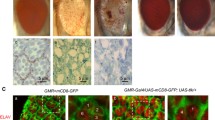
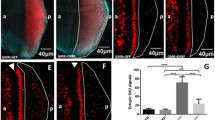
Abstract
Apart from their roles as chaperones, heat shock proteins are involved in other vital activities including apoptosis with mammalian Hsp60 being ascribed proapoptotic as well as antiapoptotic roles. Using conditional RNAi or overexpression of Hsp60D, a member of the Hsp60 family in Drosophila melanogaster, we show that the downregulation of this protein blocks caspase-dependent induced apoptosis. GMR-Gal4-driven RNAi for Hsp60D in developing eyes dominantly suppressed cell death caused by expression of Reaper, Hid, or Grim (RHG), the key activators of canonical cell death pathway. Likewise, Hsp60D-RNAi rescued cell death induced by GMR-Gal4-directed expression of full-length and activated DRONC. Overexpression of Hsp60D enhanced cell death induced either by directed expression of RHG or DRONC. However, the downregulation of Hsp60D failed to suppress apoptosis caused by unguarded caspases in DIAP1-RNAi flies. Furthermore, in DIAP1-RNAi background, Hsp60D-RNAi also failed to inhibit apoptosis induced by RHG expression. The Hsp60 and DIAP1 show diffuse and distinct granular overlapping distributions in the photoreceptor cells with the bulk of both proteins being outside the mitochondria. Depletion of either of these proteins disrupts the granular distribution of the other. We suggest that in the absence of Hsp60D, DIAP1 is unable to dissociate from effecter and executioner caspases, which thus remain inactive.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams JM, White K, Fessler LI, Steller H (1993) Programmed cell death during Drosophila embryogenesis. Development 117:29–43
Arikawa K, Hicks JL, Williams DS (1990) Identification of actin filaments in the rhabdomeral microvilli of Drosophila photoreceptors. J Cell Biol 110:1993–1998. DOI 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1993
Arya R, Lakhotia SC (2006) A simple nail polish imprint technique for examination of external morphology of Drosophila eyes. Curr Sci 90:1179–1180
Arya R, Mallik M, Lakhotia SC (2007) Heat shock genes—integrating cell survival and death. J Biosci 32:595–610. DOI 10.1007/s12038-007-0059-3
Benlali A, Draskovic I, Hazelett DJ, Treisman JE (2000) act up controls actin polymerization to alter cell shape and restrict hedgehog signaling in the Drosophila eye disc. Cell 101:271–281. DOI 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80837-5
Brand AH, Perrimon N (1993) Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development 118:401–415
Bukau B, Horwich AL (1998) The Hsp70 and Hsp60 chaperone machines. Cell 92:351–366. DOI 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80928-9
Chandra D, Choy G, Tang DG (2007) Cytosolic accumulation of HSP60 during apoptosis with or without apparent mitochondrial release: evidence that its pro-apoptotic or pro-survival functions involve differential interactions with caspase-3. J Biol Chem 282:31289–31301. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M702777200
Chen P, Nordstrom W, Gish B, Abrams JM (1996) grim, a novel cell death gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev 10:1773–1782. DOI 10.1101/gad.10.14.1773
Cooley L, Kelley R, Spradling A (1988) Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science 239:1121–1128. DOI 10.1126/science.2830671
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins—suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252. DOI 10.1101/gad.13.3.239
Duckett CS, Nava VE, Gedrich RW, Clem RJ, Van Dongen JL, Gilfillan MC, Shiels H, Hardwick JM, Thompson CB (1996) A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J 15:2685–2694
Ekengren S, Tryselius Y, Dushay MS, Liu G, Steiner H, Hultmark D (2001) A humoral stress response in Drosophila. Curr Biol 11:1479. DOI 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00452-3
