Abstract
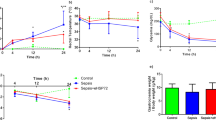
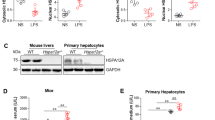
It has been previously reported that pretreatment with exogenous heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is able to protect cells and animals from the deleterious effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) produced by Gram-negative bacteria. However, the effects of Hsp70 pretreatment on lipoteichoic acid (LTA) challenge resulted from Gram-positive bacteria infection have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we demonstrated that preconditioning with human recombinant Hsp70 ameliorates various manifestations of systematic inflammation, including reactive oxygen species, TNFα, and CD11b/CD18 adhesion receptor expression induction observed in different myeloid cells after LTA addition. Therefore, exogenous Hsp70 may provide a mechanism for controlling excessive inflammatory responses after macrophage activation. Furthermore, in a rat model of LTA-induced sepsis, we demonstrated that prophylactic administration of exogenous human Hsp70 significantly exacerbated numerous homeostatic and hemodynamic disturbances induced by LTA challenge and partially normalized the coagulation system and multiple biochemical blood parameters, including albumin and bilirubin concentrations, which were severely disturbed after LTA injections. Importantly, prophylactic intravenous injection of Hsp70 before LTA challenge significantly reduced mortality rates. Thus, exogenous mammalian Hsp70 may serve as a powerful cellular defense agent against the deleterious effects of bacterial pathogens, such as LTA and LPS. Taken together, our findings reveal novel functions of this protein and establish exogenous Hsp70 as a promising pharmacological agent for the prophylactic treatment of various types of sepsis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida MC, Silva AC, Barral A, Barral Netto M (2000) A simple method for human peripheral blood monocyte isolation. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 95:221–223
Antal-Szalmas P (2000) Evaluation of Cd14 in host defence. Eur J Clin Invest 30:167–179
Baue AE (1991) Nutrition and metabolism in sepsis and multisystem organ failure. Surg Clin North Am 71:549–565
Bone R (1991) The pathogenesis of sepsis. Ann Int Med 115:457–469
Boyum A (1968) Separation of leukocytes from blood and bone narrow. J Lab Invest 22:77–85
Carbonell N, Blasco M, Ferreres J, Blanquer J, García-Ramón R, Mesejo A, Miguel A (2004) Sepsis and SOFA score: related outcome for critically ill renal patients. Clin Nephrol 62:185–192
Carratelli CR, Nuzzo I, Bentivoglio C, Galdiero M (1996) CD11a/CD18 and CD11b/18 modulation by lipoteichoic acid, N-acetyl-muramyl-alpha-alanyl-D-isoglutamine, muramic acid and protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 16:309–315
De Kimpe SJ, Thiemermann C, Vane JR (1995) Role for untracellular platelet-activating factor in the circulatory failure in a model of gram-positive shock. Br J Pharmacol 116:3191–3198
Detmers PA, Zhou D, Polizzi E, Thieringer R, Hanlon WA, Vaidya S, Bansal V (1998) Potential role of membrane internalization and vesicle fusion in adhesion of neutrophils in response to lipopolysaccharide and TNF. J Immunol 161:1921–1929
Ding XZ, Fernandez-Prada CM, Bhattacharjee AK, Hoover DL (2001) Over-expression of hsp-70 inhibits bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced production of cytokines in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Cytokine 16:210–219
Fischer W, Mannsfeld T, Hagen G (1990) On the basic structure of poly(glycerophosphate) lipoteichoic acids. Biochem Cell Biol 68:33–43
Friedman G, Silva E, Vincent JL (1998) Has the mortality of septic shock changed with time. Crit Care Med 26:2078–2086
Hawker F (1991) Liver dysfunction in critical illness. Anaesth Intensive Care 19:165–181
Helling H, Schenk HJ, Pindur G, Weinrich M, Wagner B, Stephan B (2010) Fibrinolytic and procoagulant activity in septic and haemorrhagic shock. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 45:295–300
Henderson B (2010) Integrating the cell stress response: a new view of molecular chaperones as immunological and physiological homeostatic regulators. Cell Biochem Funct 28:1–14
Hirasawa H, Oda S, Nakamura M (2009) Blood glucose control in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. World J Gastroenterol 15:4132–4136
