Abstract
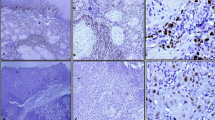
Diagnosis of basaloid squamous carcinoma (BSCC) currently relies mainly on histological criteria, with variable immunohistochemical results reported in small series. We explored the use of a battery of immunohistochemical stains to elucidate this diagnosis on 45 cases of BSCC. To further elucidate the immunohistochemical profile of BSCC, to explore potential genetic pathways of malignant transformation using proliferation markers, and to investigate a possible link with Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Forty-five cases of BSCC and 34 site-matched cases of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) were obtained from the archives of the pathology department at our institution. Extensive literature review was undertaken utilizing Medline. Ber-EP4 is a useful diagnostic marker for BSCC, positive in 82% (37/45) of the cases and in 68% (23/34) of SCC. An alternative is the combination of cytokeratins CK14 and CK7, known to be negative, and CK1, known to be positive, which achieves an accuracy of 73% (33/45) in BSCC and 88% (30/34) in SCC. The two diagnostic approaches were in agreement in 66% of the cases; both methods were equally accurate in the divergent cases. Increased expression of the proliferation markers supports the concept that BSCC is a rapidly growing tumor. Results of p16 stains support an etiological link between BSCC and HPV; interestingly, HPV was present significantly more in BSCC (71% (32/45)), than in SCC (59% (20/34)) in this study (P = 0.02).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes L, Ferlito A, Altavilla G, MacMillan C, Rinaldo A, Doglioni C. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996;105:75–82.
Cakir E, Demirag F, Ucoluk GO, Kaya S, Memis L. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: a rare tumour with a rare clinical presentation. Lung Cancer. 2007;57(1):109–11. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.01.021.
Koide N, Koike S, Watanabe H, Yazawa K, Adachi W, Amano J. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the esophagus with analysis by in situ nick end labeling and PCNA immunostaining. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999;46:265–71.
Wong CS, Tsao MS, Sharma V, Chapman WB, Pintilie M, Cummings BJ. Prognostic role of p53 protein expression in epidermoid carcinoma of the anal canal. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;45:309–14. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00188-1.
Lam KY, Chan KW. Molecular pathology and clinicopathologic features of penile tumors: with special reference to analyses of p21 and p53 expression and unusual histologic features. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1999;123:895–904.
Grayson W, Taylor LF, Cooper K. Adenoid cystic and adenoid basal carcinoma of the uterine cervix: a comparative morphologic, mucin, and immunohistochemical profile of two rare neoplasms of putative “reserve cell” origin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1999;123:448–58.
Wain SL, Kier R, Vollmer RT, Bossen EH. Basaloid-squamous carcinoma of the tongue, hypopharynx, and larynx: report of 10 cases. Hum Pathol. 1986;17(11):1158–66. doi:10.1016/S0046-8177(86)80422-1.
Beer TW, Shepherd P, Theaker JM. Ber EP4 and epithelial membrane antigen aid distinction of basal cell, squamous cell and basosquamous carcinomas of the skin. Histopathology. 2000;37:218–23. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2559.2000.00999.x.
Jones MS, Helm KF, Maloney ME. The immunohistochemical characteristics of the basosquamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 1997;23:181–4. doi:10.1016/S1076-0512(97)00105-2.
Klijanienko J, El-Najjar A, Ponzio-Prion A, Marandas P, Micheau C, Caillaud JM. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the head and neck: immunohistochemical comparison with adenoid cystic carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993;119:887–90.
Hammar SP. Approach to the diagnosis of neuroendocrine lung neoplasms: variabilities and pitfalls. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;18(3):183–90. doi:10.1053/j.semtcvs.2006.08.004.
Huang Z, Shen Y, Liang Y, Wu X. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: an immunohistochemical study of 8 cases. Chin Med J. 2001;114(10):1084–8.
Sampaio-Goes FCG, Oliviera DT, Dorta RG, Nonogaki S, Landman G, Nishimoto IN, et al. Expression of PCNA, p53, BAX, and BCL-X in oral poorly differentiated and basalooid squamous cell carcinoma: relationships with prognosis. Head Neck. 2005;27:982–9. doi:10.1002/hed.20258.
Cabanillas R, Rodrigo JP, Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Fresno AF, Aguilar C, et al. Is there an epidemiological link between human papillomavirus DNA and basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the pharynx? Oral Oncol. 2007;43(4):327-32.
Rubin MA, Kleter B, Zhou M, Ayala G, Cubilla AL, Quint WG, et al. Detection and typing of human papillomavirus DNA in penile carcinoma: evidence for multiple independent pathways of penile carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2001;159(4):1211–8.
Tellechea O, Reis JP, Domingues JC, Baptista AP. Monoclonal antibody Ber EP4 distinguishes basal-cell carcinoma from squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1993;15:452–5. doi:10.1097/00000372-199310000-00007.
Coletta RD, Almeida OP, Vargas PA. Cytokeratins 1, 7, and 14 immunoexpression are helpful in the diagnosis of basaloid squamous carcinoma. Histopathology. 2006;48:774. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2006.02345.x.
Coletta RD, Cotrim P, Almeida OP, Alves VAF, Wakamatsu A, Vargas PA. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the oral cavity: a histologic and immunohistochemical study. Oral Oncol. 2002;38:723–9. doi:10.1016/S1368-8375(02)00010-6.
Banks ER, Frierson HF, Mills SE, George E, Zarbo RJ, Swanson PE. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of the head and neck. A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 40 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992;16:939–46. doi:10.1097/00000478-199210000-00003.
