Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether metabolic tumor parameters and radiomic features extracted from 18F-FDG PET/CT (PET) can predict response to therapy and outcome in patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma.
Methods
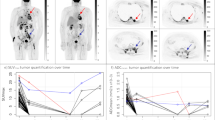
This institutional ethics board-approved retrospective study included 82 patients undergoing PET for aggressive B-cell lymphoma staging. Whole-body metabolic tumor volume (MTV) using various thresholds and tumor radiomic features were assessed on representative tumor sites. The extracted features were correlated with treatment response, disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS).
Results
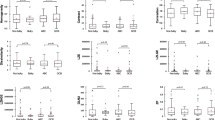
At the end of therapy, 66 patients (80.5%) had shown complete response to therapy. The parameters correlating with response to therapy were bulky disease > 6 cm at baseline (p = 0.026), absence of a residual mass > 1.5 cm at the end of therapy CT (p = 0.028) and whole-body MTV with best performance using an SUV threshold of 3 and 6 (p = 0.015 and 0.009, respectively). None of the tumor texture features were predictive of first-line therapy response, while a few of them including GLNU correlated with disease-free survival (p = 0.013) and kurtosis correlated with overall survival (p = 0.035).
Conclusions
Whole-body MTV correlates with response to therapy in patient with aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Tumor texture features could not predict therapy response, although several features correlated with the presence of a residual mass at the end of therapy CT and others correlated with disease-free and overall survival. These parameters should be prospectively validated in a larger cohort to confirm clinical prognostication.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 June 2018
In the original publication of the article, the title was incorrectly.
References
Barrington SF, Mikhaeel NG, Kostakoglu L, Meignan M, Hutchings M, Müeller SP, et al. Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma: consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J Clin Oncol 2014;32:3048–3058.
Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood. 2010;116:2040–5.
Malek E, Sendilnathan A, Yellu M, Petersen A, Fernandez-Ulloa M, Driscoll JJ. Metabolic tumor volume on interim PET is a better predictor of outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma than semiquantitative methods. Blood Cancer J. 2015;5:e326.
Xie M, Zhai W, Cheng S, Zhang H, Xie Y, He W. Predictive value of F-18 FDG PET/CT quantization parameters for progression-free survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematology. 2016;21(2):99–105.
Mikhaeel NG, Smith D, Dunn JT, Phillips M, Møller H, Fields PA, et al. Combination of baseline metabolic tumour volume and early response on PET/CT improves progression-free survival prediction in DLBCL. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:1209–19.
Cottereau AS, Lanic H, Mareschal S, Meignan M, Vera P, Tilly H, et al. Molecular profile and FDG-PET/CT total metabolic tumor volume improve risk classification at diagnosis for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:3801–9.
Gevaert O, Xu J, Hoang CD, Leung AN, Xu Y, Quon A, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: identifying prognostic imaging biomarkers by leveraging public gene expression microarray data—methods and preliminary results. Radiology. 2012;264:387–96.
Karlo CA, Di Paolo PL, Chaim J, Hakimi AA, Ostrovnaya I, Russo P, et al. Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: associations between CT imaging features and mutations. Radiology. 2014;270:464–71.
Diaz-Cano SJ. Tumor heterogeneity: mechanisms and bases for a reliable application of molecular marker design. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1951–2011.
Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB, et al. Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30:1234–48.
Nioche C, Orlhac F, Soussan M, Boughdad S, Alberini J, Buvat I. A software for characterizing intra-tumor heterogeneity in multimodality imaging and establishing reference charts. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:S156-S157.
Chihara D, Oki Y, Onoda H, Taji H, Yamamoto K, Tamaki T, et al. High maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) on PET scan is associated with shorter survival in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2011;93:502–8.
Nguygen XC, Lee WW, Amin AM, Eo JS, Bang SM, Lee JS, et al. Tumor burden assessed by the maximum standardized uptake value and greatest diameter on FDG-PET predicts prognosis in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;44:39–44.
Miyazaki Y, Nawa Y, Miyagawa M, Kohashi S, Nakase K, Yasukawa M, et al. Maximum standard uptake value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is a prognostic factor for progression-free survival of newly diagnosed patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2013;92:239–44.
Xie M, Zhai W, Cheng S, Zhang H, Xie Y, He W. Predictive value of F-18 FDG PET/CT quantization parameters for progression-free survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematology. 2016;21:99–105.
Boellaard R, O’Doherty MJ, Weber WA, Giammarile F, Tatsch K, Eschner W, et al. FDG PET and PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour PET imaging: version 1.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:181–200.
Dabaja BS, Phan J, Mawlawi O, Medeiros LJ, Etzel C, Liang FW, et al. Clinical implications of PET-negative residual CT masses after chemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:2631–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The article title was corrected.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parvez, A., Tau, N., Hussey, D. et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic tumor parameters and radiomics features in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma as predictors of treatment outcome and survival. Ann Nucl Med 32, 410–416 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-018-1260-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-018-1260-1