Geerdes HF, Ziegler D, Lode H, Hund M, Loehr A, Fangmann W, Wagner J (1992) Septicemia in 980 patients at a university hospital in Berlin: prospective studies during 4 selected years between 1979 and 1989. Clin Infect Dis 15:991–1002
Gogos CA, Drosou E, Bassaris HP, Skoutelis A (2000) Pro- versus anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in patients with severe sepsis: a marker for prognosis and future therapeutic options. J Infect Dis 181:176–180
Gong MN, Thompson BT, Williams P, Pothier L, Boyce PD, Christiani DC (2005) Clinical predictors of and mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome: potential role of red cell transfusion. Crit Care Med 33:1191–1198
Gustot T (2011) Multiple organ failure in sepsis: prognosis and role of systemic inflammatory response. Curr Opin Crit Care 17:153–159
Guzhova IV, Arnholdt AC, Darieva ZA, Kinev AV, Lasunskaya EB, Nilsson K, Bozhkov VM, Voronin AP, Margulis BA (1998) Effects of exogenous stress protein 70 on the functional properties of human promonocytes through binding to cell surface and internalization. Cell Stress Chaperones 3:67–77
Johnson JD, Fleshner M (2006) Releasing signals, secretory pathways, and immune function of endogenous extracellular heat shock protein 72. J Leukoc Biol 79:425–434
Kao SJ, Lei HC, Kuo CT, Chang MS, Chen BC, Chang YC, Chiu WT, Lin CH (2005) Lipoteichoic acid induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation and nitric oxide synthase expression via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, and p38 MAPK in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Immunology 115:366–374
Kengatharan K, De Kimpe S, Robson C, Foster S, Thiemermann C (1998) Mechanism of gram-positive shock: identification of peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid moieties essential in the induction of nitric oxide synthase, shock, and multiple organ failure. J Exp Med 188:305–315
Kustanova GA, Murashev AN, Karpov VL, Margulis BA, Guzhova IV, Prokhorenko IR, Grachev SV, Evgen’ev MB (2006) Exogenous heat shock protein 70 mediates sepsis manifestations and decreases the mortality rate in rats. Cell Stress Chaperones 11:276–286
Lappin E, Ferguson AJ (2009) Gram-positive toxic shock syndromes. Lancet Infect Dis 9:281–290
Leaver A, Burke-Gaffney A, Evans TW (2008) Gram-positive and gram-negative sepsis: two disease Entities? In J.-L. Vincent (Ed.) Yearbook of intensive care and emergency medicine (volume 2008). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-77290-3
Leon CG, Tory R, Jia J, Sivak O, Wasan KM (2008) Discovery and development of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) antagonists: a new paradigm for treating sepsis and other diseases. Pharmaceutical Res 25:1751–1761
Lotz S, Aga E, Wilde I, van Zandbergen G, Hartung T, Solbach W, Laskay T (2004) Highly purified lipoteichoic acid activates neutrophil granulocytes and delays their spontaneous apoptosis via CD14 and TLR2. J Leuk Biol 75:467–477
McCabe WR, Treadwell TL, De Maria A Jr (1983) Pathophysiology of bacteremia. Am J Med 75(1B):7–18
MacCallum NS, Evans TW (2005) Epidemiology of acute lung injury. Curr Opin Crit Care 11:43–49
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M (2003) The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med 348:1546–1554
Merkulov VA, Plekhanova TM, Zverev A, Karpov VL, Evgen'ev MB, Kadykova ON, Gordeev EV, Petrov AA, Kovtun AL, Makhlaĭ AA, Mironov AN (2011) Production of 70 kDa recombinant human heat shock protein in baculovirus expression system and assessment of its antiviral activity. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 1:54–60
Nakada J, Matsura T, Okazaki N, Nishida T, Togawa A, Minami Y, Inagaki Y, Ito H, Yamada K, Ishibe Y (2005) Oral administration of geranylgeranylacetone improves survival rate in a rat endotoxin shock model: administration timing and heat shock protein 70 induction. Shock 24:482–487
Nelson RJ, Ziegelhoffer T, Nicolet C, Werner-Washburne M, Craig EA (1992) The translation machinery and 70 kd heat shock protein cooperate in protein synthesis. Cell 71:97–105
Nilsen NJ, Deininger S, Nonstad U, Skjeldal F, Husebye H, Rodionov D, von Aulock S, Hartung T, Lien E, Bakke O, Espevik T (2008) Cellular trafficking of lipoteichoic acid and Toll-like receptor 2 in relation to signaling: role of CD14 and CD36. J Leukoc Biol 84:280–291
O’Neill LA (2003) Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for inflammatory and infectious diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:396–403