Farmer ER, Helwig EB. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of seventeen cases. Cancer. 1980;46:748–57. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19800815)46:4<748::AID-CNCR2820460419>3.0.CO;2-K.
Winzenburg SM, Niehans GA, George E, Daly K, Adams GL. Basaloid squamous carcinoma: a clinical comparison of two histological types with poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998;119:471–5. doi:10.1016/S0194-5998(98)70104-4.
Zbaren P, Nuyens M, Stauffer E. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;12:116–21. doi:10.1097/00020840-200404000-00011.
Paulino AF, Singh B, Shah JP, Huvos AG. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 2000;110:1479–82. doi:10.1097/00005537-200009000-00013.
Erisen LM, Coskun H, Ozuysal S, Basut O, Onart S, Hizalan I, et al. Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx: a report of four new cases. Laryngoscope. 2004;114:1179–83. doi:10.1097/00005537-200407000-00009.
Salerno G, Di Vizio D, Staibano S, Mottola G, Quaremba G, Mascolo M, et al. Prognostic value of p27Kip1 expression in basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. BMC Cancer. 2006;6:146. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-6-146.
Marioni G, Gaio E, Giacomelli L, Marchese-Ragona R, Staffieri A, Marino F. Endoglin (CD105) expression in head and neck basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005;125:307–11. doi:10.1080/00016480410023047.
Rodriguez-Tojo MJ, Garcia Cano FJ, Infante Sanchez JC, Velazquez Sanchez E, Aguirre Urizar M. Immunoexpression of p53, Ki-67 and E-cadherin in basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Clin Transl Oncol. 2005;7(3):110–4. doi:10.1007/BF02708743.
Gillison ML, Koch WM, Capone RB, Spafford M, Westra WH, Wu L, et al. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92(9):709–20. doi:10.1093/jnci/92.9.709.
Poetsch M, Lorenz G, Bankau A, Kleist B. Basaloid in contrast to nonbasaloid head and neck squamous cell carcinomas display aberrations especially in cell cycle control genes. Head Neck. 2003;25(11):904–10. doi:10.1002/hed.10301.
Wilczynski SP, Lin BT, Xie Y, Paz IB. Detection of human papillomavirus DNA and oncoprotein overexpression are associated with distinct morphological patterns of tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:145–56.
Davies L, Hardin NJ, Beatty BG. Can Ki-67 predict recurrence of N0 squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2006;115(1):12–7.
Bracero F, Gamiz MJ, Soldado L, Conde JM, Redondo M, Gonzalez MA, et al. Hypopharynx and larynx basaloid squamous carcinoma: our experience with 6 cases. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2001;52(3):229–36.
Akyol MU, Dursun A, Akyol G, Edalt N. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunoreactivity and the presence of p53 mutation in basaloid squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Oncology. 1998;55:382–3. doi:10.1159/000011882.
Matheny KE, Barbieri CE, Sniezek JC, Arteaga CL, Pietenpol JA. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling decreased p63 expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Laryngoscope. 2003;113(6):936–9. doi:10.1097/00005537-200306000-00004.
Senoo M, Pinto F, Crum CP, McKeon F. p63 Is essential for the proliferative potential of stem cells in stratified epithelia. Cell. 2007;129(3):523–36. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.045.
Lu DW, El-Mofty SK, Wang HL. Expression of p16, Rb, and p53 proteins in squamous cell carcinomas of the anorectal region harboring human papillomavirus DNA. Mod Pathol. 2003;16(7):692–9. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000077417.08371.CE.
Santos M, Landolfi S, Olivella A, Lloveras B, Klaustermeier J, Suarez H, et al. p16 overexpression identifies HPV-positive vulvar squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(11):1347–56. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000213251.82940.bf.
Tran N, Rose BR, O’Brein CJ. Role of human papillomavirus in the etiology of head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 2007;29(1):64–70. doi:10.1002/hed.20460.
Kleist B, Bankau A, Lorenz G, Jager B, Poetsch M. Different risk factors in basaloid and common squamous head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope. 2004;114(6):1063–8. doi:10.1097/00005537-200406000-00020.
Strati K, Pitot HC, Lambert PF. Identification of biomarkers that distinguish human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive versus HPV-negative head and neck cancers in a mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(38):14152–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0606698103.
Aguayo F, Castillo A, Koriyama C, Higashi M, Itoh T, Capetillo M, et al. Human papillomavirus-16 is integrated in lung carcinomas: a study in Chile. Br J Cancer. 2007;97:85–91. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603848.
Ota N, Kawakami K, Okuda T, Takehara A, Hiranuma C, Oyama K, et al. Prognostic significance of p16(INK4a) hypermethylation in non-small cell lung cancer is evident by quantitative DNA methylation analysis. Anticancer Res. 2006;26(5B):3729–32.
Yoo J, Jung JH, Lee MA, Seo KJ, Shim BY, Kim SH, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of non-small cell lung cancer: correlation with clinical parameters and prognosis. J Korean Med Sci. 2007;22(2):318–25.
Sturm N, Lantuejoul S, Laverriere MH, et al. Thyroid transcription factor 1 and cytokeratins 1, 5, 10, 14 (34betaE12) expression in basaloid and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:918–25. doi:10.1053/hupa.2001.27110.
Acknowledgements
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose, and funding for the project came from departmental research funds and NIH grant PHS 22435-22.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winters, R., Naud, S., Evans, M.F. et al. Ber-EP4, CK1, CK7 and CK14 are Useful Markers for Basaloid Squamous Carcinoma: A Study of 45 Cases. Head and Neck Pathol 2, 265–271 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-008-0089-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-008-0089-7