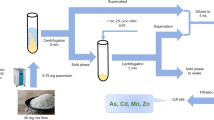
Abstract
The current study describes a fast and efficient procedure of ultrasound-assisted extraction for determination of Ca, Mg, K, Na, Cu, Zn, Mn, and Al in tea leaves by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES). The variables of procedure were optimized using the Box–Behnken design and the conditions selected were nitric acid concentration (1.0 mol L−1), sonication time (7 min), and sonication temperature (75 °C). The extraction efficiency was calculated using the analyte concentration obtained by a total digestion procedure as reference. Accuracy was confirmed by analysis of certified reference material of apple leaves (NIST 1515) and spinach leaves (NIST 1570a) using the procedure proposed. A statistical evaluation using Student’s t test showed that there is no significant difference between the value obtained with the proposed procedure and the certified value, at 95% confidence level. The proposed procedure was successfully applied and is a good alternative to conventional acid digestion procedure and can be applied to routine analysis for determination of Ca, Mg, K, Na, Zn, Mn, Cu, and Al in tea leaves used for the preparation of infusions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim FAC, Costa VC, Guedes WN, Sá IP, Santos MC, Silva EGP, Lima DC (2016) Multivariate optimization of method of slurry sampling for determination of iron and zinc in starch samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 9(6):1719–1726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0296-2
Amorim FAC, Costa VC, Silva EGP, Lima DC, Jesus RM, Bezerra MA (2017) Multivariate optimization of simple procedure for determination of Fe and Mg in cassava starch employing slurry sampling and FAAS. Food Chem 227:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.12.029
Andrade DF, Pereira-Filho ER, Konieczynski P (2017) Comparison of ICP OES and LIBS analysis of medicinal herbs rich in flavonoids from eastern Europe. J Braz Chem Soc 28:838–847
ANVISA – Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. Resolução RDC n° 269, de 22 de setembro de 2005. Available in: http://portal.anvisa. gov.br/wps/wcm/connect/1884970047457811857dd53fbc4c6735/RDC_269_2005.pdf? MOD=AJPERES. Accessed 15 Nov 2017
Armenta S, Garrigues S, De la Guardia M (2015) The role of green extraction techniques in green analytical chemistry. Trends Anal Chem 71:2–8
Ashraf W, Mian AA (2008) Levels of selected heavy metals in black tea varieties consumed in Saudi Arabia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81(1):101–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9402-0
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76(5):965–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.05.019
Bezerra MA, Castro JT, Macedo RC, Da Silva DG (2010) Use of constrained mixture design for optimization of method for determination of zinc and manganese in tea leaves employing slurry sampling. Anal Chim Acta 670(1-2):33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.04.063
Bezerra MA, Dos Santos QO, Santos AG, Novaes CG, Ferreira SLC, De Souza VS (2016) Simplex optimization: a tutorial approach and recent applications in analytical chemistry. Microchem J 124:45–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.07.023
Capote FP, De Castro MDL (2007) Ultrasound in analytical chemistry. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:249–257
Castro MDL, Silva MP (1997) Strategies for solid sample treatment. Trends Anal. Chem 16:16–24
Chen Y, Yu M, Xu J, Chen X, Shi J (2009) Differentiation of eight tea (Camellia Sinensis) cultivars in China by elemental fingerprint of their leaves. J Sci Food Agr 89(14):2350–2355. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3716
Da Silva Pinto M (2013) Tea: a new perspective on health benefits. Food Res Int 53(2):558–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2013.01.038
Dambiec M, Polechońska L, Klink A (2013) Level of essentials and non-essential elements in black teas commercialized in Poland and their transfer to tea infusion. J. Food Compost. Anal 31:62–66
Diniz PHGD, Pistonesi MF, Alvarez MB, Band BSF, Araújo MCU (2015) Simplified tea classification based on a reduced chemical composition profile via successive projections algorithm linear discriminant analysis (SPA-LDA). J. Food Compost. Anal 39:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2014.11.012
Ferreira SLC, Dos Santos WNL, Quintella CM, Barros Neto B, Bosque Sendra JM (2004) Doehlert matrix: a chemometric tool for analytical chemistry—review. Talanta 63(4):1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.01.015
Ferreira SLC, Bruns RE, Ferreira HS, Matos GD, David JM, Brandão GC, Silva EGP, Portugal LA, Reis PS, Santos AS, Santos WNL (2007) Box-Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal Chim Acta 2007:179–186
