Abstract
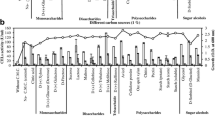
A cellulase, En5H, from halophilic, alkalithermophilic Alkalilimnicola sp. NM-DCM1 was expressed and purified. En5H had maximal hydrolytic activity at 55 °C, pH 8.8, and 2.5 M NaCl. En5H is β-1,4 linkage-specific, hydrolyzing carboxymethyl cellulose, Avicel, cellobiose, and p-nitrophenyl β-d-glucopyranoside. En5H was resistant to inhibitors and organic solvents. The half-life of En5H was increased 16–43-fold when incubated in 20% (v/v) of ionic liquids (IL) at 55 °C in the presence of 2.5 M NaCl, and maximal hydrolytic activity of En5H in 10% (v/v) 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and 1,3-dimethylimidazolium dimethyl phosphate was 122 and 110%, respectively, as compared with activity in buffer. A cellulase-IL system combining IL pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification was tested. With an enzyme load of 110 U/g rice straw, the conversion of rice straw cellulose and hemicellulose increased by 28% compared with unpretreated rice straw. En5H has potential for use in transformation of lignocellulose to glucose in a single-step process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sindhu R, Binod R, Pandey A (2016) Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass—an overview. Bioresour Technol 199:76–82
Xu J, Xiong P, He B (2016) Advances in improving the performance of cellulase in ionic liquids for lignocellulose biorefinery. Bioresour Technol 200:961–970
Sun S, Sun S, Cao X, Sun R (2016) The role of pretreatment in improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials. Bioresour Technol 199:49–58
Sun N, Liu H, Sathitsuksanoh N, Stavila V, Sawant M, Bonito A, Tran K, George A, Sale KL, Singh S (2013) Production and extraction of sugars from switchgrass hydrolyzed in ionic liquids. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:1–15
Xu J, He B, Wu B, Wang B, Wang C, Hu L (2014) An ionic liquid tolerant cellulase derived from chemically polluted microhabitats and its application in in situ saccharification of rice straw. Bioresour Technol 157:166–173
Wahlstrom R, Rovio S, Suurnakki A (2012) Partial enzymatic hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose in ionic liquids by Trichoderma reesei endoglucanases. RSC Adv 2:4472–4480
Kamiya N, Matsushita Y, Hanaki M, Nakashima K, Narita M, Goto M, Takahashi H (2008) Enzymatic in situ saccharification of cellulose in aqueous-ionic liquid media. Biotechnol Lett 30:1037–1040
Orencio-Trejo M, De la Torre-Zavala S, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Aviles-Arnaut H, Gastelum-Arellanez A (2016) Assessing the performance of bacterial cellulases: the use of Bacillus and Paenibacillus strains as enzyme sources for lignocellulose saccharification. Bioenerg Res. doi:10.1007/s12155-12016-19797-12150
Shi R, Li Z, Ye Q, Xu J, Liu Y (2013) Heterologous expression and characterization of a novel thermo-halotolerant endoglucanase Cel5H from Dictyoglomus thermophilum. Bioresour Technol 142:338–344
Anish R, Rahman MS, Rao M (2007) Application of cellulases from an alkalothermophilic Thermomonospora sp. in biopolishing of denims. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:45–56
Mesbah NM, Wiegel J (2014) Halophilic alkali- and thermostable amylase from a novel polyextremophilic Amphibacillus sp. NM-Ra2. Int J Biol Macromol 70:222–229
Brettin T, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Overbeek R, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Shukla M, Thomason JA, Stevens R, Vonstein V, Wattan AR, Xia F (2015) RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci Rep 5:8365. doi:10.1038/srep08365
Wilson K (1997) Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE et al (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York, pp 2.4.1–2.4.5
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2010) Determinaton of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden Technical Report:NREL/TP-510-42618
Henrissat B, Callebaut I, Fabrega S, Lehn P, Mornon JP, Davies G (1996) Conserved catalytic machinery and the prediction of a common fold for several familiies of glycosyl hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 28:5674
Kim JS, Lee YY, Kim TH (2016) A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 199:42–48
Yin J, Chen J-C, Wu Q, Chen G-Q (2015) Halophiles, coming stars for industrial biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 33:1433–1442
Aspeborg H, Coutinho PM, Wang Y, Brumer H III, Henrissat B (2012) Evolution, substrate specificity and subfamily classification of glycoside hydrolase family 5 (GH5). BMC Evol Biol 12:186
Benhmad I, Boudabbous M, Yaich A, Rebai M, Gargouri A (2016) A novel neutral, halophile Stachybotrys microspora-based endoglucanase active impact on β-glucan. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39:685–693
