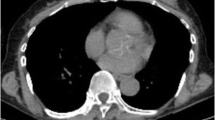
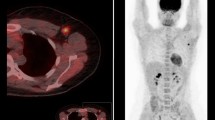
Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to analyze the clinical significance of maxSUV with clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical prognostic factors in patients with primary breast cancer.
Methods
Ninety-one women (48.5 ± 11.2 years of age) with breast cancer who underwent 18F-FDG PET (PET) before surgery were recruited. All of the breast cancers were invasive ductal carcinomas and ≥1 cm in size to exclude a partial volume effect. The maxSUV of breast cancers was compared with histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Additionally, the ability of PET to discriminate axillary nodal status (ANS) and correlation between ANS and tumor characteristics were evaluated.
Results
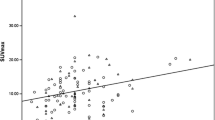
A high maxSUV of breast cancer was significantly correlated with the following poor prognosis factors: tumor invasiveness >2 cm (2.9 vs. 5.4; p < 0.001); high score of nuclear (3.5 vs. 5.3; p = 0.008) or histologic grade (3.3 vs. 5.5; p < 0.001); MIB-1 ≥10% (3.0 vs. 4.9; p < 0.002); ER-negativity (4.8 vs. 3.8; p = 0.019); PR-negativity (5.0 vs. 3.6; p = 0.029); and triple negativity (ER-, PR-, and c-erbB-2-negative; 5.3 vs. 3.8; p < 0.016). MaxSUV was not affected by menopausal status, ANS, lymphovascular invasion, including CD34 and D2-40 (LVIs), p53, and c-erbB-2 status. Additionally, the sensitivity and specificity of PET for discriminating ANS were 51.1 and 97.8%, respectively. ANS was correlated with tumor invasiveness >2 cm (p = 0.046), LVIs (all of variables; p < 0.001), and triple negativity (p = 0.049).
Conclusions
A high FDG uptake of breast tumor is correlated with several poor prognosis factors, such as tumor invasiveness >2 cm, higher tumor grade, higher MIB-1, hormonal receptor negativity, and triple negativity. However, PET has a limited value in discriminating axillary lymph nodes. Pre-operative PET is a useful modality to predict biologic poor prognosis factors which could affect adjunctive therapy of breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett SV. Breast cancer. J R Coll Physic Edinb. 2010;40(4):335–8. (quiz 9).
Berriolo-Riedinger A, Touzery C, Riedinger JM, Toubeau M, Coudert B, Arnould L, et al. [18F]FDG-PET predicts complete pathological response of breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34(12):1915–24.
Groheux D, Giacchetti S, Rubello D, Al-Nahhas A, Moretti JL, Espie M, et al. The evolving role of PET/CT in breast cancer. Nucl Med Commun. 2010;31(4):271–3.
Basu S, Chen W, Tchou J, Mavi A, Cermik T, Czerniecki B, et al. Comparison of triple-negative and estrogen receptor-positive/progesterone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast carcinoma using quantitative fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose/positron emission tomography imaging parameters: a potentially useful method for disease characterization. Cancer. 2008;112(5):995–1000.
Groheux D, Giacchetti S, Moretti JL, Porcher R, Espie M, Lehmann-Che J, et al. Correlation of high 18F-FDG uptake to clinical, pathological and biological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38(3):426–35.
Heusner TA, Kuemmel S, Hahn S, Koeninger A, Otterbach F, Hamami ME, et al. Diagnostic value of full-dose FDG PET/CT for axillary lymph node staging in breast cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36(10):1543–50.
Ueda S, Tsuda H, Asakawa H, Shigekawa T, Fukatsu K, Kondo N, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of uptake level using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography fusion imaging (18F-FDG PET/CT) in primary breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008;38(4):250–8.
Veronesi U, De Cicco C, Galimberti VE, Fernandez JR, Rotmensz N, Viale G, et al. A comparative study on the value of FDG-PET and sentinel node biopsy to identify occult axillary metastases. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(3):473–8.
Avril N, Rose CA, Schelling M, Dose J, Kuhn W, Bense S, et al. Breast imaging with positron emission tomography and fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose: use and limitations. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(20):3495–502.
Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. C. W. Elston & I. O. Ellis. Histopathology. 1991;19:403–10. (Histopathology. 2002;41(3A):151–2 (discussion 2–3)).
Robbins P, Pinder S, de Klerk N, Dawkins H, Harvey J, Sterrett G, et al. Histological grading of breast carcinomas: a study of interobserver agreement. Hum Pathol. 1995;26(8):873–9.
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM. Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 1998;11(2):155–68.
Zafrani B, Aubriot MH, Mouret E, De Cremoux P, De Rycke Y, Nicolas A, et al. High sensitivity and specificity of immunohistochemistry for the detection of hormone receptors in breast carcinoma: comparison with biochemical determination in a prospective study of 793 cases. Histopathology. 2000;37(6):536–45.
Hauser-Kronberger C, Dandachi N. Comparison of chromogenic in situ hybridization with other methodologies for HER2 status assessment in breast cancer. J Mol Histol. 2004;35(6):647–53.
