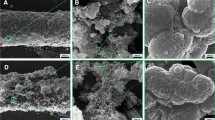
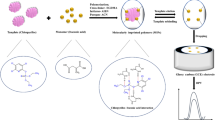
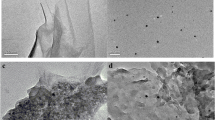
Abstract
The molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensor has been attending recently, due to their exceptional advantages and specificity. Here, we successfully designed and fabricated a novel electrochemical nanosensor for determination of gallic acid (GA) based on its specific MIP. The MIP was synthesized using precipitation polymerization technique, via polymerization of methacrylic acid as a functional monomer. The MIP was applied in the multiwalled carbon nanotube-modified carbon paste electrode (MWCNT–CPE), and similarly, MIP and MWCNT-modified CPE (MIP–MWCNT–CPE) was prepared, which acted as the selective recognition element and pre-concentrator agent for GA. The effect of different factors such as quantity of MIP and MWCNT, GA solution pH, and GA accumulation time on an oxidation current of accumulated GA at the electrode were investigated and optimized by central composite design (CCD) as a an experimental design and response surface methodology. The results showed that fabricated nanosensors (MIP–MWCNT–CPE) have higher sensitivity compared with bare CPE, MWCNT–CPE, and MIP–CPE. This sensor showed a linear response range of 0.12–380.0 μM and detection limit of 47.0 nM. Finally, the nanosensor was applied to determine GA in apple, pineapple, orange juices, and a commercial green tea drink as real samples with satisfactory results.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Daneshfar A, Hamdghadareh S, Farmany A (2011) Quantification of sub-nanomolar levels of gallic acid by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:4843–4852
Abdel-Hamid R, Newair E (2011) Electrochemical behavior of antioxidants: I. Mechanistic study on electrochemical oxidation of gallic acid in aqueous solutions at glassy-carbon electrode. J Electroanal Chem 657:107–112
Abdel-Hamid R, Newair EF (2013) Adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of gallic acid using an electrochemical sensor based on polyepinephrine/glassy carbon electrode and its determination in black tea sample. Electroanal Chem 704:32–37
Alizadeh T, Ganjali MR, Zare M, Norouzi P (2012) Selective determination of chloramphenicol at trace level in milk samples by the electrode modified with molecularly imprinted polymer. J Food Chem 130:1108–1114
Azimzadeh M, Rahaie M, Nasirizadeh N, NaderiManesh H (2015) Application of oracet blue in a novel and sensitive electrochemical biosensor for the detection of microRNA. Anal Methods 7:9495–9503
Azimzadeh M, Rahaie M, Nasirizadeh N, Ashtari K, NaderiManesh H (2016) An electrochemical nanobiosensor for plasma miRNA-155, based on graphene oxide and gold nanorod, for early detection of breast cancer. Biosens Bioelectron 77:99–106
Davoodi D, Hassanzadeh-khayyat M, Asgharian Rezaei M, Mohajeri SA (2014) Preparation, evaluation and application of diazinon imprinted polymers as the sorbent in molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography analysis in cucumber and aqueous samples. Food Chem 158:421–428
Ghaani M, Nasirizadeh N, Yasini Ardakani SA, Zare Mehrjardi F, Scampicchio M, Farris S (2016) Development of an electrochemical nanosensor for the determination of gallic acid in food. Anal Methods 8:1103–1110
Ghoreishi SM, Behpour M, Khayatkashani M, Motaghedifard MH (2011) Simultaneous determination of ellagic and gallic acid in Punica granatum, Myrtus communis and Itriphal formulation by an electrochemical sensor based on a carbon paste electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Anal Methods 3:636–645
Gohary NAE, Madbouly A, Nashar RME, Mizaikoff B (2015) Synthesis and application of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the voltammetric determination of famciclovir. Biosens Bioelectron 65:108–114
Granado VLV, Gutierrez-Capitan M, Fernandez-Sanchez C, Gomes MTSR, Rudnitskaya A, Jimenez-Jorquera C (2014) Thin-film electrochemical sensor for diphenylamine detection using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chim Acta 809:141–147