Pfister H, Hennet T, Jungi TW (1992) Lipopolysaccharide synergizes with tumour necrosis factor-alpha in cytotoxicity assays. Immunology 77:473–476
Pinsky MR, Vincent JL, Deviere J, Alegre M, Kahn RJ, Dupont E (1993) Serum cytokine levels in human septic shock. Relation to multiple-system organ failure and mortality. Chest 103:565–575
Power C, Fanning N, Redmond HP (2002) Cellular apoptosis and organ injury in sepsis: a review. Shock 18:197–211
Rozhkova E, Yurinskaya M, Zatsepina O, Garbuz D, Karpov V, Surkov S, Murashev A, Ostrov V, Margulis B, Evgen’ev M, Vinokurov M (2010) Exogenous mammalian extracellular HSP70 reduces endotoxin manifestations at the cellular and organism levels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1197:94–107
Rozhkova EA, Zatsepina OG, Iurinskaia MM, Vinokurov MG, Evgen'ev MB (2011) The effect of extracellular recombinant human heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) on protein pattern observed after endotoxin-induced macrophage activation. Mol Biol (Mosk) 45:386–390
Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Osuchowski MF, Valentine C, Kurosawa S, Remick DG (2011) The pathogenesis of sepsis. Annu Rev Pathol 6:19–48
Suganuma T, Irie K, Fujii E, Yoshioka T, Muraki T (2002) Effect of heat stress on lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular permeability change in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:656–663
Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Muhlradt PF, Morr M, Radolf JD, Zychlinsky A, Takeda K, Akira S (2001) Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol 13:933–940
Tsan MF, Gao B (2004) Cytokine function of heat shock proteins. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C739–C744
Tsan MF, Gao B (2009) Heat shock proteins and immune system. J Leukoc Biol 85:905–910
Victor VM, Rocha M, Esplugues JV, De la Fuente M (2005) Role of free radicals in sepsis: antioxidant therapy. Curr Pharm Des 11:3141–3158
Vincent J-L (2008) Yearbook of intensive care and emergency medicine (volume 2008). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-77290-3.
Vinokurov MG, Yurinskaya MM, Suslikov AV, Pechatnikov VA, Grachev SV (2006) Dynamics of the Fas- and stress-induced apoptosis of human neutrophils under the action of endotoxins. Dokl Biol Sci 410:355–357
Wang JE, Dahle MK, McDonald M, Foster SJ, Aasen AO, Thiemermann C (2003) Peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid in gram-positive bacterial sepsis: receptors, signal transduction, biological effects, and synergism. Shock 20:402–414
Wang YH, Wang WY, Liao JF, Chen CF, Hou YC, Liou KT, Chou YC, Tien JH, Shen YC (2004) Prevention of macrophage adhesion molecule-1 (Mac-1)-dependent neutrophil firm adhesion by taxifolin through impairment of protein kinase-dependent NADPH oxidase activation and antagonism of G protein-mediated calcium influx. Biochem Pharmacol 67:2251–2262
Wheeler DS, Dunsmore KE, Denenberg AG, Muething L, Poynter SE, Wong HR (2011) Biological activity of truncated C-terminus human heat shock protein 72. Immunol Lett 135:173–179
Young JC (2010) Mechanisms of the Hsp70 chaperone system. Biochem Cell Biol 88:291–300
Yurinskaya MM, Vinokurov MG, Zatcepina OG, Garbuz D, Guzhova IV, Rozhkova EA, Suslikov AV, Karpov VL, Evgen’ev MB (2009) Exogenous heat shock proteins (HSP70) significantly inhibit endotoxin-induced activation of human neutrophils. Dokl Biol Sci 426:298–301
Zanotti-Cavazzoni SL, Goldfarb RD (2009) Animal models of sepsis. Crit Care Clin 25:703–719
Zheng H, Nagaraja G, Kaur P, Asea E, Asea A (2010) Chaperokine function of recombinant Hsp72 produced in insect cells using baculovirus expression system is retained. J Biol Chem 285:349–356
Zhou J, An H, Xu H, Liu S, Cao X (2005) Heat shock up-regulates expression of Toll-like receptor-2 and Toll-like receptor-4 in human monocytes via p38 kinase signal pathway. Immunology 114:522–530
Acknowledgements
Work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project 09-04-00643 and 09-04-00660, project from “Genofond dynamics” program, Grant of the Program of Molecular and Cellular Biology RAN to M.E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinokurov, M., Ostrov, V., Yurinskaya, M. et al. Recombinant human Hsp70 protects against lipoteichoic acid-induced inflammation manifestations at the cellular and organismal levels. Cell Stress and Chaperones 17, 89–101 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-011-0288-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-011-0288-0