Abstract
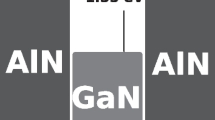
In this paper, we proposed quantum dot (QD) based structure for implementation of white light emitting diode (WLED) based on InGaN/GaN. The proposed structure included three layers of InGaN QD with box shapes and GaN barriers. By using of single band effective mass method and considering strain effect, piezoelectric and spontaneous polarizations internal fields, then solving Schrödinger and Poisson equations self consistently, we obtained electron and hole eigen energies and wave functions. By evaluating dipole moment matrix elements for interband transitions, the output intensity was calculated due to the interband transition between two energy levels with highest emission probability. We adjusted QDs dimensions and material compositions so that the output light can be close to the ideal white light in chromaticity diagrams. Finally, effects of temperature variations on output spectrum and chromaticity coordinates were studied. We demonstrated that temperature variations in the range of 100 to 400 K decrease output intensity, broaden output spectral profile and cause a red shift in three main colors spectrums. This temperature variation deviates (x, y) are coordinated in the chromaticity diagram, but the output color still remains close to white.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakamura S, Mukai T, Senoh M. Candela-class high-brightness InGaN/AIGaN double-heterostructure blue-light-emitting diodes. Applied Physics Letters, 1994, 64(13): 1687–1689
Nakamura S. Zn-doped InGaN growth and InGaN/A1GaN doubleheterostructure blue-light-emitting diodes. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1994, 145(1–4): 911–917
Vurgaftmana I, Meyer J R, Ram-Mohan L R. Band parameters for III–V compound semiconductors and their alloys. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(11): 5815–5875
Wu J, Walukiewicz W, Yu K M, Ager J W, Haller E E, Lu H, Schaff W J. Small band gap bowing in In1 − x GaxN alloys. Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 80(25): 4741–4743
Piprek J. Nitride Semiconductor Devices: Principles and Simulation. NewYork: WILEY-VCH, 2007
Allen S C, Steck A J. A nearly ideal phosphor-converted white lightemitting diode. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(14): 143309–143311
Xie R J, Hirosaki N, Kimura N, Sakuma K, Mitomo M. 2-phosphorconverted white light-emitting diodes using oxynitride/ nitride phosphors. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(19): 191101–191103
Khoshnegar M, Sodagar M, Eftekharian A, Khorasani S. Design of a GaN white light-emitting diode through envelope function analysis. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2010, 46(2): 228–237
Anikeeva P O, Halpert J E, Bawendi M G, Bulović V. Electroluminescence from a mixed red-green-blue colloidal quantum dot monolayer. Nano Letters, 2007, 7(8): 2196–2200
Schubert E F, Kim J K. Solid-state light sources getting smart. Science, 2005, 308(5726): 1274–1278
Chen C H, Su Y K, Sheu J K, Chen J F, Kuo C H, Lin Y C. Nitridebased cascade near white light-emitting diodes. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2002, 14(7): 908–910
Ozden I, Makarona E, Nurmikko A V, Takeuchi T, Krames M. A dual-wavelength indium gallium nitride quantum well light emitting diode. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 79(16): 2532–2534
Park K, Kwon M K, Cho C Y, Lim J H, Park S J. Phosphor-free white light-emitting diode with laterally distributed multiple quantum wells. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(9): 091110–091112
Shei S C, Sheu J K, Tsai C M, Lai W C, Lee M L, Kuo C H. Emission mechanism of mixed-color InGaN/GaN multi-quantumwell light-emitting diodes. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2006, 45(4): 2463–2466
Rostami A, Rasooli Saghai H, Baghban Asghari Nejad H. A proposal for enhancement of optical nonlinearity in GaN/AlGaN centered defect quantum box (CDQB) nanocrystal. Solid-State Electronics, 2008, 52(7): 1075–1108
Lai C Y, Hsu T M. Polarization field effect on group III-nitride semiconductors. Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Taiwan, China, 2003
Winkelnkemper M, Schliwa A, Bimberg D. Interrelation of structural and electronic properties in InxGa1 − x N/GaN quantum dots using an eight-band k·p model. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2006, 74(15): 155322–155333
Wu Y R, Lin Y Y, Huang H H, Singh J. Electronic and optical properties of InGaN quantum dot based light emitters for solid state lighting. Applied Physics, 2009, 105: 13117–13123
Ranjan V, Allan G, Priester C, Delerue C. Self-consistent calculations of the optical properties of GaN quantum dots. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2003, 68(11): 115305–115311
Sakamoto A, Sugawara M. Theoretical calculation of lasing spectra of quantum-dot lasers: effect of homogeneous broadening of optical gain. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2000, 12(2): 107–109
Sugawara M. Self-Assembled InGaAs/GaAs Quantum Dots. London: Academic press, 1999
Asada M, Miyamoto Y, Suematsu Y. Gain and the threshold of three-dimensional quantum-box lasers. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1986, QE-22(9): 1915–1921
Fairman H S, Brill M H, Hemmendinger H. How the CIE 1931 color-matching functions were derived from Wright-Guild data. Color Research and Application, 1998, 22(1): 11–23
Han D S, Asryan L V. Output power of a double tunneling-injection quantum dot laser. Nanotechnology, 2010, 21(1): 15201–15214
Schubert E F, Gessmann T, Kim J K. Light-Emitting Diodes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12200-014-0385-7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjbaran, A. Temperature effects on output characteristics of quantum dot white light emitting diode. Front. Optoelectron. 5, 284–291 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-012-0275-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-012-0275-9