Ellis RJ, van der Vies SM (1991) Molecular chaperones. Ann Rev Biochem 60:321–347. DOI 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001541
Ellis MC, O’Neill EM, Rubin GM (1993) Expression of Drosophila glass protein and evidence for negative regulation of its activity in non-neuronal cells by another DNA-binding protein. Development 119:855–865
Fink AL (1999) Chaperone-mediated protein folding. Physiol Rev 79:425–449
Franceschini N (1972) Pupil and pseudopupil in the compound eye of Drosophila. In: Wehner R (ed) Information processing in the visual system of Drosophila. Springer, Berlin, pp 75–82
Freeman M (1994) The spitz gene is required for photoreceptor determination in the Drosophila eye where it interacts with the EGF receptor. Mech Dev 48:25–33. DOI 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90003-5
Giordano E, Rendina R, Peluso I, Furia M (2002) RNAi triggered by symmetrically transcribed transgenes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 160:637–648
Goyal G, Fell B, Sarin A, Youle RJ, Sriram V (2007) Role of mitochondrial remodeling in programmed cell death in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Cell 12:807–816. DOI 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.02.002
Grether ME, Abrams JM, Agapite J, White K, Steller H (1995) The head involution defective gene of Drosophila melanogaster functions in programmed cell death. Genes Dev 9:1694–1708. DOI 10.1101/gad.9.14.1694
Gupta RS (1990) Microtubules, mitochondria, and molecular chaperones: a new hypothesis for in vivo assembly of microtubules. Biochem Cell Biol 68:1352–1363
Hawkins CJ, Ekert PG, Uren AG, Holmgreen SP, Vaux DL (1998) Anti-apoptotic potential of insect cellular and viral IAPs in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ 5:569–576. DOI 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400389
Hay BA, Guo M (2006) Caspase-dependent cell death in Drosophila. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:623–650. DOI 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.21.012804.093845
Hay BA, Wolff T, Rubin GM (1994) Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development 120:2121–2129
Hay BA, Wassarman DA, Rubin GM (1995) Drosophila homologs of baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins function to block cell death. Cell 83:1253–1262. DOI 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90150-7
Igaki T, Kanda H, Yamamoto-Goto Y, Kanuka H, Kuranaga E, Aigaki T, Miura M (2002) Eiger, a TNF superfamily ligand that triggers the Drosophila JNK pathway. EMBO J 21:3009–3018. DOI 10.1093/emboj/cdf306
Ikawa S, Weinberg RA (1992) An interaction between p21ras and heat shock protein hsp60, a chaperonin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:2012–2016. DOI 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2012
Jones M, Gupta RS, Englesberg E (1994) Enhancement in amount of P1 (hsp60) in mutants of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells exhibiting increases in the A system of amino acid transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:858–862. DOI 10.1073/pnas.91.3.858
Jones G, Jones D, Zhou L, Steller H, Chu Y (2000) Deterin, a new inhibitor of apoptosis from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem 275:22157–22165. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M000369200
Kanuka H, Sawamoto K, Inohara N, Matsuno K, Okano H, Miura M (1999) Control of the cell death pathway by Dapaf-1, a Drosophila Apaf-1/CED-4-related caspase activator. Mol Cell 4:757–769. DOI 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80386-X
Kauppila S, Maaty WS, Chen P, Tomar RS, Eby MT, Chapo J, Chew S, Rathore N, Zachariah S, Sinha SK, Abrams JM, Chaudhary PM (2003) Eiger and its receptor, Wengen, comprise a TNF-like system in Drosophila. Oncogene 22:4860–4867. DOI 10.1038/sj.onc.1206715
