Abstract
Objective
Wegener’s granulomatosis (WG) is a rare disorder characterized by granulomatous necrotizing vasculitis which mainly affects small- and medium-sized vessels. While the classical triad of involvement is upper and lower respiratory system and glomerulonephritis, WG may involve any organ or system in the body. The aim of our study was to investigate the role of positron emission tomography/computerized tomography (PET/CT) both in the initial evaluation and follow-up of patients with WG.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated PET/CT data from 13 patients (6 males; 7 females) with a mean age of 45 ± 12.4 years (range 28–63) who underwent either initial evaluation (n = 12) or response evaluation (n = 2) by conventional imaging methods and FDG with PET/CT. PET/CT images were both visually and quantitatively evaluated. The demographic data, clinical and laboratory findings of each patient were also recorded from the hospital files.
Results
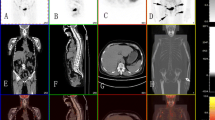
Lung (n = 13), parapharyngeal space (n = 8), nose (n = 8), and ear (n = 3) were the most common disease sites detected on PET/CT. The entire initial evaluation patients had either solitary or multiple pulmonary nodular/mass lesions with marked increased FDG uptake (mean SUVmax 12 ± 4, range 3.53–19.51) on PET/CT. There was no significant pathological FDG uptake in patients consistent with complete treatment response after appropriate immunosuppressive therapy. PET/CT clearly demonstrated unexpected disease sites besides the respiratory system, with WG involvement except kidneys. Possibly due to physiological urinary excretion of FDG, urine analysis, BUN and creatinine levels were accepted still the best way for diagnosis of renal involvement.
Conclusion
FDG with PET/CT is a valuable tool in the management of patients with WG for a more accurate clinical evaluation regarding disease extension and treatment response.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woywodt A, Matteson EL. Wegener’s granulomatosis—probing the untold past of the man behind the eponym. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(10):1303–6.
Frankel SK, Cosgrove GP, Fischer A, Meehan RT, Brown KK. Update in the diagnosis and management of pulmonary vasculitis. Chest. 2006;129(2):452–65.
Fries JF, Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of vasculitis. Summary. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(8):1135–6.
Hagen EC, Daha MR, Hermans J, Andrassy K, Csernok E, Gaskin G, et al. Diagnostic value of standardized assays for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in idiopathic systemic vasculitis. EC/BCR Project for ANCA Assay Standardization. Kidney Int. 1998;53(3):743–53.
Choi HK, Liu S, Merkel PA, Colditz GA, Niles JL. Diagnostic performance of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody tests for idiopathic vasculitides: metaanalysis with a focus on antimyeloperoxidase antibodies. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(7):1584–90.
Pretorius ES, Stone JH, Hellmann DB, Fishman EK. Wegener’s granulomatosis: spectrum of CT findings in diagnosis, disease progression, and response to therapy. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 2000;41(4):279–313.
Seo P, Stone JH. The antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides. Am J Med. 2004;117(1):39–50.
Frankel SK, Cosgrove GP, Fischer A, Meehan RT, Brown KK. Update in the diagnosis and management of pulmonary vasculitis. Chest. 2006;129(2):452–65.
Levin A, Kasem S, Mader R, Naparstek Y, Friedman G, Ben-Yehuda A. Wegener granulomatosis with back pain, periaortitis, and dural inflammation developing while receiving monthly cyclophosphamide. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006;12(6):294–7.
Ito K, Minamimoto R, Yamashita H, Yoshida S, Morooka M, Okasaki M. Evaluation of Wegener’s granulomatosis using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Ann Nucl Med. 2012.
Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Hunder GG, Arend WP. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(8):1101–7.
Bleeker-Rovers CP, Bredie SJ, van der Meer JW, Corstens FH, Oyen WJ. F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in diagnosis and follow-up of patients with different types of vasculitis. Neth J Med. 2003;61(10):323–9.
Walter MA, Melzer RA, Schindler C, Müller-Brand J, Tyndall A, Nitzsche EU. The value of [18F]FDG-PET in the diagnosis of large-vessel vasculitis and the assessment of activity and extent of disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32(6):674–81.
Fuchs M, Briel M, Daikeler T, Walker UA, Rasch H, Berg S. The impact of 18F-FDG PET on the management of patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39(2):344–53.
Beggs AD, Hain SF. F-18 FDG-positron emission tomographic scanning and Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27(10):705–6.
Lapraik C, Watts R, Bacon P, Carruthers D, Chakravarty K, D’Cruz D. BSR and BHPR guidelines for the management of adults with ANCA associated vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(10):1615–6.
Fries JF, Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of vasculitis. Summary. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33(8):1135–6.
Maranhão AS, Chen VG, Rossini BA, Testa JR, Penido Nde O. Mastoiditis and facial paralysis as initial manifestations of Wegener’s granulomatosis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;78(2):80–6.
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides: proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37(2):187–92.
Blockmans D, Baeyens H, Van Loon R, Lauwers G, Bobbaers H. Periaortitis and aortic dissection due to Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin Rheumatol. 2000;19(2):161–4.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Aysenaz Ozcan, Dr. Belgin Samurkasoglu, Dr. Nermin Capan, Dr. Nilgun Kalac, Dr. Sema Canbakan, Dr. Sukran Atikcan, Dr. Yurdanur Erdogan for referring their patients to our department and cooperation. The abstract of the manuscript has also been accepted to be presented at 26th Annual Congress of the EANM in October 2013.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozmen, O., Tatci, E., Gokcek, A. et al. Integration of 2-deoxy-2-[18F] fluoro-d-glucose PET/CT into clinical management of patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Ann Nucl Med 27, 907–915 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-013-0769-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-013-0769-6