Ferreira SLC, Silva LOB, Santana FA, Junior MMS, Matos GD, Santos WNL (2012) A review of reflux systems using cold finger for sample preparation in the determination of volatile elements. Microchem J 106:307–310
Han W (2007) Effect of liming and seasonal variation on lead concentration of tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Chemosphere 66(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.017
Huxley R, Lee CM, Barzi F, Timmermeister L, Czernichow S, Perkovic V, Grobbee DE, Batty D, Woodward M (2009) Coffee, decaffeinated coffee, and tea consumption in relation to incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 169(22):2053–2063. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2009.439
IUPAC, Analytical Chemistry Division. Comission on Spectrochemical and Optical 484 Procedures for Analysis (1978) Nomenclature, symbols, units and their usage in485 spectrochemical analysis-II. Data interpretation. Spectrochim. Acta B 33:242–245
Jeszka-Skowron M, Krawczyk M, Zgoła-Grzeskowiak A (2015) Determination of antioxidant activity, rutin, quercetin, phenolic acids and trace elements in tea infusions: influence of citric acid addition on extraction of metals. J. Food Compost. Anal 40:70–77
Karak T, Bhagat RM (2010) Trace elements in tea leaves, made tea and tea infusion: a review. Food Res Int 43(9):2234–2252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.08.010
Kartika H, Shido J, Nakamoto ST, Li QX, Iwaoka WT (2011) Nutrient and mineral composition of dried mamaki leaves (Pipturus albidus) and infusions. J. Food Compost. Anal 24(1):44–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2010.03.027
Korn MGA, Morte ESB, Santos DCMB, Castro JT, Barbosa JTP, Teixeira AP, Welz B, Santos WPC, Santos EBGN, Korn M (2008) Sample preparation for the determination of metals in food samples using spectroanalytical methods—a review. Appl Spectrosc Rev 43(2):67–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704920701723980
Krewski D, Yokel RA, Nieboer E, Borchelt D, Cohen J, Harry J, Kacew S, Lindsay J, Mahfouz AM, Rondeau V (2007) Human health risk assessment for aluminum, aluminum oxide, and aluminum hydroxide. J Toxicol Environ Health, Part B: Crit Rev 10(sup1):1–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937400701597766
Krug FJ, Rocha FRP (2016) Métodos de preparo de amostras. Fundamentos sobre o preparo de amostras orgânicas e inorgânicas para análise elementar. Editora, EditSBQ, São Paulo
Kumar A, Nair AGC, Reddy AVR, Garg AN (2005) Availability of essential elements in Indian and US tea brands. Food Chem 89(3):441–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.03.003
Lima AF, Lima FF, Richter EM, Munoz RAA (2016) Combination of sonication and heating for metal extraction from inorganic fertilizers prior to microwave-induced plasma spectrometry determinations. Appl Acoust 103:124–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2015.03.009
Marqués AM, Cervera ML, Guardia M (2016) Mineral analysis of human diets by spectrometry methods. Trends Anal Chem 82:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.07.007
Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral nutrient of higher plants (2nd ed.). London: Academic Press
Martins CA, Cerveira C, Scheffler GL, Pozebon D (2014) Metal determination in tea, wheat, and wheat flour using diluted nitric acid, high-efficiency nebulizer, and axially viewed ICP OES. Food Anal Methods 8:1652–1660
MATLAB (2017) The MathWorks, Natick, USA
Milani RF, Morgano MA, Saron ES, Silva FF, Cadore S (2015) Evaluation of direct analysis for trace elements in tea and herbal beverages by ICP-MS. J Braz Chem Soc 6:1211–1217
Miranda K, Pereira-Filho ER (2013) Sequential determination of Cd, Cu and Pb in tea leaves by slurry introduction to thermospray flame furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 6(6):1607–1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9574-z
Nascentes CC, Korn M, Arruda MAZ (2001) A fast ultrasound-assisted extraction of Ca, Mg, Mn and Zn from vegetables. Microchem J 69:37–43
Novaes CG, Bezerra MA, Da Silva EGP, Dos Santos AMP, Da Silva ILR, Santos JHN (2016) A review of multivariate designs applied to the optimization of methods based on inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES). Microchem J 128:331–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.05.015
Pereira JB, Dantas KGF (2016) Evaluation of inorganic elements in cat’s claw teas using ICP OES and GF AAS. Food Chem 196:331–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.057
Pereira-Filho ER (2015) Planejamento Fatorial Em Química: Maximizando a Obtenção de Resultos. Edufscar, Editora, p 88