Gaur R, Tiwari S (2015) Isolation, production, purification and characterization of an organic-solvent-thermostable alkalophilic cellulase from Bacillus vallismortis RG-07. BMC Biotechnol 15:19
Yu H-Y, Li X (2015) Alkali-stable cellulase from a halophilic isolate, Gracilibacillus sp. SK1 and its application in lignocellulosic saccharification for ethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 81:19–25
Ogino H, Ishikawa H (2001) Enzymes which are stable in the presence of organic solvents. J Biosci Bioeng 91:109–116
Dougherty MJ, Tran HM, Stavila V, Knierim B, George A, Auer M, Adams PD, Hadi MZ (2014) Cellulosic biomass pretreatment and sugar yields as a function of biomass particle size. PLoS One 9:e100836
Farahani SV, Kim Y-W, Schall CA (2016) A coupled low temperature oxidative and ionic liquid pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Catal Today 269:2–8
Wahlstrom R, Suurnakki A (2015) Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic polysaccharides in the presence of ionic liquids. Green Chem 17:694
Reddy AP, Simmons CW, Claypool J, Jabusch L, Burd H, Hadi MZ, Simmons BA, Singer SW, Vander Gheynst JS (2012) Thermophilic enrichment of microbial communities in the presence of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium acetate. J Appl Microbiol 113:1362–1370
Xu J, Wang X, Liu X, Xia J, Zhang T, Xiong P (2016) Enzymatic in situ saccharificaion of lignocellulosic biomass in ionic liquids using an ionic liquid-tolerant cellulases. Biomass Bioenergy 93:180–186
Constatinescu D, Herrmann C, Weingartner H (2010) Patterns of protein unfolding and protein aggregation in ionic liquids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:1756–1763
Nordwald EM, Kaar JL (2013) Stabilization of enzymes in ionic liquids via modification of enzyme charge. Biotechnol Bioeng 110:2352–2360
Oren A (2010) Industrial and environmental applications of halophilic microorganisms. Environ Technol 31:825–834
Zavrel M, Bross D, Funke M, Buchs J, Spiess AC (2009) High-throughput screening for ionic liquids dissolving (ligno-)cellulose. Bioresour Technol 100:2580–2587
Maki-Arvela P, Anugworn I, Virtanen P, Sjoholm R, Mikkola J-P (2010) Dissolution of lignocellulosic materials and its constituents using ionic liquids—a review. Ind Crop Prod 32:175–201
Zhang T, Datta S, Eichler J, Ivanova N, Axen SD, Kerfeld CA, Chen F, Kyrpides N, Hugenholtz P, Cheng J-F, Sale KL, Simmons B, Rubin E (2011) Identification of a haloalkaliphilic and thermostable cellulase with improved ionic liquid tolerance. Green Chem 13:2083–2090
Gunny AAN, Arbain D, Gumba RE, Jong BC, Jamal P (2014) Potential halophilic cellulases for in situ enzymatic saccharification of ionic liquids pretreated lignocelluloses. Bioresour Technol 155:177–181
Trivedi N, Gupta V, Reddy CR, Jha B (2013) Detection of ionic liquid stable cellulase produced by the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. isolated from brown alga Sargassum polycystum C. Agardh. Bioresour Technol 132:313–319
Raddadi N, Cherif A, Daffonchio D, Fava F (2013) Halo-alkalitolerant and thermostable cellulases with improved tolerance to ionic liquids and organic solvents from Paenibacillus tarimensis isolated from the Chott El Fejej, Sahara desert, Tunisia. Bioresour Technol 150:121–128
Fu D, Mazza G (2011) Aqueous ionic liquid pretreatment of straw. Bioresour Technol 102:7008–7011
Li Q, Jiang X, He Y, Li L, Xian M, Yang J (2010) Evaluation of the biocompatibile ionic liquid 1-methyl-3-methylimidazolium dimethylphosphite pretreatment of corn cob for improved saccharification. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:117–126
Wang Y, Radosevich M, Hayes D, Labbe N (2011) Compatible ionic liquid-cellulases system for hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:1042–1048
Shi J, Gladden JM, Sathitsuksanoh N, Kambam P, Sandoval L, Mitra D, Zhang S, George A, Singer SW, Simmons BA, Singh S (2013) One-pot ionic liquid pretreatment and saccharification of switchgrass. Green Chem 15:2579–2589
Xu J, Wu B, Hu L, Wu Z, Xu N, Dai B, He J (2015) Enzymatic in situ saccharification of lignocellulose in a compatible ionic liquid-cellulase system. Chem Eng J 267:163–169
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the US-Egypt Science and Technology Joint Fund in cooperation with the Suez Canal University (Egypt) under project number 1841 and the University of Georgia (USA) under project number NSF-OISE-1132412.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesbah, N.M., Wiegel, J. A Halophilic, Alkalithermostable, Ionic Liquid-Tolerant Cellulase and Its Application in In Situ Saccharification of Rice Straw. Bioenerg. Res. 10, 583–591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-017-9825-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-017-9825-8