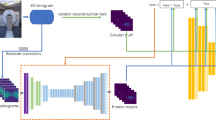
Abstract
Although deep learning for application in positron emission tomography (PET) image reconstruction has attracted the attention of researchers, the image quality must be further improved. In this study, we propose a novel convolutional neural network (CNN)-based fast time-of-flight PET (TOF-PET) image reconstruction method to fully utilize the direction information of coincidence events. The proposed method inputs view-grouped histo-images into a 3D CNN as a multi-channel image to use the direction information of such events. We evaluated the proposed method using Monte Carlo simulation data obtained from a digital brain phantom. Compared with a case without direction information, the peak signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity were improved by 1.2 dB and 0.02, respectively, at a coincidence time resolution of 300 ps. The calculation times of the proposed method were significantly lower than those of a conventional iterative reconstruction. These results indicate that the proposed method improves both the speed and image quality of a TOF-PET image reconstruction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phelps ME. PET: molecular imaging and its biological applications. New York: Springer; 2012.
Defrise M, Kinahan PE. Data acquisition and image reconstruction for 3D PET in The Theory and Practice of 3D PET. Dordrecht: Springer; 1998.
Wang Y, Yu B, Wang L, Zu C, Lalush DS, Lin W, et al. 3D conditional generative adversarial networks for high-quality PET image estimation at low dose. Neuroimage. 2018;174:550–62.
Chen KT, Gong E, de Carvalho MFB, Xu J, Boumis A, Khalighi M, et al. Ultra-low-dose 18F-Florbetaben amyloid PET imaging using deep learning with multi-contrast MRI inputs. Radiology. 2019;290(3):649–56.
Gong K, Guan J, Liu CC, Qi J. PET image denoising using a deep neural network through fine tuning. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2018;3(2):153–61.
Hashimoto F, Ohba H, Ote K, Teramoto A, Tsukada H. Dynamic PET image denoising using deep convolutional neural networks without prior training datasets. IEEE Access. 2019;7:96594–603.
Hashimoto F, Ohba H, Ote K, Kakimoto A, Tsukada H, Ouchi Y. 4D deep image prior: dynamic PET image denoising using an unsupervised four-dimensional branch convolutional neural network. Phys Med Biol. 2021;66(1):015006.
Hashimoto F, Ito M, Ote K, Isobe T, Okada H, Ouchi Y. Deep learning-based attenuation correction for brain PET with various radiotracers. Ann Nucl Med. 2021;35(6):691–701.
Sanaat A, Shiri I, Arabi H, Mainta I, Nkoulou R, Zaidi H. Deep learning-assisted ultra-fast/low-dose whole-body PET/CT imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48(8):2405–15.
Yang B, Ying L, Tang J. Artificial neural network enhanced Bayesian PET image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2018;37(6):1297–309.
Gong K, Guan J, Kim K, Zhang X, Yang J, Seo Y, et al. Iterative PET image reconstruction using convolutional neural network representation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019;38(3):675–85.
Gong K, Catana C, Qi J, Li Q. PET image reconstruction using deep image prior. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2019;38(7):1655–65.
Whiteley W, Luk WK, Gregor J. DirectPET: full-size neural network PET reconstruction from sinogram data. J Med Imaging. 2020;7(3):032503.
Reader AJ, Corda G, Mehranian A, da Costa-Luis C, Ellis S, Schnabel JA. Deep learning for PET image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2021;5(1):1–25.
Hu Z, Xue H, Zhang Q, Gao J, Zhang N, Zou S, et al. DPIR-Net: direct PET image reconstruction based on the wasserstein generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2021;5(1):35–43.
Kandarpa VSS, Bousse A, Benoit D, Visvikis D. DUG-RECON: a framework for direct image reconstruction using convolutional generative networks. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2021;5(1):44–53.
Mehranian A, Reader AJ. Model-based deep learning PET image reconstruction using forward-backward splitting expectation maximization. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2021;5(1):54–64.
Zhu B, Liu JZ, Cauley SF, Rosen BR, Rosen MS. Image reconstruction by domain-transform manifold learning. Nature. 2018;555(7697):487–92.
Häggström I, Schmidtlein CR, Campanella G, Fuchs TJ. DeepPET: a deep encoder–decoder network for directly solving the PET image reconstruction inverse problem. Med Image Anal. 2019;54:253–62.
Hudson HM, Larkin RS. Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1994;13(4):601–9.
Whiteley W, Panin V, Zhou C, Cabello J, Bharkhada D, Gregor J. FastPET: near real-time reconstruction of PET histo-image data using a neural network. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2021;5(1):65–77.
Matej S, Surti S, Jayanthi S, Daube-Witherspoon ME, Lewitt RM, Karp JS. Efficient 3-D TOF PET reconstruction using view-grouped histo-images: DIRECT—Direct image reconstruction for TOF. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009;28(5):739–51.
Snyder DL, Thomas LJ, Ter-Pogossian MM. A matheematical model for positron-emission tomography systems having time-of-flight measurements. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1981;28(3):3575–83.
Tomitani T. Image reconstruction and noise evaluation in photon time-of-flight assisted positron emission tomography. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1981;28(6):4581–9.
Tanaka E. Line-writing data acquisition and singal-to-noise ratio in time-of-flight positron emission tomography. IEEE Comput Soc. 1982;448:101–8.
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O. 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin S, Joskowicz L, Sabuncu MR, Unal G, Wells W, editors. Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) LNCS, vol. 9901. Cham: Springer; 2016. p. 424–32.
Collins DL, Zijdenbos AP, Kollokian V, Sled JG, Kabani NJ, Holmes CJ, Evans AC. Design and construction of a realistic digital brain phantom. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1998;17(3):463–8.
Saito A, Yoshikawa E, Omura T, Yamanaka T, Ote K, Isobe T, et al. Development of a brain PET scanner with motion correction using motion capture technology. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Med Imaging Conf 2018;M-07–146
Tanaka E, Kudo H. Subset-dependent relaxation in block-iterative algorithms for image reconstruction in emission tomography. Phys Med Biol. 2003;48(10):1405–22.
Nakayama T, Kudo H. Derivation and implementation of ordered-subsets algorithms for list-mode PET data. IEEE Nuc Sci Symp Med Imaging. Conf Rec 2005;3540-3
Vandenberghe S, Daube-Witherspoon ME, Lewitt RM, Karp JS. Fast reconstruction of 3D time-of-flight PET data by axial rebinning and transverse mashing. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51(6):1603–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors are employees of the Hamamatsu Photonics K.K. The company had no control over the interpretation, writing, or publication of this manuscript.
Ethical approval
This study did not include research on human subjects or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ote, K., Hashimoto, F. Deep-learning-based fast TOF-PET image reconstruction using direction information. Radiol Phys Technol 15, 72–82 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-022-00652-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-022-00652-8