Javanbakht M, EynollahiFard S, Mohammadi A, Abdouss M, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P, Safaraliee L (2008) Molecularly imprinted polymer based potentiometric sensor for the determination of hydroxyzine in tablets and biological fluids. Anal Chim Acta 612:65–74
Kahl M, Golden TD (2014) Electrochemical determination of phenolic acids at a Zn/Al layered double hydroxide film modified glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 26:1664–1670
Li S, Sun H, Wang D, Qian L, Zhu Y, Tao S (2013) Determination of gallic acid by flow injection analysis based on luminol-AgNO3-Ag NPs chemiluminescence system. Chin J Chem 30:837–841
Li ZY, Quan HJ, Gong CB, Yang YZ, Tang Q, Wei YB, Ma XB, Lam HW (2015) Photocontrolled solid-phase extraction of guanine from complex samples using a novel photoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem 172:56–62
Liu J, Song H, Liu J, Liu Y, Li L, Tang H, Li Y (2015) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer with double templates for rapid simultaneous determination of melamine and dicyandiamide in dairy products. Talanta 134:761–767
Luo JH, Li BL, Li NB, Luo HQ (2013) Sensitive detection of gallic acid based on polyethyleneimine-functionalized graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens Actuators B 186:84–89
Madrakian T, Haghshenas E, Ahmadi M, Afkhami A (2015) Construction a magneto carbon paste electrode using synthesized molecularly imprinted magnetic nanospheres for selective and sensitive determination of mefenamic acid in real samples. Biosens Bioelectron 68:712–718
Narum K, Sonoda JI, Shiotani K, Shigeru M, Kawachi A, Tomishige E, Sato K, Motoya T (2014) Simultaneous detection of green tea catechin and gallic acid in human serum after ingestion of green tea tablets using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr B 945–946:147–153
Narumi K, Sonoda JI, Shiotani K, Shigeru M, Shibata M, Kawachi A, Tomishige E, Sato K, Motoya T (2014) Simultaneous detection of green tea catechins and gallic acid inhuman serum after ingestion of green tea tablets using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr B 945–946:147–153
Nasirizadeh N, Zare HR, Fakhari AR, Ahmar H, Ahmadzadeh MR, Naeimi A (2011) A study of the electrochemical behavior of an oxadiazole derivative electrodeposited on multi-wall carbon nanotube-modified electrode and its application as a hydrazine sensor. J Solid State Electrochem 15:2683–2693
Nasirizadeh N, Dehghanizadeh H, Yazdanshenas ME, RohaniMoghadam M, Karimi A (2012) Optimization of wool dyeing with rutin as natural dye by central composite design method. Ind Crop Prod 40:361–366
Nasirizadeh N, Shekari Z, Zare HR, Makarem S (2013a) Electrocatalytic determination of dopamine in the presence of uric acid using an indenedione derivative and multiwall carbon nanotubes spiked in carbon paste electrode. Mater Sci Eng C 33:1491–1497
Nasirizadeh N, Shekari Z, Zare HR, Shishehbore MR, Fakhari AR, Ahmar H (2013b) Electrosynthesis of an imidazole derivative and its application as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, adrenaline, acetaminophen, and tryptophan at a multi-wall carbon nanotubes modified electrode surface. Biosens Bioelectron 41:608–614
Nasirizadeh N, Shekari Z, Ghaani M (2015) A novel electrochemical biosensor based on a modified gold electrode for hydrogen peroxide determination in different beverage samples. Food Anal Methods 8:1546–1555
Panizza M, Cerisalo G (2009) Electrochemical of gallic acid on a BDD anode. Chemosphere 77:1060–1064
Petkovic BB, Stankovic D, Milcic M, Sovilj SP, Manojlovic D (2015) Dinuclear copper(II) octaazamacrocyclic complex in a PVC coated GCE and graphite as a voltammetric sensor for determination of gallic acid and antioxidant capacity of wine samples. Talanta 132:513–519
Phakthong W, Liawruangrath B, Liawruangrath S (2014) Determination of gallic acid with rhodanine by reverse flow injection analysis using simplex optimization. Talanta 130:577–584