Kozlova T, Perezgasga L, Reynaud E, Zurita M (1997) The Drosophila melanogaster homologue of the hsp60 gene is encoded by the essential locus l(1)10Ac and is differentially expressed during fly development. Dev Genes Evol 207:253–263. DOI 10.1007/s004270050113
Kramer JM, Staveley BE (2003) GAL4 causes developmental defects and apoptosis when expressed in the developing eye of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Mol Res 2:43–47
Kulkarni MM, Booker M, Silver SJ, Friedman A, Hong P, Perrimon N, Mathey-Prevot B (2006) Evidence of off-target effects associated with long dsRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster cell-based assays. Nat Methods 3:833–838
Kumar S, Colussi PA (1999) Prodomains–adaptors–oligomerization: the pursuit of caspase activation in apoptosis. Trends Biochem Sci 24:1–4. DOI 10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01332-2
Kuranaga E, Kanuka H, Tonoki A, Takemoto K, Tomioka T, Kobayashi M, Hayashi S, Miura M (2006) Drosophila IKK-related kinase regulates nonapoptotic function of caspases via degradation of IAPs. Cell 126:583–596. DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.048
Lakhotia SC, Singh AK (1989) A novel heat shock polypeptide in Malpighian tubule of Drosophila melanogaster. J Genet 68:129–268
Lakhotia SC, Singh BN (1996) Synthesis of a ubiquitously present new HSP60 family protein is enhanced by heat shock only in the Malpighian tubules of Drosophila. Experientia 52:751–756. DOI 10.1007/BF01923984
Lakhotia SC, Rajendra TK, Prasanth KV (2001) Developmental regulation and complex organization of the promoter of the non-coding hsr(omega) gene of Drosophila melanogaster. J Biosci 26:25–38. DOI 10.1007/BF02708978
Lakhotia SC, Srivastava P, Prasanth KV (2002) Regulation of heat shock proteins, Hsp70 and Hsp64, in heat-shocked Malpighian tubules of Drosophila melanogaster larvae. Cell Stress Chaperones 7:347–356. DOI 10.1379/1466-1268(2002)007<0347:ROHSPH>2.0.CO;2
Lanneau D, Brunet M, Frisan E, Solary E, Fontenay F, Garrido C (2008) Heat shock proteins: essential proteins for apoptosis regulation. J Cell Mol Med (in press)
Leulier F, Ribeiro PS, Palmer E, Tenev T, Takahashi K, Robertson D, Zachariou A, Pichaud F, Ueda R, Meier P (2006) Systematic in vivo RNAi analysis of putative components of the Drosophila cell death machinery. Cell Death Differ 13:1663–1674. DOI 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401868
Martin CS, Flores AI, Cuezva JM (1995) Cpn60 is exclusively localized into mitochondria of rat liver and embryonic Drosophila cells. J Cell Biochem 59:235–245. DOI 10.1002/jcb.240590212
McMullin TW, Hallberg RL (1988) A highly evolutionarily conserved mitochondrial protein is structurally related to the protein encoded by the Escherichia coli groEL gene. Mol Cell Biol 8:371–380
Meier P, Silke J, Leevers SJ, Evan GI (2000) The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1. EMBO J 19:598–611. DOI 10.1093/emboj/19.4.598
Montell DJ (2006) A kinase gets caspases into shape. Cell 126:450–452. DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.017
Moreno E, Yan M, Basler K (2002) Evolution of TNF signaling mechanisms: JNK-dependent apoptosis triggered by Eiger, the Drosophila homolog of the TNF superfamily. Curr Biol 12:1263–1268. DOI 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00954-5
Mukamel Z, Kimchi A (2004) Death-associated protein 3 localizes to the mitochondria and is involved in the process of mitochondrial fragmentation during cell death. J Biol Chem 279:36732–36738. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M400041200
Muro I, Berry DL, Huh JR, Chen CH, Huang H, Yoo SJ, Guo M, Baehrecke EH, Hay BA (2006) The Drosophila caspase Ice is important for many apoptotic cell deaths and for spermatid individualization, a nonapoptotic process. Development 133:3305–3315. DOI 10.1242/dev.02495
Nicholson DW (1999) Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 6:1028–1042. DOI 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400598