Santos D, Krug FJ, Pereira MG, Korn M (2006) Currents on ultrasound-assisted extraction for sample preparation and spectroscopic analytes determination. Appl Spectrosc Rev 41:305–321
Santos WPC, Castro JT, Bezerra MA, Fernandes APF, Ferreira SLC, Korn MGA (2009) Application of multivariate optimization in the development of an ultrasound-assisted extraction procedure for multielemental determination in bean seeds samples using ICP OES. Microchem J 91(2):153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2008.10.001
Santos DCMB, Carvalho LSB, Lima DC, Leão DJ, Teixeira LSG, Korn MGA (2014) Determination of micronutrient minerals in coconut milk by ICP OES after ultrasound-assisted extraction procedure. J Food Compost Anal 34(1):75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2014.02.008
Shaltout AA, Abdel-Aal MS, Welz B, Castilho INB (2013) Determination of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Pb in black tea from Saudi Arabia using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after microwave-assisted acid digestion. Anal Lett 46(13):2089–2100. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2013.784918
Solomon D, Lehmann J, Tekalign M, Fritzsche F, Zech W (2001) Sulfur fractions in particle-size separates of the sub-humid Ethiopian highlands as influenced by land use changes. Geoderma 102:41–59
Szymczycha-Madeja A, Welna M, Pohl P (2012) Elemental analysis of teas and their infusions by spectrometric methods. Trends Anal Chem 35:165–181
Szymczycha-Madeja A, Welna M, Pohl P (2016) Comparison and validation of different alternative sample preparation procedures of tea infusions prior to their multi-element analysis by FAAS and ICP OES. Food Anal Methods 9:1398–1411
Tarley CRT, Silveira G, Santos WNL, Matos GD, Silva EGP, Bezerra MA, Miro M, Ferreira SLC (2009) Chemometric tools in electroanalytical chemistry: methods for optimization based on factorial design and response surface methodology. Microchem J 92(1):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2009.02.002
Tiwari BK (2015) Ultrasound: a clean, green extraction technology. Trends Anal Chem 71:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.04.013
Villa JEL, Pereira CD, Cadore S (2015) A novel, rapid and simple acid extraction for multielemental determination in chocolate bars. Microchem J 121:199–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.03.008
Wang ZM, Zhou B, Wang YS, Gong QY, Wang QM, Yan JJ, Gao W, Wang LS (2011) Black and green tea consumption and the risk of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr 93(3):506–515. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.110.005363
Welna M, Szymczycha-Madeja A, Pohl P (2013) A comparison of samples preparation strategies in the multi-elemental analysis of tea by spectrometric methods. Food Res Int 53:922–930
Wong MH, Fung KF, Carr HP (2003) Aluminium and fluoride contents of tea, with emphasis on brick tea and their health implications. Toxicol Lett 137(1-2):111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(02)00385-5
Yemane M, Chandravanshi BS, Wondimu T (2008) Levels of essential and non-essential metals in leaves of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) and soil of Wushwush farms. Ethiopia, Food Chem 107:1236–1243
Yokel RA, Florence RL (2008) Aluminum bioavailability from tea infusion. Food Chem Toxicol 46(12):3659–3663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2008.09.041
Zhao H, Zhang S, Zhang Z (2017) Relationship between multi-element composition in tea leaves and in provenance soils for geographical traceability. Food Control 76:82–87
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia (FAPESB), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This is an original research article that has neither been published previously nor considered presently for publication elsewhere.
All authors named in the manuscript are entitled to the authorship and have approved the final version of the submitted manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
Vinicius Câmara Costa declares that he has no conflict of interest. Wesley Nascimento Guedes declares that he has no conflict of interest. Antonio de Santana Santos declares that he has no conflict of interest. Madson Moreira Nascimento declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, V.C., Nascimento Guedes, W., de Santana Santos, A. et al. Multivariate Optimization for the Development of a Fast and Simple Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Procedure for Multielemental Determination in Tea Leaves by Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP OES). Food Anal. Methods 11, 2004–2012 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1171-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1171-8