Abstract
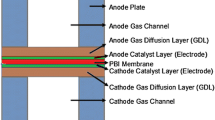
An investigation of electrochemical behavior of PEMFC (proton exchange membrane fuel cell) is performed by using a single-phase two-dimensional finite element analysis. Equations of current balance, mass balance, and momentum balance are implemented to simulate the behavior of PEMFC. The analysis results for the co-flow and counter-flow mode of gas flow direction are examined in detail in order to compare how the gas flow direction affects quantitatively. The characteristics of internal properties, such as gas velocity distribution, mass fraction of the reactants, fraction of water and current density distribution in PEMFC are illustrated in the electrode and GDL (gas diffusion layer). It is found that the dry reactant gases can be well internally humidified and maintain high performance in the case of the counter-flow mode without external humidification while it is not advantageous for highly humidified or saturated reactant gases. It is also found that the co-flow mode improves the current density distribution with humidified normal condition compared to the counter-flow mode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Marr and X. Li, Two-dimensional finite element method study of the resistance of membranes in polymer electrolyte fuel cells, Electrochimica Acta, 45 (2000) 1741–1751.
D. M. Bernardi and M. W. Verbrugge, Mathematical model of a gas diffusion electrode bonded to a polymer electrolyte, AIChe Journal, 37 (1991) 1151–1163.
C. K. Dyer, Fuel Cells for Portable Applications, Journal of Power Sources, 106 (2002) 31–34.
J. P. Meyers and H. L. Maynard, Design considerations for miniaturized PEM fuel cells, Journal of Power Sources, 109 (2002) 76–88.
J. W. Raadschelders and T. Jansen, Energy sources for the future dismounted soldier: the total integration of the energy consumption within the soldier system, Journal of Power Sources, 96 (2001) 160–166.
C. Heinzel et al., Fuel cells for low power applications, Journal of Power Sources, 2(105) (2002) 250–255.
W. C. Yang, Fuel cell electric vehicle: Recent advances and challenges, International Journal of Automotive Technology, 1(1) (2000) 9–16.
T. F. Fuller and J. Newman, Water and thermal management in solid-polymer-electrolyte fuel cells, Journal of Electrochemical Society, 140 (1993) 1218–1226.
J. S. Yi and T. V. Nguyen, An along the channel model for PEMFC, Journal of Electrochemical Society, 145 (1998) 1149–1156.
J. S. Yi and T. V. Nguyen, Multi-component transport in porous electrodes in proton exchange membrane fuel cells using the interdigitated gas distributors, Journal of Electrochemical Society, 146 (1999) 38–45.
He, W. et al., Two-phase flow model of the cathode of pem fuel cells using interdigitated flow field, AIChe Journal., 46 (2000) 2053–2059.
H. G. Kim, et al., Electric voltage and current characteristics of fuel cell for machine tool power supply, Journal of Korean Society for Machine Tool Engineers, 14 (2005) 1–7.
COMSOL AB, Comsol Multiphysics Manual Ver. 3.3: The proton exchange membrane fuel cell, Burlington, MA, USA, (2006).
H. S. Fogler, Element of Chemical Reaction Engineering, Third Ed., Prentice Hall, (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwac, L.K., Kim, H.G. Investigation of gas flow characteristics in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J Mech Sci Technol 22, 1561–1567 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0318-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0318-8