Nover L (1984) Heat shock response of eukaryotic cells. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–78
Oshima K, Takeda M, Kuranaga E, Ueda R, Aigaki T, Miura M, Hayashi S (2006) IKK epsilon regulates F actin assembly and interacts with Drosophila IAP1 in cellular morphogenesis. Curr Biol 16:1531–1537
Perezgasga L, Segovia L, Zurita M (1999) Molecular characterization of the 5′ control region and of two lethal alleles affecting the hsp60 gene in Drosophila melanogaster. FEBS Lett 456:269–273. DOI 10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00963-1
Perrimon N, Mathey-Prevot B (2007) Off targets and genome scale RNAi screens in Drosophila. Fly 1:1–5
Pfister G, Stroh CM, Perschinka H, Kind M, Knoflach M, Hinterdorfer P, Wick G (2005) Detection of HSP60 on the membrane surface of stressed human endothelial cells by atomic force and confocal microscopy. J Cell Sci 118:1587–1594. DOI 10.1242/jcs.02292
Pilling AD, Horiuchi D, Lively CM, Saxton WM (2006) Kinesin-1 and Dynein are the primary motors for fast transport of mitochondria in Drosophila motor axons. Mol Biol Cell 17:2057–2068. DOI 10.1091/mbc.E05-06-0526
Prasanth KV, Rajendra TK, Lal AK, Lakhotia SC (2000) Omega speckles—a novel class of nuclear speckles containing hnRNPs associated with noncoding hsr-omega RNA in Drosophila. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 19):3485–3497
Retzlaff C, Yamamoto Y, Hoffman PS, Friedman H, Klein TW (1994) Bacterial heat shock proteins directly induce cytokine mRNA and interleukin-1 secretion in macrophage cultures. Infect Immun 62:5689–5693
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:897–907. DOI 10.1038/nrm1496
Rodriguez A, Chen P, Oliver H, Abrams JM (2002) Unrestrained caspase-dependent cell death caused by loss of Diap1 function requires the Drosophila Apaf-1 homolog, Dark. EMBO J 21:2189–2197. DOI 10.1093/emboj/21.9.2189
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS (2002) IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:401–410. DOI 10.1038/nrm830
Samali A, Cai J, Zhivotovsky B, Jones DP, Orrenius S (1999) Presence of a pre-apoptotic complex of pro-caspase-3, Hsp60 and Hsp10 in the mitochondrial fraction of jurkat cells. EMBO J 18:2040–2048. DOI 10.1093/emboj/18.8.2040
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA
Sarkar S, Lakhotia SC (2005) The Hsp60C gene in the 25F cytogenetic region in Drosophila melanogaster is essential for tracheal development and fertility. J Genet 84:265–281. DOI 10.1007/BF02715797
Sarkar S, Lakhotia SC (2008) Hsp60C is required in follicle as well as germline cells during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Dyn 237:1334–1347. DOI 10.1002/dvdy.21524
Sarkar S, Arya R, Lakhotia SC (2006) Chaperonins: in life and death. In: Sreedhar AS, Srinivas UK (eds) Stress responses: a molecular biology approach. Signpost, Trivandrum, India, pp 43–60
Sawamoto K, Okano H, Kobayakawa Y, Hayashi S, Mikoshiba K, Tanimura T (1994) The function of argos in regulating cell fate decisions during Drosophila eye and wing vein development. Dev Biol 164:267–276. DOI 10.1006/dbio.1994.1197
Sawamoto K, Okabe M, Tanimura T, Mikoshiba K, Nishida Y, Okano H (1996) The Drosophila secreted protein Argos regulates signal transduction in the Ras/MAPK pathway. Dev Biol 178:13–22. DOI 10.1006/dbio.1996.0194
Sawamoto K, Taguchi A, Hirota Y, Yamada C, Jin M, Okano H (1998) Argos induces programmed cell death in the developing Drosophila eye by inhibition of the Ras pathway. Cell Death Differ 5:548. DOI 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400398
Schweitzer R, Shaharabany M, Seger R, Shilo BZ (1995) Secreted Spitz triggers the DER signaling pathway and is a limiting component in embryonic ventral ectoderm determination. Genes Dev 9:1518–1529. DOI 10.1101/gad.9.12.1518
Soltys BJ, Gupta RS (1999) Mitochondrial-matrix proteins at unexpected locations: are they exported? Trends Biochem Sci 24:174–177. DOI 10.1016/S0968-0004(99)01390-0
