Abstract
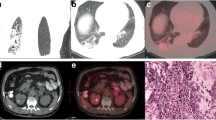
Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis (PAM) is a rare lung disease characterized by progressive intra-alveolar calcification. We present a case of PAM with abnormal accumulation of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) in both lungs. A 55-year-old man was referred to our hospital for progressive dyspnea. He had been diagnosed with PAM 25 years earlier by transbronchial lung biopsy. High-resolution computed tomography revealed multiple dense calcifications with little aerated lung. Combined positron emission tomography and computed tomography using 18F-FDG (FDG-PET/CT) showed the abnormal accumulation of FDG in both lungs with a maximal standardized uptake value of 7.3. High FDG uptake was observed mainly in the lung regions showing sparing calcification. The patient died of respiratory failure a month later and an autopsy revealed no significant inflammatory changes in either lung. We suspect that the markedly enhanced pulmonary FDG uptake may have some relation to the pathophysiology of PAM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G Castellama M Gentile M Castellana P Fiorente V Lamorgese (2002) ArticleTitlePulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: clinical features, evolution of phenotype, and review of the literature Am J Med Genet 111 220–4 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ajmg.10530
C Sigeno M Fukunaga R Morita H Maeda M Hino K Torizuka (1982) ArticleTitleBone scintigraphy in pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: a comparative study of radioactivity and density distribution Clin Nucl Med 7 103–7 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003072-198203000-00003
JL Coolens P Devos M De Roo (1985) ArticleTitleDiffuse pulmonary uptake of 99mTc bone-imaging agent: case report and survey Eur J Nucl Med 11 36–42 Occurrence Handle3899657 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00440959 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL28%2FgsVOktQ%3D%3D
H Hoshino H Koba S Inomata K Kurokawa Y Morita K Yoshida et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCase report. pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: high-resolution CT and MR findings J Comput Assist Tomogr 22 245–8 Occurrence Handle9530388 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004728-199803000-00016 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ptFCltA%3D%3D
CP Bleeker-Rovers EM de Kleijn FH Corstens JW van der Meer WJ Oyen (2004) ArticleTitleClinical value of FDG PET in patients with fever of unknown origin and patients suspected of focal infection or inflammation Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31 29–37 Occurrence Handle14551752 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00259-003-1338-3
H Zhuang A Alavi (2002) ArticleTitle18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomographic imaging in the detection and monitoring of infection and inflammation Semin Nucl Med 32 47–59 Occurrence Handle11839069 Occurrence Handle10.1053/snuc.2002.29278
KD Stumpe H Dazzi A Schaffner GK von Schulthess (2000) ArticleTitleInfection imaging using whole-body FDG-PET Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 27 822–32 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002590000277 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXktVOjsLs%3D
Y Sugawara DK Braun PV Kison JE Russo KR Zasadny RL Wahl (1998) ArticleTitleRapid detection of human infections with fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography: preliminary results Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 25 1238–43 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002590050290 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czptFOisA%3D%3D
Y Ichiya Y Kuwabara M Sasaki T Yoshida Y Akashi S Murayama et al. (1996) ArticleTitleFDG-PET in infectious lesions: the detection and assessment of lesion activity Ann Nucl Med 10 185–91 Occurrence Handle8800447 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28zptlKktg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF03165391
L Puhr (1933) ArticleTitleMikrolithiasis alveolaris pulmonum Virchow Arch Pathol Anat 290 156–60 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01979722
S Mariotta A Ricci M Papale F De Clementi B Sposato F Guidi et al. (2004) ArticleTitlePulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: report on 576 cases published in the literature Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 21 173–81 Occurrence Handle15554073
A Corut A Senyigit SA Ugur S Altin U Ozcelik H Calisir et al. (2006) ArticleTitleMutations SLC34A2 cause pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis and are possibly associated with testicular microlithiasis Am J Hum Genet 79 650–6 Occurrence Handle16960801 Occurrence Handle10.1086/508263 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28XhtVChurrM
O Achour P Carole F Isabelle V Alexandra C Christine (1999) ArticleTitleHypoxia upregulates activity and expression of the glucose transporter GULT1 in alveolar epithelial cells Am J Respir Cell Mor Biol 21 710–8
C Christine AM Micheal (2000) ArticleTitleHypoxia regulates gene expression of alveolar epithelial transport proteins J Appl Physiol 88 1890–6
AJ Heather C Christian (2004) ArticleTitleF-18 FDG PET/CT in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a case report Clin Nucl Med 32 786–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, K., Kubota, K., Yukihiro, M. et al. FDG-PET/CT finding of high uptake in pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Ann Nucl Med 21, 415–418 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0039-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-007-0039-6