.
A. Koszewski, Z. Rymuza and F. Reuther, Evaluation of nanomechanical, nanotribological and adhesive properties of ultrathin polymer resist film by AFM, Microelectronic Eng. 85 (2008) 1189–1192.
K. S. Kim, Y. Ando and K. W. Kim, The effect of temperature on the nanoscale adhesion and friction behaviors of thermoplastic polymer films, Nanotechnology 19 (2008) 105701.
K. S. Kim, J. C. Heo and K. W. Kim, Effect of temperature on the micro-scale adhesion behavior of thermoplastic polymer film, J. KSTLE 25(2) (2009) 86–95.
S. Park, H. Schift, C. Padeste, B. Schnyder, R. Kotz and J. Gobrecht, Anti-adhesive layers on nickel stamps for nanoimprint lithography, Microelectronic Eng. 73–74 (2004) 196–201.
K. S. Kim, J. H. Kang and K. W. Kim, Adhesion characteristics between mold and thermoplastic polymer film in thermal nanoimprint lithography, J. KSTLE 24(5) (2008) 255–263.
K. S. Kim, J. C. Heo and K. W. Kim, Effects of temperature on the tribological characteristics of thermoplastic polymer film, J. KSTLE 25(4) (2009) 207–216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sang-Rok Lee received his B.S. in Naval Architecture Engineering from Seoul National University in 1976. He then received his M.S. in Production Engineering from KAIST, and Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from Washington State University in 1987. Dr. Lee is currently a director of Center for Nanoscale Mechatronics & Manufacturing. His research interests include development of nanoscale manufacturing process and related equipment, and industrialization of the emerging nanotechnology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KS., Kim, JH., Lee, HJ. et al. Tribology issues in nanoimprint lithography. J Mech Sci Technol 24, 5–12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-1216-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-1216-4