Spreij TE (1971) Cell death during the development of the imaginal discs of Calliphora erythrocephala. Neth J Zool 21:221–264. DOI 10.1163/002829670X00295
Srivastava P (2004) Studies on the constitutively expressed members of Hsp60 and Hsp70 families in Drosophila melanogaster. Ph.D. Thesis, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi
Tepass U, Harris KP (2007) Adherens junctions in Drosophila retinal morphogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 17:26–35. DOI 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.11.006
Timakov B, Zhang P (2001) The hsp60B gene of Drosophila melanogaster is essential for the spermatid individualization process. Cell Stress Chaperones 6:71–77. DOI 10.1379/1466-1268(2001)006<0071:THGODM>2.0.CO;2
Tissieres A, Mitchell HK, Tracy UM (1974) Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol 84:389–98. DOI 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1
Vaux DL, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) Cell death in development. Cell 96:245–254. DOI 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80564-4
Vernooy SY, Copeland J, Ghaboosi N, Griffin EE, Yoo SJ, Hay BA (2000) Cell death regulation in Drosophila: conservation of mechanism and unique insights. J Cell Biol 150:F69–F76. DOI 10.1083/jcb.150.2.F69
Wells AD, Rai SK, Salvato MS, Band H, Malkovsky M (1997) Restoration of MHC class I surface expression and endogenous antigen presentation by a molecular chaperone. Scand J Immunol 45:605–612. DOI 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1997.d01-436.x
White K, Grether ME, Abrams JM, Young L, Farrell K, Steller H (1994) Genetic control of programmed cell death in Drosophila. Science 264:677–683. DOI 10.1126/science.8171319
Woodlock TJ, Chen X, Young DA, Bethlendy G, Lichtman MA, Segel GB (1997) Association of HSP60-like proteins with the L-system amino acid transporter. Arch Biochem Biophys 338:50–56. DOI 10.1006/abbi.1996.9798
Xanthoudakis S, Roy S, Rasper D, Hennessey T, Aubin Y, Cassady R, Tawa P, Ruel R, Rosen A, Nicholson DW (1999) Hsp60 accelerates the maturation of pro-caspase-3 by upstream activator proteases during apoptosis. EMBO J 18:2049–2056. DOI 10.1093/emboj/18.8.2049
Yoo SJ, Huh JR, Muro I, Yu H, Wang L, Wang SL, Feldman RM, Clem RJ, Muller HA, Hay BA (2002) Hid, Rpr and Grim negatively regulate DIAP1 levels through distinct mechanisms. Nat Cell Biol 4:416–424. DOI 10.1038/ncb793
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. M. Freeman (Cambridge, UK), B. Hay, and I. Muro (California Institute of Technology, USA), P. Meier and G.I. Evan (Breakthrough Toby Robins Breast Cancer Research Centre, UK), M. Miura (Brain Science Institute, RIKEN), Dr. V. Sriram (National Centre for Biological Sciences, Bangalore, India) and the Bloomington Fly Stock Centre (Indiana, USA) for providing different fly stocks used in this study. We also thank Dr. K. White (CBRC, Massachusetts General Hospital) and Dr. S. Ganesh (IIT Kanpur, India) for providing DIAP1 and Grp75 antibodies, respectively. We thank Dr. L. S. Shashidhara for his help in the generation of the Hsp60D transgenic flies at the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (Hyderabad). This work was supported by a research grant from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, N. Delhi, to SCL. The Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope Facility is supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, N. Delhi. RA is supported by a research fellowship from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, N. Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arya, R., Lakhotia, S.C. Hsp60D is essential for caspase-mediated induced apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster . Cell Stress and Chaperones 13, 509–526 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-008-0051-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-008-0051-3