Ruela ALM, Figueiredo EC, Pereira GR (2014) Molecularly imprinted polymers as nicotine transdermal delivery systems. Chem Eng J 248:1–8
Sangeetha NS, Narayanan SS (2014) A novel bimediator amperometric sensor for electrocatalytic oxidation of gallic acid and reduction of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Chim Acta 828:34–45
Sarjit A, Wang Y, Dykes GA (2015) Antimicrobial activity of gallic acid against thermophilic Campylobacter is strain specific and associated with a loss of calcium Ions. Food Microbiol 46:227–233
Sharma PS, Iskierko Z, Pietrzyk-Le A, Souza FD, Kutner W (2015) Bioinspired intelligent molecularly imprinted polymers for chemosensing: a mini review. Electrochem Commun 50:81–87
Shi S, Guo J, You Q, Chen X, Zhang Y (2014) Selective and simultaneous extraction and determination of hydroxybenzoic acids in aqueous solution by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem Eng J 243:485–493
Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Nieman TA (1998) Principles of instrumental analysis, 5th edn. Harcourt Brace, Philadelphia
Song B, Zhou Y, Jin H, Jing T, Zhou T, Hao Q, Zhou Y, Mei S, Lee Y (2014) Selective and sensitive determination of erythromycin in honey and dairy products by molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical sensor. Microchem J 116:183–190
Srivastava N, Verma S, Pragyadeep S, Srivastava S, Singh Rawat A (2014) Evaluation of successive fractions for optimum quantification of bergenin and gallic acid in three industrially important Bergenia species by high-performance thin-layer chromatography. J Planar Chromatogr 27:69–71
Su YL, Chen S-H (2015) Sensitive and selective determination of gallic acid in green tea samples based on an electrochemical platform of poly(melamine) film. Anal Chim Acta 901:41–50
Sundaram S, Jagannathan M, Kadir MRA, Palanivel S, Hadibarata T, Yusoff ARM (2015) A new electro-generated o-dinisidine derivative stabilized MWCNT-modified GCE for low potential gallic acid detection. RSC Adv 5:45996–46006
Szekely G, Valtcheva IB, Kim JF, Livingston AG (2015) Molecularly imprinted organic solvent nanofiltration membranes—revealing molecular recognition and solute rejection behavior. React Funct Polym 86:215–224
Tashkhourian J, Nami-Ana SF (2015) A sensitive electrochemical sensor for determination of gallic acid based on SiO2 nanoparticle modified carbon paste electrode. Mater Sci Eng C 52:103–110
Tashkhourian J, Nami Ana SF, Hashemnia S, Hormozi-Nezhad MR (2013) Construction of a modified carbon paste electrode based on TiO2 nanoparticles for the determination of gallic acid. J Solid State Electrochem 17:157–165
Tiwari MP, Prasad A (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer based enantioselective sensing devices: a review. Anal Chim Acta 853:1–18
Wang H, Chen D, Wel Y, Chang Y, Zhao J (2011) A simple and sensitive assay of gallic acid based on localized surface plasmon resonance light scattering of silver nanoparticles through modified tollens process. Anal Sci 27:937–941
Zhao P, Hao J (2013) Tert-butylhydroquinone recognition of molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor based on core–shell nanoparticles. Food Chem 139:1001–1007
Ziyatdinova G, Kozlova E, Budnikov H (2016) Chronocoulometry of wine on multi-walled carbon nanotube modified electrode: antioxidant capacity assay. Food Chem 196:405–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Shahrzad Shojaei declares no conflict of interest. Navid Nasirizadeh declares no conflict of interest. Mehdi Entezam declares no conflict of interest. Mojtaba Koosha declares no conflict of interest. Mostafa Azimzadeh declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shojaei, S., Nasirizadeh, N., Entezam, M. et al. An Electrochemical Nanosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) for Detection of Gallic Acid in Fruit Juices. Food Anal. Methods 9, 2721–2731 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0459-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0459-9