Van den Eynden GG, Van der Auwera I, Van Laere SJ, Colpaert CG, van Dam P, Dirix LY, et al. Distinguishing blood and lymph vessel invasion in breast cancer: a prospective immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(11):1643–9. PMCID: 2361306.
Avril N, Menzel M, Dose J, Schelling M, Weber W, Janicke F, et al. Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18F-FDG PET: histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis. J Nucl Med. 2001;42(1):9–16.
Cermik TF, Mavi A, Basu S, Alavi A. Impact of FDG PET on the preoperative staging of newly diagnosed breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35(3):475–83.
Heudel P, Cimarelli S, Montella A, Bouteille C, Mognetti T. Value of PET-FDG in primary breast cancer based on histopathological and immunohistochemical prognostic factors. Int J Clin Oncol. 2010;15(6):588–93.
Chung A, Liou D, Karlan S, Waxman A, Fujimoto K, Hagiike M, et al. Preoperative FDG-PET for axillary metastases in patients with breast cancer. Arch Surg. 2006;141(8):783–8. (discussion 8–9).
Gil-Rendo A, Martinez-Regueira F, Zornoza G, Garcia-Velloso MJ, Beorlegui C, Rodriguez-Spiteri N. Association between [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and prognostic parameters in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2009;96(2):166–70.
Crippa F, Seregni E, Agresti R, Chiesa C, Pascali C, Bogni A, et al. Association between [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and postoperative histopathology, hormone receptor status, thymidine labelling index and p53 in primary breast cancer: a preliminary observation. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998;25(10):1429–34.
Shimoda W, Hayashi M, Murakami K, Oyama T, Sunagawa M. The relationship between FDG uptake in PET scans and biological behavior in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2007;14(3):260–8.
Kumar R, Chauhan A, Zhuang H, Chandra P, Schnall M, Alavi A. Clinicopathologic factors associated with false negative FDG-PET in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;98(3):267–74.
Ikenaga N, Otomo N, Toyofuku A, Ueda Y, Toyoda K, Hayashi T, et al. Standardized uptake values for breast carcinomas assessed by fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography correlate with prognostic factors. Am Surg. 2007;73(11):1151–7.
Mavi A, Cermik TF, Urhan M, Puskulcu H, Basu S, Yu JQ, et al. The effects of estrogen, progesterone, and C-erbB-2 receptor states on 18F-FDG uptake of primary breast cancer lesions. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(8):1266–72.
Osborne JR, Port E, Gonen M, Doane A, Yeung H, Gerald W, et al. 18F-FDG PET of locally invasive breast cancer and association of estrogen receptor status with standardized uptake value: microarray and immunohistochemical analysis. J Nucl Med. 2010;51(4):543–50.
Buck A, Schirrmeister H, Kuhn T, Shen C, Kalker T, Kotzerke J, et al. FDG uptake in breast cancer: correlation with biological and clinical prognostic parameters. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29(10):1317–23.
Peto R, Boreham J, Clarke M, Davies C, Beral V. UK and USA breast cancer deaths down 25% in year 2000 at ages 20–69 years. Lancet. 2000;355(9217):1822.
Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE Jr, Davidson NE, et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1673–84.
Piccart M, Lohrisch C, Di Leo A, Larsimont D. The predictive value of HER2 in breast cancer. Oncology. 2001;61(Suppl 2):73–82.
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hortobagyi GN, Esteva FJ. Adjuvant therapy with trastuzumab for HER-2/neu-positive breast cancer. Oncologist. 2006;11(8):857–67.
Bos R, van Der Hoeven JJ, van Der Wall E, van Der Groep P, van Diest PJ, Comans EF, et al. Biologic correlates of (18)fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in human breast cancer measured by positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(2):379–87.
Manie E, Vincent-Salomon A, Lehmann-Che J, Pierron G, Turpin E, Warcoin M, et al. High frequency of TP53 mutation in BRCA1 and sporadic basal-like carcinomas but not in BRCA1 luminal breast tumors. Cancer Res. 2009;69(2):663–71.
Schoppmann SF, Bayer G, Aumayr K, Taucher S, Geleff S, Rudas M, et al. Prognostic value of lymphangiogenesis and lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg. 2004;240(2):306–12.
Isasi CR, Moadel RM, Blaufox MD. A meta-analysis of FDG-PET for the evaluation of breast cancer recurrence and metastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;90(2):105–12.
Zangheri B, Messa C, Picchio M, Gianolli L, Landoni C, Fazio F. PET/CT and breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31(Suppl 1):S135–42.
Braun M, Flucke U, Debald M, Walgenbach-Bruenagel G, Walgenbach KJ, Holler T, et al. Detection of lymphovascular invasion in early breast cancer by D2-40 (podoplanin): a clinically useful predictor for axillary lymph node metastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;112(3):503–11.
Schacht V, Dadras SS, Johnson LA, Jackson DG, Hong YK, Detmar M. Up-regulation of the lymphatic marker podoplanin, a mucin-type transmembrane glycoprotein, in human squamous cell carcinomas and germ cell tumors. Am J Pathol. 2005;166(3):913–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.S., Sung, S.H. Usefulness of 18F-FDG uptake with clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical prognostic factors in breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med 26, 175–183 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-011-0556-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-011-0556-1